Auscultation of Heart Sounds | Assessing Heart Sounds | Listening to the Heart with a Stethoscope
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Sarah from Register Nurse Orion Comm teaches viewers how to auscultate heart sounds. She demonstrates the process on a real person, explaining the significance of S1 and S2 sounds, which correspond to the closure of the heart's valves. Sarah provides anatomical landmarks for accurate auscultation and discusses additional heart sounds like S3, S4, and murmurs. She offers tips for distinguishing between sounds and the importance of patient positioning to detect subtleties in heart sounds, concluding with a guide on how to identify and grade heart murmurs.
Takeaways
- 👂 The purpose of auscultating heart sounds is to assess the heart's rhythm, rate, and the closure of heart valves.
- 📍 Heart sounds are associated with specific valves: S1 with tricuspid and mitral valves, and S2 with aortic and pulmonic valves.
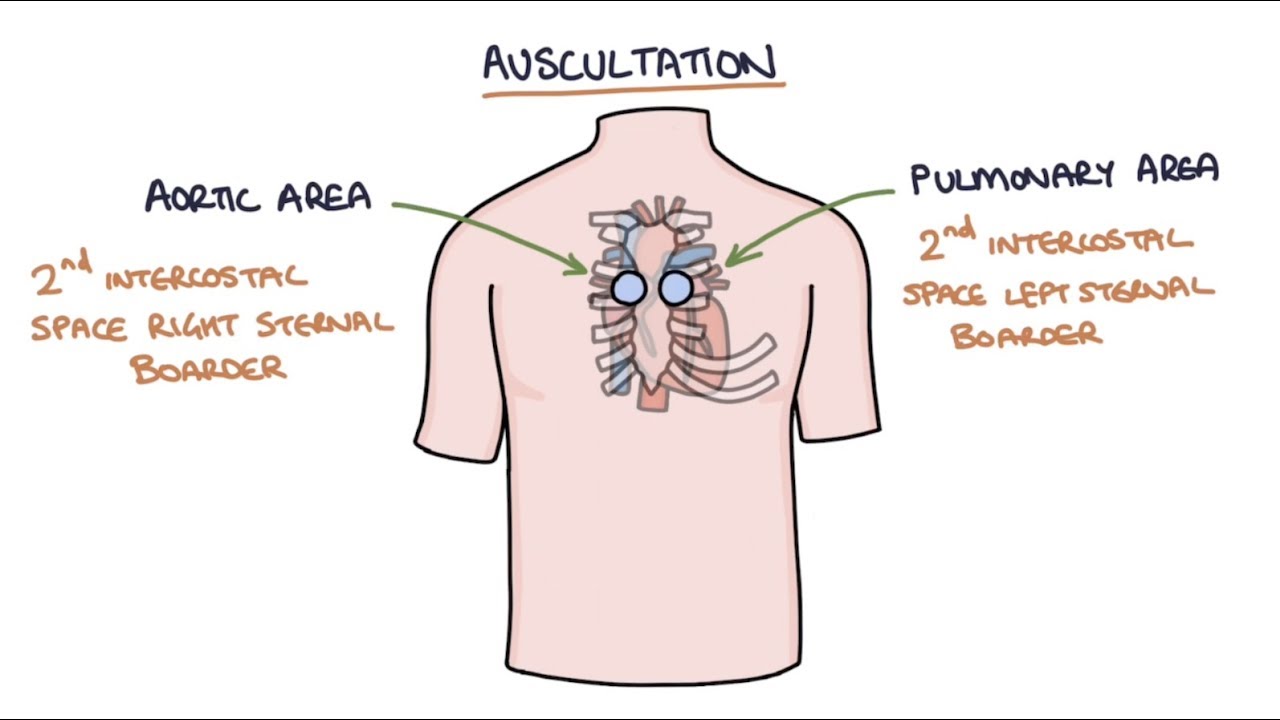
- 📌 Anatomical sites for auscultation include the aortic area, pulmonic area, the apex (heart's base), and the mitral area.
- 🔍 Auscultation begins by finding the clavicle, angle of Louis, and the second intercostal space to locate the valves.
- 👆 The aortic and pulmonic valves close together, producing the louder S2 sound, usually heard at the base of the heart.
- 👇 The tricuspid and mitral valves close simultaneously to produce S1, typically louder at the apex.
- 🎧 Using a stethoscope, start with the diaphragm to hear S1 and S2 clearly, then switch to the bell to listen for murmurs.
- 🔊 S2 is louder at the base, and S1 is louder at the apex, which helps in distinguishing between the two sounds.
- 🛏️ Positioning the patient differently, such as on their left side, can help in identifying additional heart sounds like S3 and S4.
- 👂🏼 Auscultation for S3 and S4 involves listening at the apex with the bell of the stethoscope, as these sounds are low-pitched.
- 📊 Heart murmurs are extra sounds that may indicate issues with blood flow through the heart valves and should be graded if present.
Q & A
What is the primary purpose of auscultating heart sounds?
-The primary purpose of auscultating heart sounds is to assess the regularity of the heart rhythm, count the rate, and evaluate the function of the heart valves by listening to the sounds they make when closing.
What are the two main heart sounds, S1 and S2, associated with?
-S1 is associated with the closing of the tricuspid and mitral valves, while S2 is associated with the closing of the aortic and pulmonic valves.
How can you locate the anatomical sites for auscultating heart sounds on a patient?
-To locate the anatomical sites, find the clavicle on the patient, then go down to find the angle of Louis, where the second rib comes out. The right side of this border is the aortic valve, and the left side is the pulmonic valve. The tricuspid valve is found in the fourth intercostal space, and the mitral valve is found in the fifth intercostal space at the mid-clavicular line.
What is the significance of the point of maximal impulse (PMI) in auscultation?
-The point of maximal impulse (PMI) is significant because it is where the heart's contraction is most easily felt and heard, typically located at the mitral valve area, and can help in identifying the location for auscultation.
What is the mnemonic 'ALL PATIENTS TAKE MEDICINE' used for in auscultation?
-The mnemonic 'ALL PATIENTS TAKE MEDICINE' is used to remember the order of auscultation sites: Aortic, Left sternal border (mid-clavicular line), Pulmonic, Apex, and Mitral, which helps in systematically assessing the heart sounds.
Why is it important to differentiate between S1 and S2 when auscultating heart sounds?
-Differentiating between S1 and S2 is important because it helps in identifying the specific valves that are closing, which is crucial for diagnosing any abnormalities in heart valve function.
What are some tips for distinguishing between S1 and S2 sounds?
-S2 is typically louder at the base of the heart, while S1 is louder at the apex. Additionally, feeling the carotid pulse while listening to the apex can help identify S1, as the sound coincides with the pulse. Observing the QRS complex on a bedside monitor can also help, as S1 occurs with the spike of the QRS complex.
Why is the patient positioned on their left side during auscultation?
-Positioning the patient on their left side helps because most of the heart is on the left side, and turning them to that side allows the heart to move over slightly, making it easier to hear the anatomical sites, especially the apex.
What are S3 and S4 heart sounds, and why are they significant?
-S3 and S4 are extra heart sounds that can be heard in certain conditions. S3 is a sound heard just after S2 and may be normal in children and young adults but can indicate heart problems in older adults. S4 is heard just before S1 and is not typically present in a normal heart, indicating a possible issue when heard.
How can auscultation help in identifying heart murmurs?
-Auscultation can help identify heart murmurs by listening for blowing or swishing noises, which may indicate turbulent blood flow due to valve issues. The patient may be asked to lean forward and exhale to enhance the sounds, and the diaphragm of the stethoscope is used to pick up these murmurs at the aortic and pulmonic areas.
What is the grading scale for heart murmurs, and what does it indicate?
-The grading scale for heart murmurs ranges from one to six, with grade one being hard to hear and grade six being so loud that the stethoscope can be lifted off the chest and the murmur can still be heard. The grading indicates the intensity of the murmur, which can help in assessing the severity of the underlying condition.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Diabetic Ketoacidosis DKA Nursing | DKA Pathophysiology Treatment Management NCLEX
Heart Murmurs and Heart Sounds: Visual Explanation for Students
Left-Sided Heart Failure vs Right-Sided Heart Failure Pathophysiology Nursing NCLEX Review

Lung Sounds Collection - EMTprep.com

Hypovolemia Fluid Volume Deficit | Dehydration Nursing NCLEX Treatment, Pathophysiology

Anatomy & Physiology Integumentary Skin System Overview
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
