The Evolution of Drafting
Summary
TLDRThis script explores the evolution of architectural design from ancient drawings to modern Building Information Modeling (BIM). It highlights the transition from physical to digital mediums and the introduction of parametric intelligence in BIM, which enhances precision, coordination, and understanding of building systems. BIM's 3D modeling allows stakeholders to virtually walk through structures, making the design process more efficient and collaborative, ultimately leading to energy-efficient, well-integrated buildings.
Takeaways
- 🏛 The process of constructing a building starts with an idea communicated through drawings, which has been the norm for centuries.
- 📏 In the 13th century, scalar drawing emerged, allowing architects to represent actual measurements on a smaller scale.
- 🏗 The triadic system, involving plans, sections, and elevations, has been used for 800 years to describe a building's three-dimensionality.
- 📚 The transition from clay tablets to paper and from vellum to Xerox signifies the evolution of the medium but not the method of architectural communication.
- 💻 The advent of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) in the 1980s increased precision but maintained the reliance on two-dimensional drawings to represent three-dimensional objects.
- 🔍 The limitation of traditional drawings is the potential for varied interpretation, leading to information loss and miscommunication.
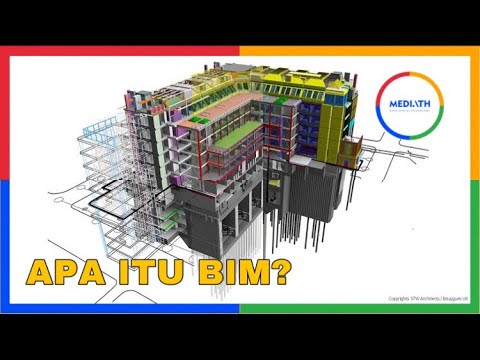
- 🛠 Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a disruptive technology that allows for the virtual construction of all building systems in 3D.
- 🌐 BIM embeds parametric intelligence in each component, enabling detailed understanding and coordination of the building's systems.
- 🏢 BIM facilitates pre-construction planning, allowing owners to virtually walk through and understand space interactions and make informed design changes.
- 🔄 The parametric intelligence in BIM aids in identifying conflicts and coordinating systems more effectively before construction begins.
- 📈 BIM's intelligence can be used to predict and optimize a building's energy usage and design, tailoring it to its climate and environment.
- 🛡️ BIM serves as a virtual history of the building, providing invaluable information for facility management and system integration post-construction.
Q & A
What is the traditional starting point for constructing a building according to the script?
-The process of constructing a building traditionally begins with an idea, which is then communicated to a builder through a drawing.
What was the method used by architects in ancient Rome to represent life-size temples and columns in stone?
-In ancient Rome, architects used full-scale drawings directly on the stone floors of a mason's quarry to represent life-size temples, columns, and entablatures.
What is a scalar drawing and when did it first emerge?
-A scalar drawing is a method where a much smaller unit equals the actual measurement of what is being drawn, for example, 1/8 of an inch equals 1 foot. It first emerged in the 13th century.
What is the triadic system and how was it used in the design of medieval cathedrals?
-The triadic system is a method that utilizes plans, sections, and elevations to describe a building from specific viewpoints. It was used by master builders to design medieval cathedrals, helping to communicate the three-dimensionality of the building.
What is the difference between a plan, an elevation, and a section in architectural drawings?
-A plan shows what you would see if you cut through the building three feet above the floor and looked directly downward. An elevation is a view of each side of the building. A section is what you would see if you cut through the building vertically and looked to the open side.
How did the drafting tools and mediums evolve from the Middle Ages to the 20th century?
-Drafting tools evolved from clay and stone tablets to linen and then to paper. The mediums changed from vellum to paper as Xerox and other reproduction processes became commonplace.
What is computer-aided drafting (CAD) and when did it become popular?
-Computer-aided drafting (CAD) is a technology that uses computers to create precise drawings, replacing hand drafting. It began to gain popularity in the 1980s and became the norm in the 1990s.
What is the main flaw in traditional architectural drawings as described in the script?
-The main flaw in traditional architectural drawings is that they rely on lines to represent three-dimensional objects, which can lead to different interpretations by different people, resulting in a loss of valuable information.
What is BIM (Building Information Modeling) and how does it differ from traditional CAD?
-BIM is a technology that allows for the virtual construction of all building systems using 3-dimensional components. Unlike traditional CAD, BIM embeds parametric intelligence in each component, allowing for more precise coordination and understanding of the building systems.
How does BIM improve the efficiency and accuracy of the construction process?
-BIM improves efficiency and accuracy by allowing for virtual construction and walk-throughs, enabling better understanding of space interactions and system coordination. It also helps in identifying conflicts and making design adjustments before construction begins.
What are the potential benefits of integrating BIM with facility management software and building control systems?
-Integrating BIM with facility management software and building control systems can create a more efficient and responsive building. It allows for precise tuning of mechanical systems, security systems, and other technologies, potentially saving clients money by optimizing performance.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

The Evolution of Drafting

DEFINISI BIM DARI 2D, 3D, 4D, 5D, 6D, 7D (Bahasa Indonesia)

How BIM is Changing and Is Data Truly the Future of BIM

The History Of Engineering Drawings

StrategicERP Version 24.1 Launch! : Witness Business Brilliance With A Burst Of Vigor!
mengenal lebih dekat apa itu BIM (building information modeling)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
