Comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells | High school biology | Khan Academy
Summary
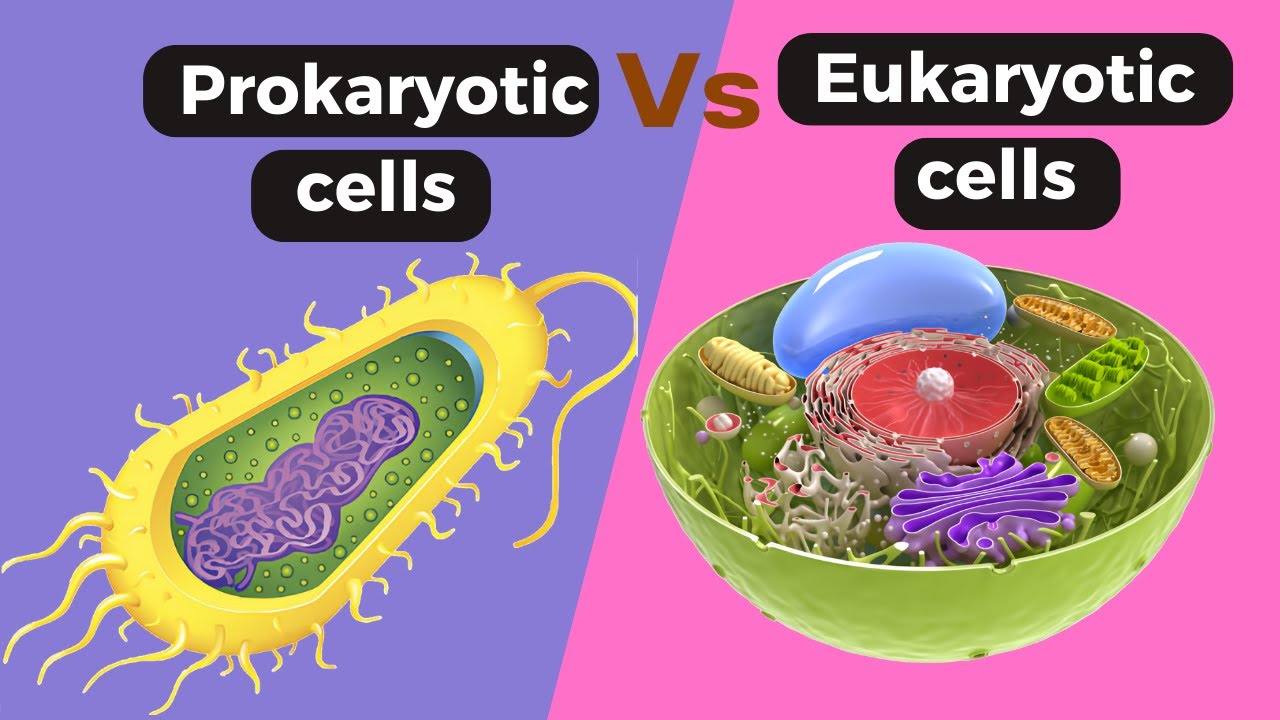
TLDRIn this video, the instructor explains the key similarities and differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Both types of cells share fundamental features such as a plasma membrane, DNA, ribosomes, and cytosol. However, eukaryotic cells are larger, more complex, and contain membrane-bound organelles like a nucleus, while prokaryotic cells lack these structures. The video also highlights differences in DNA organization, cell walls, reproduction, and examples of organisms with each type of cell, emphasizing the diversity and complexity of life at the cellular level.
Takeaways
- 😀 Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells are the two main categories of cells, with differences in complexity and structure.
- 😀 Both cell types have a plasma membrane, which defines the boundaries of the cell and separates it from the environment.
- 😀 Genetic material (DNA) is present in both cell types, but prokaryotic cells typically have a single strand of DNA, while eukaryotic cells have multiple strands of DNA inside a nucleus.
- 😀 Ribosomes, which are responsible for protein synthesis, are present in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
- 😀 Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells contain cytosol, a jelly-like substance where the cell's components float.
- 😀 Eukaryotic cells are generally larger than prokaryotic cells, often about 10 times bigger.
- 😀 Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles like the nucleus, which are present in eukaryotic cells.
- 😀 Eukaryotic cells can be unicellular organisms, but they are often part of multicellular organisms like humans and plants.
- 😀 Prokaryotic cells generally have a cell wall, while eukaryotic cells may or may not have one (e.g., plant cells have cell walls, but animal cells do not).
- 😀 Prokaryotic cells reproduce asexually, while eukaryotic cells can reproduce both sexually and asexually depending on the organism.
- 😀 Examples of prokaryotic cells include bacteria and archaea, while eukaryotic cells are found in animals, plants, fungi, and certain protists.
Q & A
What are the two main categories of cells discussed in the video?
-The two main categories of cells discussed are prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.
What is the main difference in size between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-Eukaryotic cells are generally about 10 times larger than prokaryotic cells.
What is the plasma membrane, and is it common to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-The plasma membrane is an outer layer that separates the cell's interior from its surrounding environment. It is common to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Where is the genetic material located in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-In prokaryotic cells, the genetic material is typically a single strand of DNA found in the nucleoid region. In eukaryotic cells, the genetic material is organized into multiple strands of DNA housed inside a membrane-bound organelle called the nucleus.
What are ribosomes, and do both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have them?
-Ribosomes are small structures that build proteins by using the genetic information. Both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have ribosomes, although their size and complexity may vary.
What is cytosol, and how does it relate to cytoplasm in the context of cells?
-Cytosol is the jelly-like substance inside the cell where ribosomes, DNA, and other components float. Cytoplasm refers to the cytosol plus all the other components within the cell membrane.
What is the main structural difference between the DNA in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-Prokaryotic cells typically have a single circular strand of DNA, while eukaryotic cells have multiple strands of DNA arranged in chromosomes, contained within a membrane-bound nucleus.
How does the complexity of prokaryotic cells compare to eukaryotic cells?
-Prokaryotic cells are generally simpler and lack membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells are more complex and contain multiple membrane-bound organelles, such as the nucleus and mitochondria.
What is the role of cell walls in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
-Prokaryotic cells typically have cell walls for added rigidity and strength. Eukaryotic cells may have cell walls (e.g., plant cells), but many eukaryotic cells, such as animal cells, do not have them.
What types of organisms have prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells?
-Prokaryotic cells are found in organisms like bacteria and archaea. Eukaryotic cells are found in a wide variety of organisms, including animals, plants, fungi, and certain unicellular organisms like yeast.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

CÉLULAS EUCARIONTES E PROCARIONTES - DIFERENÇAS | ANIMAÇÃO

Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes

Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell | Differences and Similarities | Video 16

Citologia 1/2: Estrutura Básica das Células | Anatomia e etc

Perbedaan Sel Prokariotik & Sel Eukariotik | Pembelajaran Daring - Dunia Biologi
Prokaryotic cell Vs Eukaryotic cells|| Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)