Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes
Summary
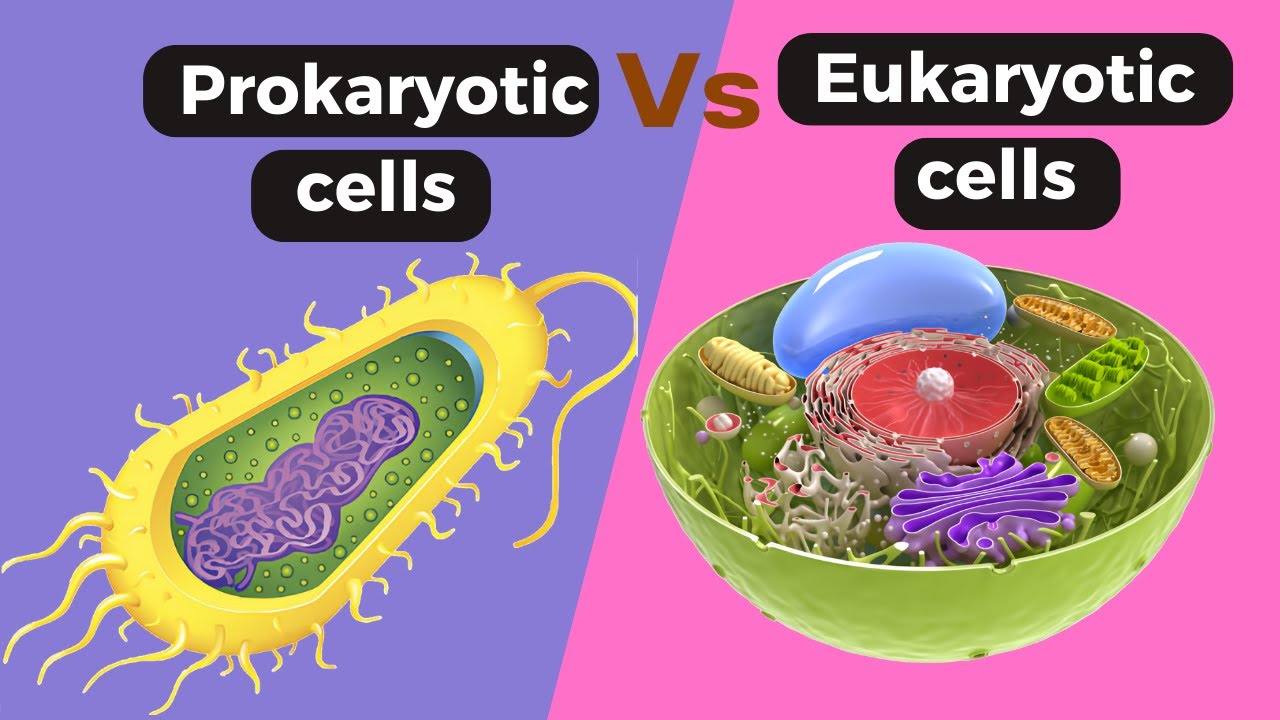
TLDRThis presentation explores the fundamental differences and similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are more complex with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and these organelles. Both cell types share a plasma membrane, DNA, ribosomes, and cytoplasm. The endosymbiosis theory suggests eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic ancestors, incorporating engulfed bacteria as mitochondria and chloroplasts. The presentation also acknowledges photographers for the visual content.
Takeaways
- 🧬 Eukaryotic cells are more complex due to the presence of a protective nucleus that houses their DNA.
- 🔬 Membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria and chloroplasts, are characteristic features of eukaryotic cells, contributing to their complexity.
- 🌿 Chloroplasts are unique to plant cells and are involved in photosynthesis, while other organelles like lysosomes and the endoplasmic reticulum have specific roles in cellular processes.
- 🔍 Eukaryotic cells are generally larger, with the example given being about 20 micrometers in size.
- 🏷️ The classification of eukaryotic organisms includes Kingdoms Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
- 🌱 Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, are less complex, lacking a nucleus and most membrane-bound organelles.
- 📏 Prokaryotic cells are significantly smaller than eukaryotic cells, with the example being about three micrometers in size.
- 🧪 Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells share basic cellular components like a plasma membrane, DNA, ribosomes, and cytoplasm.
- 🔬 The endosymbiosis theory suggests that eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells that engulfed other organisms, which eventually became organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts.
- 🌐 The presentation acknowledges the photographers who contributed images to the presentation, highlighting the importance of visual aids in scientific communication.
Q & A
What are the two broad categories of cells mentioned in the presentation?
-The two broad categories of cells mentioned are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.
What is the primary characteristic that makes eukaryotic cells more complex than prokaryotic cells?
-Eukaryotic cells are more complex because their DNA is housed within a protective nucleus and they have membrane-bound organelles.
What is an example of a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells?
-Mitochondria is an example of a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells, which is responsible for making energy for the cell.
What is the function of the chloroplast in plant cells?
-Chloroplasts are involved in photosynthesis, allowing plant cells to manufacture their own food by converting sunlight into energy.
How do lysosomes contribute to the cell's function in eukaryotic cells?
-Lysosomes help to digest and break down certain food particles within eukaryotic cells.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells?
-The endoplasmic reticulum, both rough and smooth, is involved in the production of proteins and the buildup of fats and lipids, respectively.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus in eukaryotic cells?
-The Golgi apparatus helps to sort, package, and distribute proteins within the cell.
How is the size of a typical eukaryotic cell compared to a prokaryotic cell?
-A typical eukaryotic cell is much larger, about 20 micrometers in size, compared to a prokaryotic cell, which is only about 3 micrometers.
What are the four kingdoms of life that are considered eukaryotic?
-The four eukaryotic kingdoms of life are Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells in terms of organelles?
-Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and the Golgi apparatus, which are present in eukaryotic cells.
What is the endosymbiosis theory and how does it relate to the evolution of eukaryotic cells from prokaryotic cells?
-The endosymbiosis theory suggests that eukaryotic cells evolved from prokaryotic cells by engulfing and incorporating other organisms that eventually became organelles like mitochondria and chloroplasts.
What are the two kingdoms of life that consist of prokaryotic cells?
-The two kingdoms of life that consist of prokaryotic cells are Kingdom Monera (bacteria) and Kingdom Archaea.
What do ribosomes do in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-Ribosomes in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are responsible for building proteins, which are essential for various cellular functions.
What is the common feature between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have a plasma membrane, DNA, ribosomes, and a fluid interior called cytoplasm.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells | High school biology | Khan Academy

CÉLULAS EUCARIONTES E PROCARIONTES - DIFERENÇAS | ANIMAÇÃO

Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells - High School Biology

Prokaryotic Vs. Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic cell Vs Eukaryotic cells|| Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell

Perbedaan Sel Prokariotik & Sel Eukariotik | Pembelajaran Daring - Dunia Biologi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
