Understanding 'Levels of Evidence' - What are Levels of Evidence?
Summary
TLDRThis tutorial outlines the importance of understanding levels of evidence in physiotherapy practice, emphasizing the Pyramid of Evidence for identifying the best research studies. It highlights the hierarchy, starting from lab and animal studies to randomized control trials (RCTs), systematic reviews, and meta-analyses at the top. The video explains how higher levels of evidence, such as RCTs and systematic reviews, contribute to evidence-informed practice, guiding clinical decisions. It also introduces the concept of practice guidelines, which synthesize literature to recommend best practices, sometimes incorporating expert opinions and consensus. The tutorial aims to equip viewers with the skills to navigate the physiotherapy evidence database, PEDro, for effective clinical decision-making.
Takeaways
- 📚 The tutorial focuses on understanding levels of evidence based on research study design for evidence-informed practice in physiotherapy.
- 🔍 Evidence-informed practice combines the best available evidence, clinical expertise, and patient values to guide clinical decision-making.
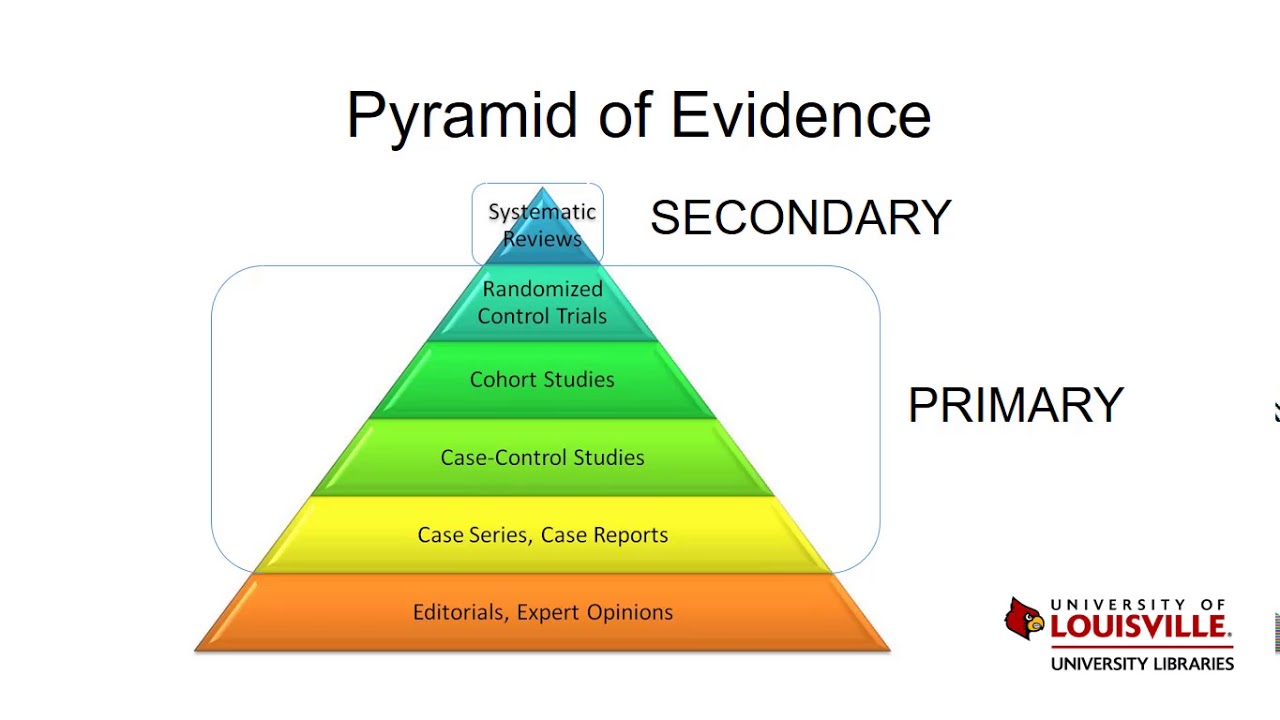
- 📈 The Pyramid of Evidence illustrates the hierarchy of research study designs, with higher levels indicating more rigorous research and stronger evidence.
- 🧪 At the base of the pyramid are preliminary studies like lab investigations and animal studies, while the top includes more rigorous designs like RCTs and systematic reviews.
- 🧐 The higher the level of evidence, the more confidence one can have in applying the findings to clinical practice.
- 🤔 Not every topic will have the highest level of evidence available, especially for rare conditions or new therapies.
- 🔬 Randomized Control Trials (RCTs) are considered high-level evidence due to the random allocation of similar participants to intervention and control groups.
- 📝 Systematic reviews and meta-analyses save clinicians time by summarizing and combining the results of multiple studies, providing a comprehensive overview.
- 📊 A meta-analysis statistically combines results from studies using the same outcome measures, while a systematic review may include different measures.
- 📋 Practice guidelines are developed to assist in healthcare decisions, summarizing literature to guide best practices, and may include expert opinions and consensus.
- 🔍 The next tutorial will demonstrate how to use the Physiotherapy Evidence Database (PEDro) to find the highest levels of evidence.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of the tutorial?
-The main purpose of the tutorial is to explain the levels of evidence based on research study design, helping viewers find the best evidence for their practice.
Why is it important to learn about levels of evidence in healthcare practice?
-It is important to learn about levels of evidence because it ties into evidence-informed practice, aiding in the search for information and applying the best available evidence, clinical expertise, and patient values and expectations to clinical decision-making.
What does 'evidence-informed practice' mean in the context of this tutorial?
-Evidence-informed practice refers to the application of the best available evidence, combined with clinical expertise and patient values and expectations, to make clinical decisions.
What does the Pyramid of Evidence represent?
-The Pyramid of Evidence represents different levels of research study designs, with the most rigorous and highest level of evidence at the top and less rigorous designs at the bottom.
What types of studies are considered to be at the bottom of the Pyramid of Evidence?
-At the bottom of the Pyramid of Evidence are lab investigations with test tubes or animal studies, which are considered to have a lower level of evidence.
What is a Randomized Control Trial (RCT) and why is it considered a high level of evidence?
-A Randomized Control Trial (RCT) is a study where participants are randomly allocated to either a group that receives a standardized intervention or a control group that receives usual care or a placebo. It is considered a high level of evidence due to its ability to control for confounding variables and provide strong evidence for cause-and-effect relationships.
What is the difference between a systematic review and a meta-analysis?
-A systematic review methodically searches, assesses, and summarizes studies according to predetermined criteria, often including RCTs. A meta-analysis, on the other hand, statistically combines the results of several studies that address a set of related research hypotheses, using the same outcome measures.
Why are systematic reviews and meta-analyses considered timesavers for clinicians?
-Systematic reviews and meta-analyses are considered timesavers because they combine the results of multiple studies, saving clinicians the effort of reading numerous individual articles to answer a clinical question.
What is a practice guideline and how does it help in evidence-informed practice?
-A practice guideline is a systematically developed statement that helps practitioners and patients make decisions about appropriate healthcare. It summarizes literature to guide best practice and may include opinions and consensus processes, making it a valuable resource for evidence-informed practice.
What is the physiotherapy evidence database mentioned in the tutorial, and what is its purpose?
-The physiotherapy evidence database, also known as PEDro, is a resource developed for members of the physiotherapy associations. Its purpose is to help users find the highest levels of evidence to inform their clinical practice.
How can viewers find more information or tutorials like this one?
-Viewers can find more information and tutorials through the organization's YouTube channel and website, as mentioned at the end of the tutorial.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)