Hydrolysis and Dehydration Synthesis
Summary
TLDRThis script delves into the formation of biological polymers through the process of dehydration synthesis, where monomers—such as amino acids and glucose—join to create proteins and carbohydrates, respectively. It highlights the crucial role of water in these reactions, with the removal of hydrogen and hydroxyl groups to form bonds between monomers. Conversely, hydrolysis is presented as the reverse process, where water is used to break these bonds, returning polymers to their monomer form. The script succinctly explains these fundamental biological reactions, emphasizing the dynamic interplay between synthesis and breakdown.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Biological molecules like proteins and carbohydrates are composed of repeating subunits known as monomers.
- 🔬 When monomers come together, they form polymers through a process called dehydration synthesis.
- 💧 Dehydration synthesis involves the removal of a hydrogen atom from one monomer and a hydroxyl group from another, forming water and a bond between the monomers.
- 🔄 The opposite of dehydration synthesis is hydrolysis, where water is added to break the bond between monomers, resulting in the separation of polymers into their constituent monomers.
- 🧬 Amino acid monomers specifically join to create protein polymers, which are essential for various biological functions.
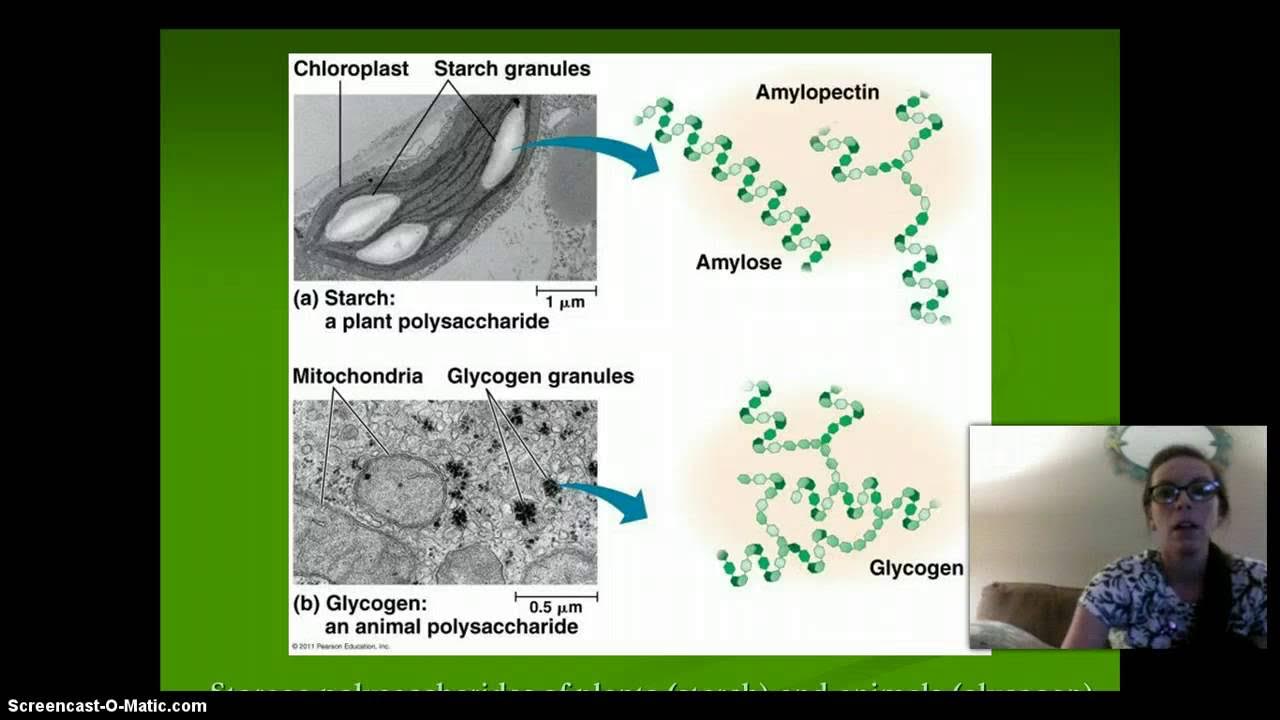
- 🍬 Glucose monomers combine to form complex carbohydrates, which are a primary source of energy for living organisms.
- 🌿 The term 'hydrolysis' is derived from the process of breaking water molecules to facilitate the breakdown of polymers.
- 💦 During hydrolysis, a water molecule's hydroxyl group attaches to one monomer, and its hydrogen atom attaches to another, effectively splitting the polymer.
- 🔄 The process of hydrolysis can be summarized as the addition of water to break down polymers into monomers.
- 🔬 Both dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis are crucial reactions in biology, playing key roles in the formation and breakdown of biological polymers.
- 📚 Understanding these processes is fundamental to grasping how biological molecules are assembled and disassembled in living organisms.
Q & A
What are monomers in the context of biological molecules?
-Monomers are the repeating subunits that form the basic building blocks of many important biological molecules.
How do monomers combine to create a polymer?
-Monomers join together to form a polymer through a process called dehydration synthesis, where water is released as a byproduct.
What is the role of amino acids in protein formation?
-Amino acids are monomers that join to form protein polymers, which are essential for various functions in living organisms.
How do glucose monomers contribute to the formation of carbohydrates?
-Glucose monomers combine to form complex carbohydrates through dehydration synthesis, creating chains that are vital for energy storage and other functions.
What is the significance of the dehydration synthesis reaction in biological polymer formation?
-Dehydration synthesis is crucial for the formation of biological polymers as it links monomers together while releasing water, creating stable polymer structures.
What happens during a dehydration synthesis reaction at the molecular level?
-During dehydration synthesis, a hydrogen atom is removed from one monomer and a hydroxyl group from another, forming water and a bond that links the two monomers.
What is hydrolysis and how is it related to dehydration synthesis?
-Hydrolysis is the opposite of dehydration synthesis. It is a reaction where a polymer is broken down into its monomer subunits by the addition of water.
What does the term 'hydrolysis' literally mean?
-The term 'hydrolysis' literally means 'break water', reflecting the process where water molecules are used to break the bonds between monomers in a polymer.
How does the hydroxyl group from a water molecule participate in the hydrolysis reaction?
-In hydrolysis, the hydroxyl group from a water molecule attaches to one monomer, and the remaining hydrogen attaches to the other, effectively breaking the bond between the monomers.
What is the outcome of a hydrolysis reaction in terms of the polymer and water?
-The outcome of a hydrolysis reaction is the reduction of a polymer into its monomer subunits, with water being used to facilitate the breaking of the bonds between the monomers.
How does the process of hydrolysis differ from dehydration synthesis in terms of water involvement?
-During dehydration synthesis, water is released as monomers join to form a polymer. In contrast, during hydrolysis, water is added to the reaction to break the polymer into monomers.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)