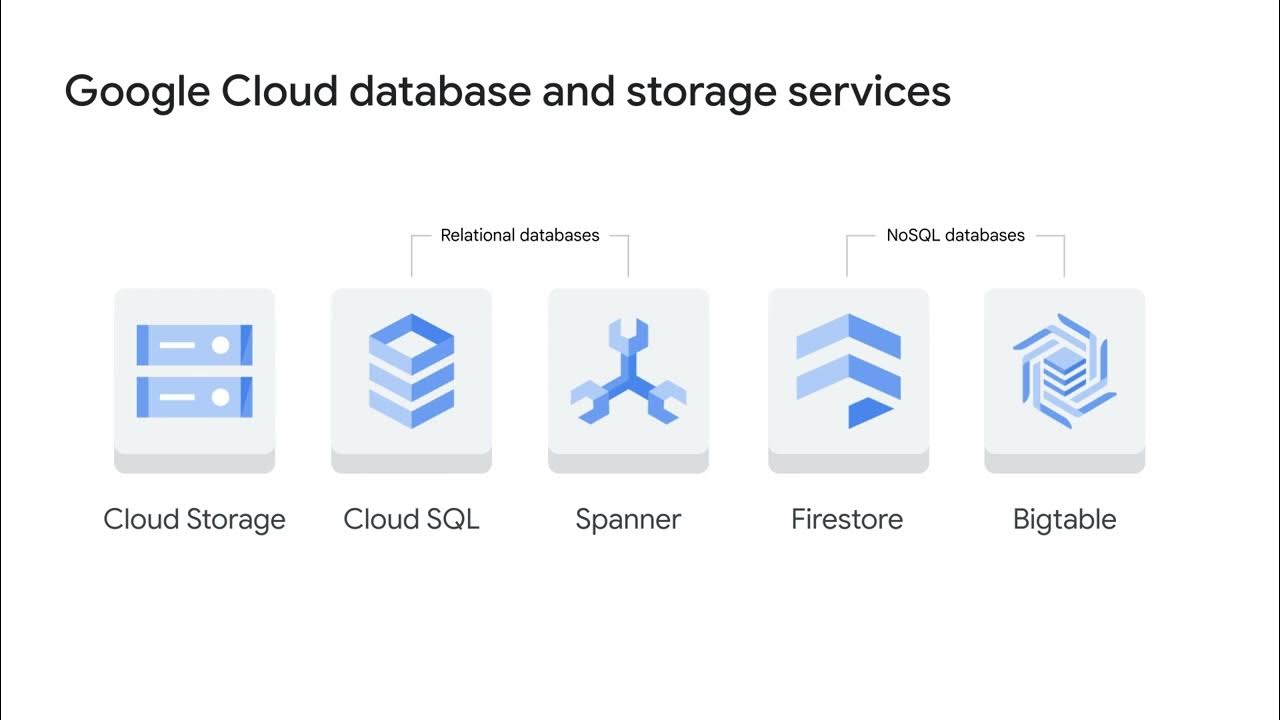
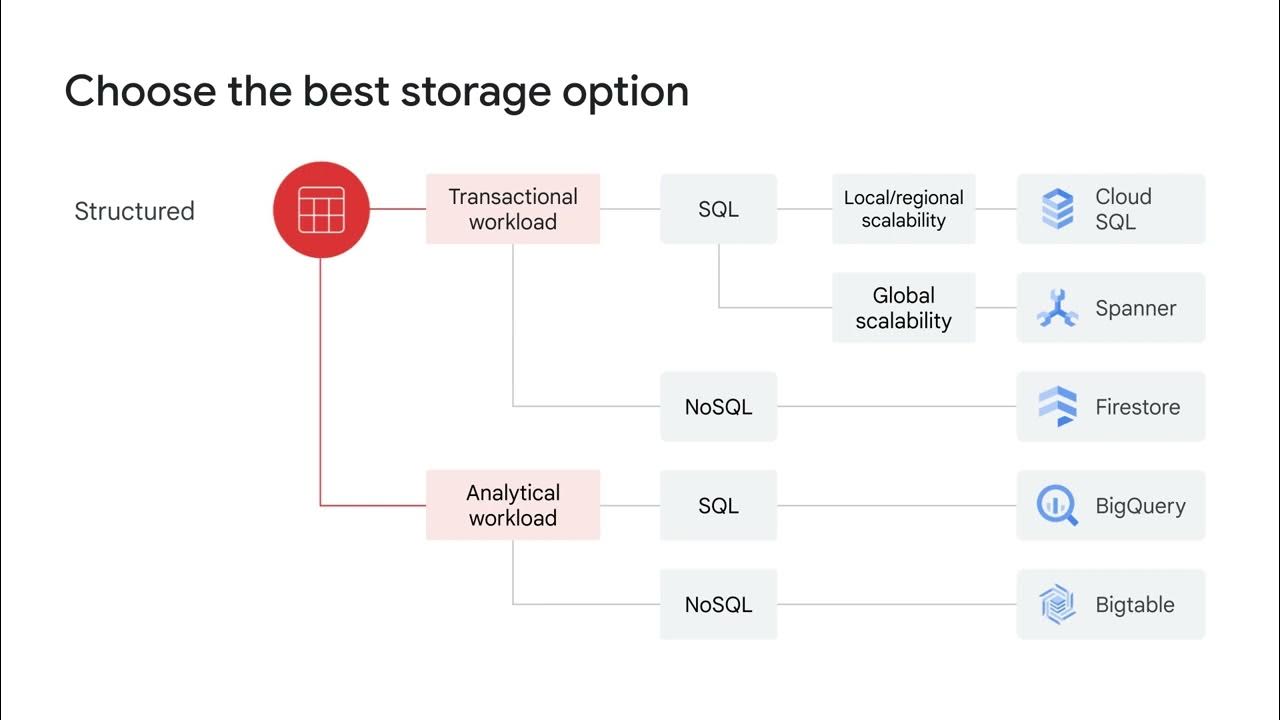
Unstructured storage using Cloud Storage
Summary
TLDRCloud Storage is a fully managed, scalable service for storing unstructured data, such as videos, photos, and backup files. It is an object storage system where data is managed as objects with metadata and a globally unique identifier. The service offers four storage classes: Standard, Nearline, Coldline, and Archive, each suited for different data access frequencies and costs. Cloud Storage provides high durability, low latency, and geo-redundancy. Key features include versioning, lifecycle management, and tight integration with other Google Cloud services, making it ideal for large-scale, distributed data storage and management.
Takeaways
- 😀 Cloud Storage is a fully managed, scalable service ideal for storing unstructured data like videos, photos, and backups.
- 😀 Object storage refers to managing data as 'objects,' which include the actual data, metadata, and a globally unique identifier.
- 😀 Google Cloud Storage is a product designed for storing and retrieving any amount of data, with flexible usage for many different types of content.
- 😀 There are four main Cloud Storage classes: Standard, Nearline, Coldline, and Archive, each suited to different data access needs and costs.
- 😀 Standard Storage is for frequently accessed data, while Nearline Storage is best for infrequently accessed data (once a month on average).
- 😀 Coldline Storage is a low-cost option for data accessed less than once every 90 days, whereas Archive Storage is meant for rarely accessed data (less than once a year).
- 😀 Cloud Storage offers characteristics like unlimited storage, worldwide accessibility, low latency, high durability, and geo-redundancy for data protection.
- 😀 Data in Cloud Storage is organized into buckets, which must have a globally unique name and a specific geographic location to optimize latency.
- 😀 Cloud Storage objects are immutable, meaning new versions are created with changes, and versioning can be enabled to track modifications.
- 😀 Lifecycle management policies in Cloud Storage allow users to manage object retention, such as deleting old objects or keeping only recent versions.
- 😀 Cloud Storage integrates tightly with other Google Cloud products, offering easy ways to move data between services like BigQuery, Cloud SQL, and Compute Engine.
Q & A
What is Cloud Storage and how is it used?
-Cloud Storage is a fully managed scalable service primarily used for storing unstructured data. It's ideal for use cases such as serving website content, backing up data for archival and disaster recovery, and distributing large data objects like videos and photos.
What is object storage, and how does it differ from file and block storage?
-Object storage is a data storage architecture that stores data as objects, rather than in file/folder hierarchies (file storage) or as chunks of a disk (block storage). Each object contains the actual data, associated metadata, and a globally unique identifier, often in the form of a URL.
What types of data are typically stored in Cloud Storage?
-Cloud Storage is commonly used to store data such as videos, photos, audio recordings, backup data, and archived information, especially when dealing with binary large objects (BLOBs).
How does Cloud Storage manage and bill data?
-Cloud Storage categorizes data into four storage classes, and billing is based on the storage class assigned. These classes include Standard, Nearline, Coldline, and Archive, each designed for specific access frequencies and durations.
What are the key characteristics shared across all Cloud Storage classes?
-Regardless of the storage class, Cloud Storage offers unlimited storage with no minimum object size requirement, worldwide accessibility, low latency, high durability, a uniform experience across tools and APIs, and geo-redundancy to protect against catastrophic events.
What are the four primary storage classes in Cloud Storage?
-The four primary storage classes are: 1) Standard Storage (for frequently accessed data), 2) Nearline Storage (for infrequently accessed data, about once per month), 3) Coldline Storage (for data accessed less than once every 90 days), and 4) Archive Storage (for long-term data access with minimal retrieval).
How does the versioning feature work in Cloud Storage?
-Versioning in Cloud Storage allows users to keep track of every change made to an object. When enabled, each modification creates a new version, preserving previous versions. Without versioning, new versions overwrite the old ones.
What is the purpose of lifecycle management in Cloud Storage?
-Lifecycle management allows users to automatically manage the data within Cloud Storage. For example, data can be deleted after a certain period, or only a set number of recent versions of an object can be kept. This helps automate data retention and cleanup.
How does Cloud Storage integrate with other Google Cloud services?
-Cloud Storage integrates tightly with other Google Cloud products, enabling users to import and export data to/from BigQuery and Cloud SQL, store App Engine logs, Firestore backups, Compute Engine images, and objects used by Compute Engine applications.
What factors should be considered when choosing the geographic location for a Cloud Storage bucket?
-When selecting a location for a Cloud Storage bucket, factors like minimizing latency should be considered. For example, if most users are in Europe, it is ideal to choose a European region or EU multi-region to ensure faster access times.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)