CÉLULAS EUCARIONTES E PROCARIONTES - DIFERENÇAS | ANIMAÇÃO
Summary
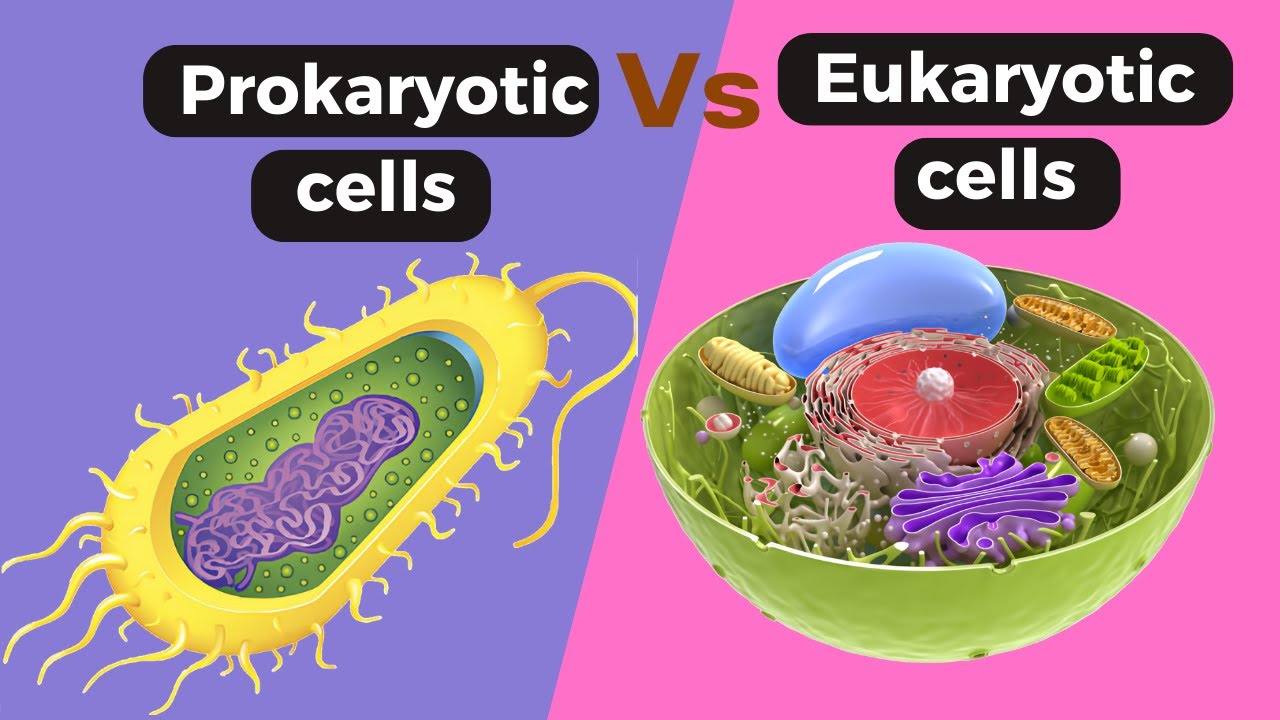
TLDRIn this video, Professor Lucas explains the key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. He breaks down the etymology of both terms, showing that prokaryotes are 'before the nucleus' and eukaryotes are 'true nucleus.' Prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, are simpler and smaller, lacking a defined nucleus, while eukaryotic cells, found in organisms like plants and animals, are larger and more complex with membrane-bound organelles. The video highlights the evolutionary connection between the two types of cells, emphasizing their similarities and distinctions through visual diagrams and clear examples.
Takeaways
- 😀 Prokaryotes are cells without a defined nucleus, and their genetic material is free-floating in the cytoplasm.
- 😀 Eukaryotes have a true nucleus that encloses their genetic material within a membrane.
- 😀 The word 'prokaryote' comes from the Greek 'pro' meaning 'before' and 'karyon' meaning 'nucleus', indicating they lack a nucleus.
- 😀 The term 'eukaryote' is derived from 'eu' meaning 'true' and 'karyon' meaning 'nucleus', referring to their well-defined nucleus.
- 😀 Prokaryotic cells are smaller and simpler, which allows for fast and efficient reproduction.
- 😀 Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex, with multiple internal organelles performing specialized functions.
- 😀 Prokaryotes lack membrane-bound organelles, but they do have ribosomes for protein synthesis.
- 😀 Eukaryotes contain various organelles, including the mitochondria, Golgi apparatus, and in plant cells, chloroplasts.
- 😀 Prokaryotes generally have a single, circular chromosome, whereas eukaryotes have multiple linear chromosomes.
- 😀 Prokaryotes are always unicellular organisms, while eukaryotes can be unicellular or multicellular.
- 😀 Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells share common features such as DNA, ribosomes, cytoplasm, and a plasma membrane.
Q & A
What does the term 'prokaryote' mean?
-The term 'prokaryote' comes from the Greek word 'pro', meaning 'before', and 'karyon', meaning 'nucleus'. It refers to cells that do not have a true nucleus, and their genetic material is not enclosed within a membrane.
What does the term 'eukaryote' mean?
-The term 'eukaryote' comes from the Greek word 'eu', meaning 'true', and 'karyon', meaning 'nucleus'. It refers to cells that possess a true nucleus, where the genetic material is enclosed within a membrane.
What are the main differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-Prokaryotic cells are smaller, simpler, and lack a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. In contrast, eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, and contain a true nucleus along with various organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and mitochondria.
What is the role of ribosomes in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. They are essential for cell growth and regeneration, as they help translate genetic information into proteins.
Do prokaryotic cells have a nucleus?
-No, prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus. Their genetic material is not enclosed in a membrane, and it remains free in the cytoplasm.
What structures are present in eukaryotic cells that are not found in prokaryotic cells?
-Eukaryotic cells have a true nucleus that encloses the genetic material, as well as membrane-bound organelles such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, and in plant cells, chloroplasts.
What types of organisms are made up of prokaryotic cells?
-Prokaryotic cells are found in organisms such as bacteria and cyanobacteria.
What types of organisms are made up of eukaryotic cells?
-Eukaryotic cells are found in organisms such as protozoa, algae, fungi, plants, and animals.
How is the DNA of prokaryotic cells organized?
-In prokaryotic cells, the DNA is typically organized in a single circular chromosome, which floats freely in the cytoplasm.
How is the DNA of eukaryotic cells organized?
-In eukaryotic cells, the DNA is organized into linear chromosomes, which are contained within the nucleus.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Perbedaan Sel Prokariotik & Sel Eukariotik | Pembelajaran Daring - Dunia Biologi

Comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells | High school biology | Khan Academy

Sel: Prokariotik vs Sel Eukariot | Biologi | Alternatifa
Prokaryotic cell Vs Eukaryotic cells|| Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell

CÉLULA ANIMAL E CÉLULA VEGETAL - DIFERENÇAS | ANIMAÇÃO

Citologia 1/2: Estrutura Básica das Células | Anatomia e etc
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)