Cladistics Part 1: Constructing Cladograms
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the concept of cladistics and its role in understanding evolutionary relationships. It explains how cladograms, branching diagrams, are used to classify organisms based on shared and derived characteristics, like hair or carnivorous teeth. The video highlights the importance of identifying clades, outgroups, and the differences between ancestral and derived characteristics. Through examples involving animals like tortoises, leopards, and horses, viewers learn how to build cladograms and interpret evolutionary ties. The video emphasizes how cladistics reveals common ancestry, aiding in the study of evolution across various species.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cladistics is a method of classifying organisms based on common characteristics to understand their evolutionary relationships.
- 😀 A cladogram is a branching diagram that shows the relationships between clades, which are groups of organisms sharing a common ancestor.
- 😀 An outgroup is a species that is used for comparison, showing shared ancestral characteristics with the species under study.
- 😀 Ancestral characteristics are traits shared by all members of a clade, such as hair in mammals, and are typically placed at the base of the cladogram.
- 😀 Derived characteristics are traits that appear after a divergence in the evolutionary tree, helping to define subgroups within a clade.
- 😀 Synapomorphies are shared derived characteristics that define a clade, such as the ability to purr in domestic cats.
- 😀 Cladograms can be rearranged as long as they maintain the correct evolutionary relationships, and this does not imply a more 'evolved' status for certain organisms.
- 😀 Evolutionary relationships shown in a cladogram do not imply a linear progression or hierarchy of organisms; they simply reflect shared ancestry.
- 😀 Convergent evolution, where unrelated species independently evolve similar traits, must be considered when constructing cladograms to avoid misleading conclusions.
- 😀 When building a cladogram, key characteristics like the presence of a spine or amniotic eggs help define relationships, ensuring accuracy in the evolutionary tree.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of cladistics in biology?
-Cladistics is a method of classifying organisms based on their evolutionary characteristics, which helps to show their relationships and common ancestry in a visual form using cladograms.
What is a cladogram and how is it used in biology?
-A cladogram is a branching diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships between organisms, showing how species are grouped into clades based on shared and derived traits.
What are clades in the context of cladistics?
-Clades are groups of organisms that share a common ancestor. These groups are identified based on shared characteristics that evolved from their most recent common ancestor.
What is an ancestral characteristic in a cladogram?
-An ancestral characteristic is a trait shared by all members of a group, inherited from a distant ancestor. For example, 'hair' is an ancestral characteristic of mammals.
What is a derived characteristic and how does it differ from an ancestral characteristic?
-A derived characteristic is a trait that has evolved within a particular group after its common ancestor, differentiating them from other groups. For example, the ability to purr is a derived characteristic in domestic cats.
Why are outgroups important in constructing a cladogram?
-Outgroups, like tortoises in the provided example, are used as a reference point to compare the species being studied. They help establish the evolutionary context for the characteristics shared by the group under investigation.
What is the significance of the word 'hair' in the provided cladogram example?
-The word 'hair' in the cladogram indicates an ancestral characteristic of mammals, suggesting that all organisms on the cladogram, except tortoises, have hair. This places hair as a key distinguishing trait for mammals.
How does the structure of a cladogram help determine the relatedness of organisms?
-The structure of a cladogram shows the branching of species based on shared traits. Organisms closer on the diagram are more closely related, having evolved from a more recent common ancestor.
What is convergent evolution, and how does it relate to cladograms?
-Convergent evolution occurs when different organisms independently evolve similar traits. In cladistics, this can complicate the construction of cladograms, as traits like flight in both birds and butterflies can arise separately but may not represent a true evolutionary relationship.
Why were 'flight' and 'warm-bloodedness' not used to differentiate between birds and crocodiles in the cladogram?
-Both 'flight' and 'warm-bloodedness' were excluded because they are traits that evolved independently in different lineages (convergent evolution). For example, butterflies and birds both evolved flight, making it an unreliable trait to separate them in a cladogram.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

SHS Science Classification of Organisms

How to Understand Evolutionary Trees
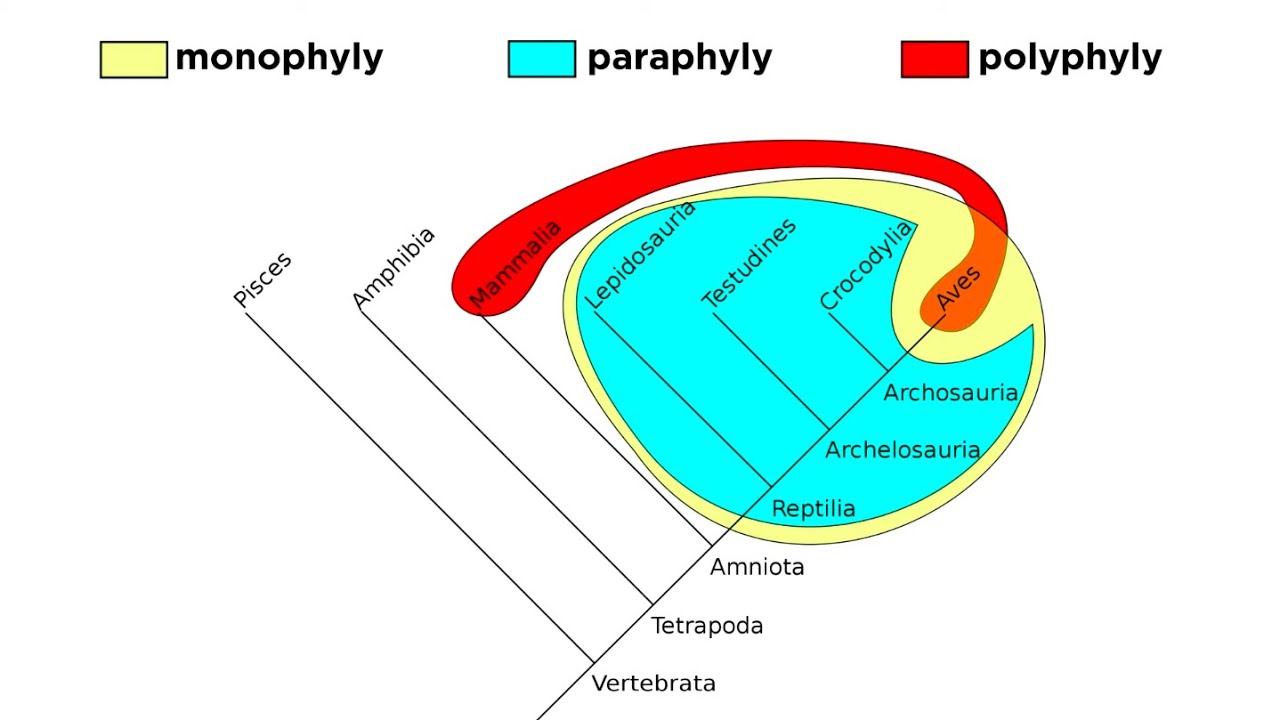
Cladistics Part 2: Monophyly, Paraphyly, and Polyphyly
1.2 Concepts & Uses of Classification Syst. IGCSE Biology 0610/0970 Syllabus 2026/2028 English Vers.

O que é BIODIVERSIDADE e qual a sua IMPORTÂNCIA 🌍🐸🌿

Biologia - Como ler um Cladograma
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)