Medidas de Almacenamiento en Informática
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an educational overview of data storage measures in computing. It explains key concepts such as bits, bytes, kilobytes (KB), megabytes (MB), gigabytes (GB), and terabytes (TB), emphasizing how each unit corresponds to increasing amounts of storage space. The video also highlights common storage devices like hard drives, USB memory sticks, and CDs, showing how data can be temporarily or permanently stored. Viewers are guided on how to understand storage capacities and how larger units can store more data. The video wraps up with a friendly message, encouraging learning about data storage.
Takeaways
- 😀 Storage measurements are units used to determine how much space is available in memory devices.
- 😀 Different storage devices exist, such as hard drives, flash drives, CDs, and portable memory, each with varying ways of storing data.
- 😀 Data can be stored temporarily or permanently on storage devices.
- 😀 The smallest unit of storage is the bit, which represents information as either a 0 or 1.
- 😀 A byte consists of 8 bits and is the next step up in storage measurement.
- 😀 A kilobyte (KB) contains 1024 bytes, representing a larger chunk of data.
- 😀 A megabyte (MB) is made up of 1024 kilobytes and is commonly used to measure storage in files.
- 😀 A gigabyte (GB) is equivalent to 1024 megabytes and is typically used to describe larger storage capacities.
- 😀 A terabyte (TB) equals 1024 gigabytes and represents a significant amount of data storage.
- 😀 As storage measurements increase, the capacity to store more data also grows, allowing for larger files and more information.
- 😀 There are even larger units of storage, such as petabytes and exabytes, which are used for extremely large data storage needs.
Q & A
What are storage units in computing?
-Storage units in computing are measurement units used to determine how much space is available on a memory device, helping to quantify data storage capacity.
What are some common storage devices mentioned in the video?
-Common storage devices include hard drives, CDs, USB flash drives, and portable memory devices.
How can information be stored on these devices?
-Information can be stored either temporarily or permanently on these devices, depending on the nature of the device and its intended use.
What is the smallest unit of information in computing?
-The smallest unit of information in computing is a bit, which can have one of two states: 0 or 1, representing binary data.
What is a byte and how many bits does it contain?
-A byte is a unit of digital information that consists of 8 bits.
What is a kilobyte (KB)?
-A kilobyte (KB) is a unit of data that contains 1024 bytes.
How many kilobytes are in a megabyte (MB)?
-A megabyte (MB) contains 1024 kilobytes (KB).
What is the storage capacity of a gigabyte (GB)?
-A gigabyte (GB) contains 1024 megabytes (MB).
How much data can a terabyte (TB) store?
-A terabyte (TB) contains 1024 gigabytes (GB), allowing it to store a large amount of data compared to smaller units like MB or GB.
What are some larger units of data storage mentioned in the video?
-Larger units of data storage include petabytes, exabytes, and zettabytes, which are progressively larger than a terabyte.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
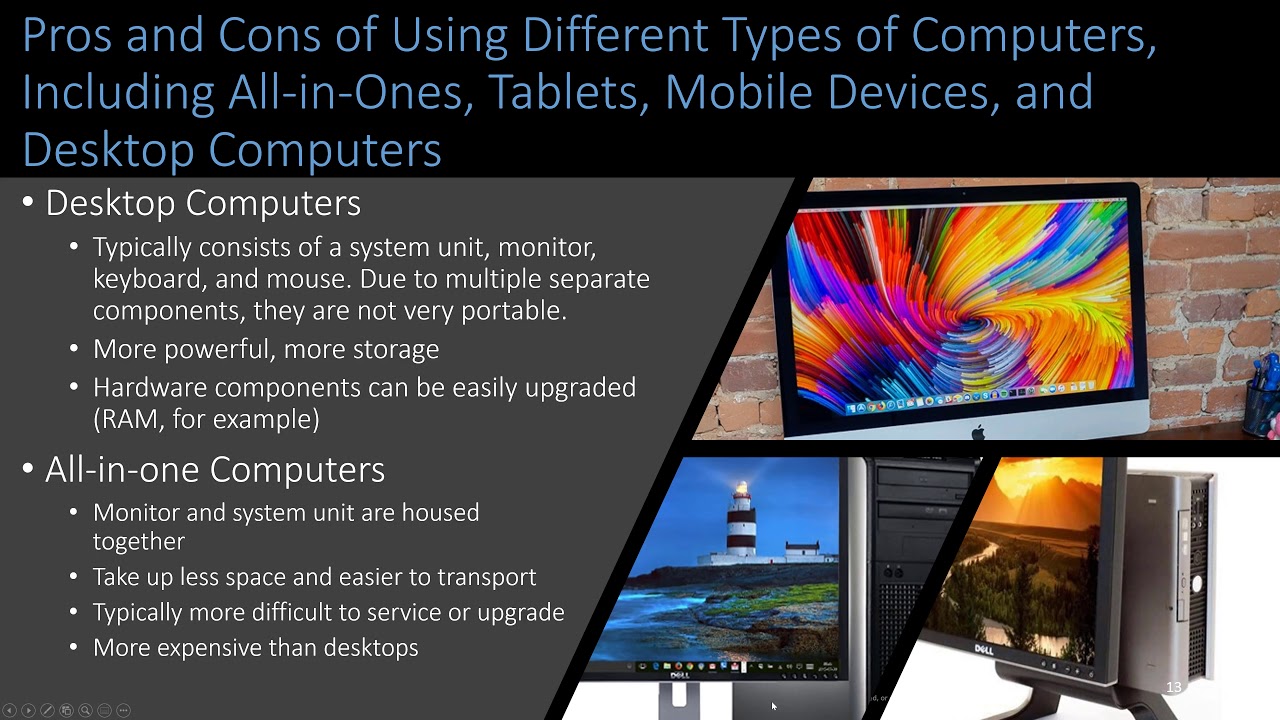
Computer Concepts - Module 3: Computer Hardware Part 1B (4K)
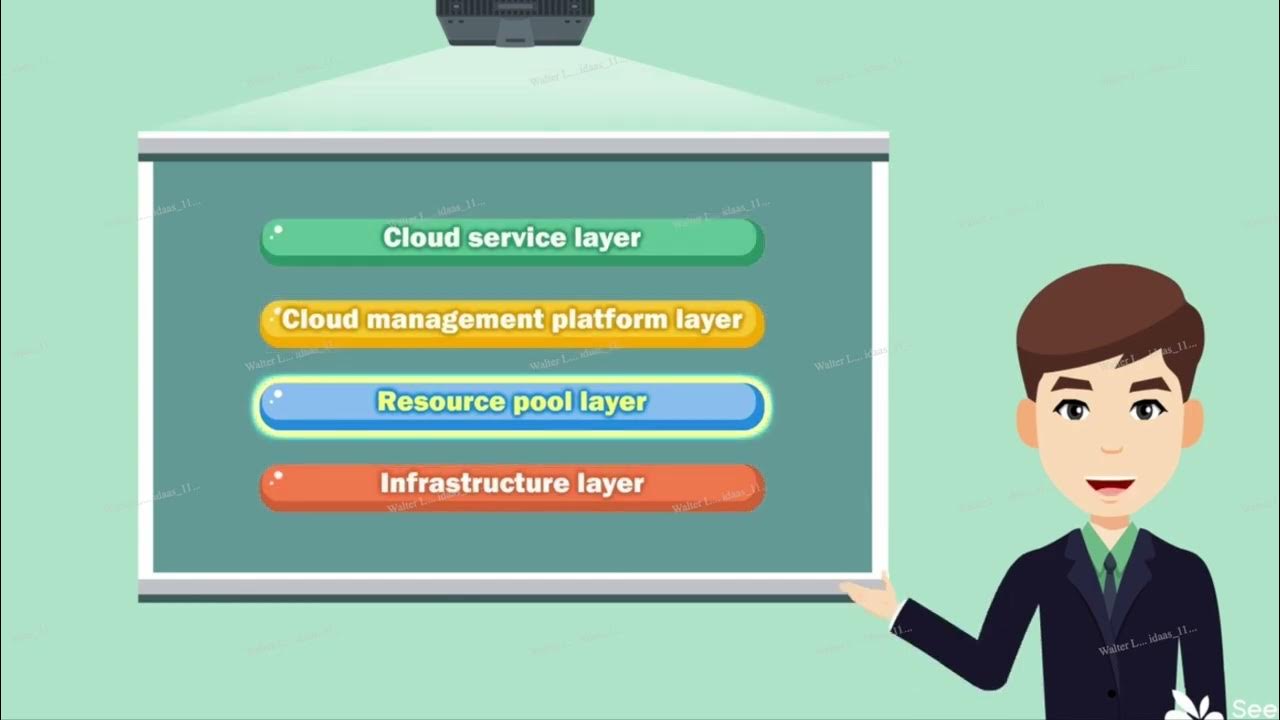
Módulo 7 - Cloud Architecture

IGCSE Computer Science FLASHCARDS 1 - DATA REPRESENTATION REVISION

Enterprise Computing Year 12 Unit 1: Data Science
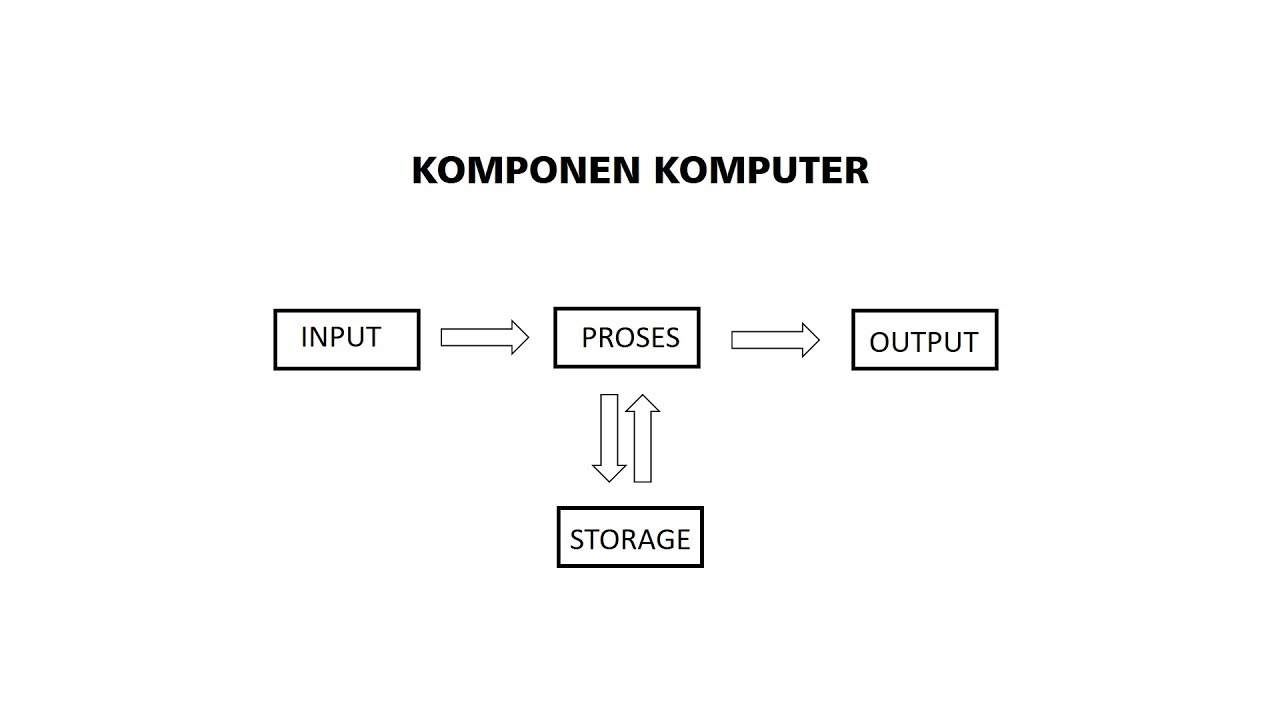
PENGERTIAN KOMPONEN KOMPUTER INPUT PROSES OUTPUT STORAGE

Primary & Secondary Storage - GCSE Computer Science
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)