Biologia - Como ler um Cladograma
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of cladograms, which are graphical representations used to illustrate the evolutionary relationships between species. It covers the basics of reading a cladogram, such as understanding the root, nodes, apomorphies (evolutionary innovations), and clades. The video also demonstrates how to interpret the evolutionary paths of various species, such as big cats, and shows how cladograms reflect the shared traits and common ancestors of organisms. With practical examples, viewers can learn how to trace evolutionary histories and understand the connections between species in an engaging way.
Takeaways
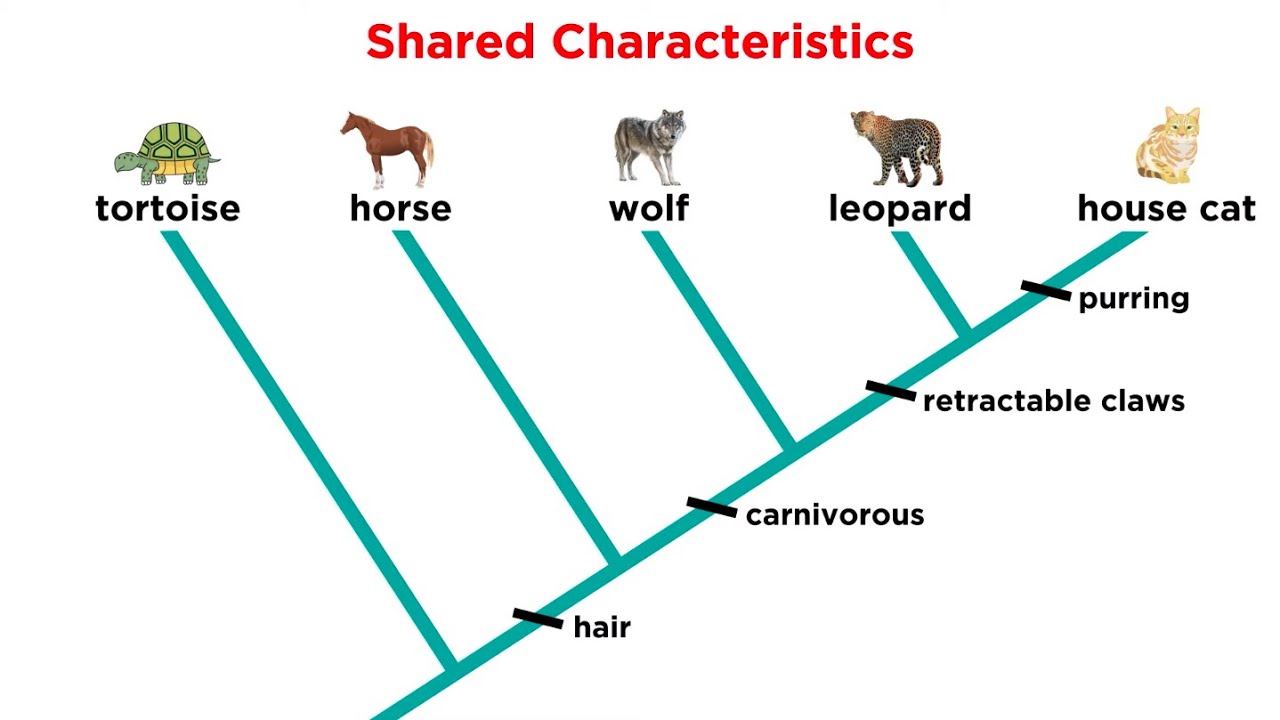
- 😀 A cladogram is a graphical representation showing the evolutionary relationships between species based on their common ancestry.
- 😀 The root of a cladogram represents the common ancestor of the species being studied.
- 😀 Apomorphies are evolutionary novelties or traits that differentiate species from their ancestors and are key in determining relationships between species.
- 😀 Nodes in a cladogram represent common ancestors where species diverge, with lower nodes representing earlier ancestors and upper nodes representing more recent ones.
- 😀 Evolutionary time is represented in the cladogram as a directional flow from the root (common ancestor) to the tips (current species).
- 😀 Clades are monophyletic groups that include a common ancestor and all of its descendants.
- 😀 The cladogram shows evolutionary pathways as branches, where species share characteristics based on the evolution from common ancestors.
- 😀 If the cladogram is mirrored, it still represents the same evolutionary relationships, just in reverse order.
- 😀 The time scale of a cladogram helps identify when species or traits evolved, showing the relative timing of evolutionary events.
- 😀 In the example of big cats, lions and leopards are more closely related to each other than either is to the jaguar, based on their shared common ancestor.
- 😀 The exercise in the transcript reinforces the concept of clades by testing the learner’s ability to identify evolutionary relationships among big cats, such as lions, leopards, and panthers.
Q & A
What is a cladogram and what does it represent?
-A cladogram is a graphic representation used to show the evolutionary relationships between species. It illustrates how species are related based on shared traits, specifically focusing on common ancestry.
How do we read a cladogram?
-To read a cladogram, start at the base where the common ancestor is located. Follow the branches upward to see how species diverged over time, with nodes representing the points where these divergences occurred.
What is an apomorphy?
-An apomorphy is an evolutionary trait or characteristic that differs from the species' ancestors. It emerges at a node and is unique to the species that appear after that point in the cladogram.
How is the time represented in a cladogram?
-Time in a cladogram is represented by the direction of the branches, from the base (common ancestor) to the top (present species). It shows the chronological progression of evolutionary traits over time.
What are clades?
-Clades are groups of species that share a common ancestor. A clade includes the ancestor and all of its descendants, forming a monophyletic group.
How does a cladogram show evolutionary paths?
-A cladogram shows evolutionary paths through branches, where each branch represents the evolutionary history of a particular group of species. The points where branches split (nodes) represent the divergence from common ancestors.
What is the significance of nodes in a cladogram?
-Nodes in a cladogram represent the common ancestors of the species that diverge from them. They are key points where evolutionary changes lead to the formation of different species or groups.
What is the relationship between apomorphies and evolutionary history?
-Apomorphies are new traits that evolve in a species after it diverges from its ancestor. These traits help define evolutionary lineages and are crucial for understanding the history of species.
In the example of big cats, how can you determine which species are more closely related?
-In the example, species that share a more recent common ancestor (represented by a node) are more closely related. For instance, lions and leopards are more closely related than lions and jaguars due to their position within the same clade.
How does the cladogram of big cats show the evolution of traits like roaring?
-The cladogram of big cats shows that species that can roar, like lions and tigers, evolved before species that cannot roar, like leopards and jaguars. This distinction is represented by branching patterns, with roaring felines forming one branch and non-roaring felines forming another.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)