CHARLES' LAW | Animation
Summary
TLDRThis video explains Charles' Law, which describes the direct relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas. Formulated by Jacques Charles in the 1800s, the law demonstrates that as the temperature of a gas increases, its volume also increases, provided pressure remains constant. The video details Charles' original experiment involving a test tube filled with air, a mercury plug, and heating and cooling to observe changes in volume. It introduces the mathematical expression \( V \propto T \) and explains how to solve problems using the equation \( \frac{V_1}{T_1} = \frac{V_2}{T_2} \), with a practical example illustrating this concept.
Takeaways
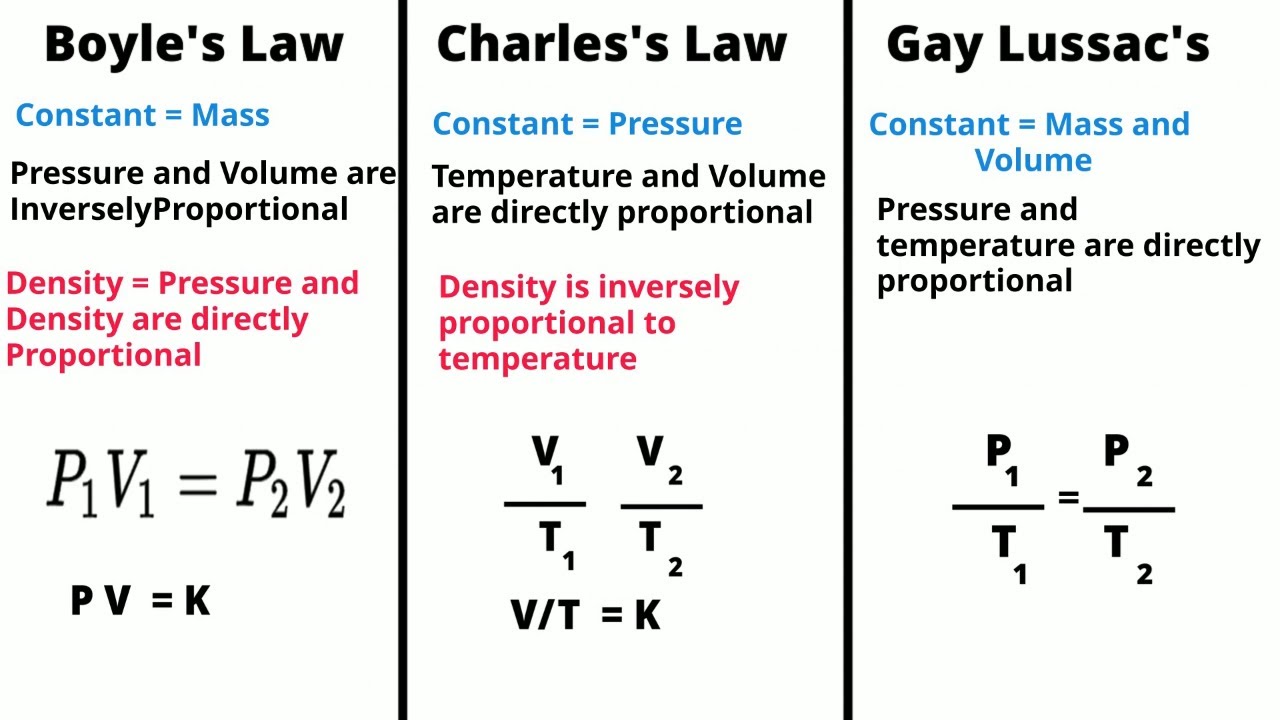
- 😀 Charles's Law describes the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas, keeping pressure constant.
- 😀 The law was formulated by Jacques Charles in 1800, explaining how gases expand when heated.
- 😀 In the experiment, Charles used a test tube with air, a mercury plug, a heating coil, and ice to change the gas's temperature.
- 😀 As the temperature of the gas changed, its volume also changed, providing the basis for the law.
- 😀 The graph of the law shows that volume and temperature are directly proportional, meaning as temperature increases, so does volume.
- 😀 Absolute zero (−273.15°C or 0 Kelvin) is a theoretical point where gas volume would reach zero, although it is not practically observed.
- 😀 The temperature must be in Kelvin for the law's calculations to work correctly.
- 😀 Charles's Law is mathematically expressed as V ∝ T or V1/T1 = V2/T2.
- 😀 The formula allows calculation of a gas's volume at different temperatures, assuming constant pressure.
- 😀 An example demonstrates how increasing the temperature of a gas from 30°C to 50°C results in an increase in volume from 5 L to approximately 5.33 L.
- 😀 The final volume after the temperature change shows a clear illustration of Charles's Law in action, with the volume increasing by 0.33 L.
Q & A
What is the focus of the video script?
-The video script focuses on Charles' Law, which describes the relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas.
Who formulated Charles' Law and when?
-Charles' Law was formulated by Jacques Charles in the 1800s, less than two centuries after Boyle.
What experiment did Jacques Charles conduct to develop his law?
-Jacques Charles conducted an experiment where he prepared a test tube with air trapped under a small mercury plug, heated it with a coil, and cooled it with ice to observe how the volume of gas changed with temperature.
What did Jacques Charles discover about the relationship between temperature and volume?
-Jacques Charles discovered that the volume of a gas increases when the temperature increases and decreases when the temperature decreases, demonstrating a direct relationship.
What does the graph in the video show about the relationship between temperature and volume?
-The graph shows that volume and temperature follow a direct proportionality, with a dashed line indicating that at absolute zero temperature, the gas theoretically reaches zero volume, though this phenomenon has never been observed.
What is the absolute zero temperature in Celsius?
-The absolute zero temperature is -273.15 degrees Celsius, which is the theoretical temperature at which gas would have zero volume.
What unit of temperature is used in the formula for Charles' Law?
-The unit of temperature used in the formula is Kelvin for the International System of Units (SI) or Rankine for English units.
How is Charles' Law mathematically expressed?
-Charles' Law is mathematically expressed as V1/T1 = V2/T2, where V represents volume and T represents temperature in Kelvin.
What does the formula V1/T1 = V2/T2 imply about changes in volume and temperature?
-The formula implies that if the temperature increases, the volume also increases, and if the temperature decreases, the volume decreases, as long as the pressure and amount of gas remain constant.
Given an initial volume of 5 liters at 30°C, how do you calculate the final volume when the temperature is increased to 50°C?
-First, convert the temperatures to Kelvin. Then, use the formula V1/T1 = V2/T2 to find the final volume. For this example, the final volume is 5.33 liters.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)