Master Slave JK Flip Flop | Digital Electronics
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker explains the Master-Slave JK flip-flop, a key component in digital electronics used to solve the race-around condition in standard JK flip-flops. The race-around condition occurs when both J and K inputs are set to '1,' leading to unpredictable outputs due to continuous feedback. The Master-Slave configuration addresses this issue by separating the flip-flop into two stages—master and slave—allowing stable output control. This solution effectively manages feedback, ensuring predictable behavior in digital circuits and preventing unwanted toggling, making it a crucial concept for digital electronics enthusiasts.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Master-Slave JK Flip-Flop is a crucial topic in digital electronics that often confuses students.
- 😀 Flip-Flops, in general, are prone to race conditions, which can cause problems in circuit behavior.
- 😀 Race conditions occur when two variables are set to the same value, creating unpredictable outcomes.
- 😀 Clock signals play a major role in controlling the behavior of Flip-Flops, where the signal level can either be positive or negative.
- 😀 The Master-Slave configuration helps to resolve the issue of race conditions by controlling feedback.
- 😀 Feedback can cause problems in circuits by triggering unnecessary changes. It needs to be carefully managed.
- 😀 A solution to controlling feedback is to use the Master-Slave configuration, which reduces issues with toggling values.
- 😀 The Master-Slave Flip-Flop works by isolating feedback to control when changes occur and ensure stable outputs.
- 😀 Proper feedback control ensures that changes happen only when necessary, preventing continuous toggling and unnecessary state changes.
- 😀 Master-Slave Flip-Flops offer a method to control the toggling behavior, ensuring a system only reacts when the appropriate trigger occurs.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video script?
-The main topic of the video is the Master-Slave JK Flip-Flop, an important concept in digital electronics.
Why do many students struggle with the Master-Slave JK Flip-Flop concept?
-Many students struggle because the concept involves complex conditions, especially regarding race-around conditions and feedback mechanisms, which are not easily understood.
What is the problem faced in the JK Flip-Flop that the Master-Slave configuration aims to solve?
-The problem is the race-around condition, where the output of the flip-flop keeps changing due to improper timing of the clock signal, leading to unpredictable results.
What does the Master-Slave JK Flip-Flop do to address the race-around condition?
-The Master-Slave JK Flip-Flop uses a feedback mechanism to control the timing of the output and prevent the race-around condition. It uses a combination of master and slave stages to ensure that the output is stable and controlled.
What is the role of the clock in a JK Flip-Flop?
-The clock in a JK Flip-Flop controls the timing of the state transitions. It triggers changes in the output based on the inputs (J, K) at specific intervals, ensuring synchronization.
What is the significance of the positive and negative levels of the clock in this system?
-The positive and negative levels of the clock determine when the flip-flop is active or inactive. This control helps to manage the transitions and avoid unwanted toggling or feedback.
How does the Master-Slave configuration help in feedback control?
-The Master-Slave configuration isolates the feedback from the input, reducing unwanted interactions. This isolation ensures that the flip-flop functions correctly without the feedback causing erratic changes.
What is the impact of feedback in the JK Flip-Flop, and how does it affect the output?
-Feedback in the JK Flip-Flop can cause the output to change unpredictably. Without proper control, feedback loops can lead to continuous toggling, but using Master-Slave configuration controls the feedback and stabilizes the output.
Can the Master-Slave JK Flip-Flop work without feedback control?
-No, without feedback control, the JK Flip-Flop can experience issues like the race-around condition, making it unreliable for stable operation.
What practical solution is suggested for avoiding issues in the JK Flip-Flop?
-The practical solution is to implement the Master-Slave configuration, which uses controlled feedback and clock timing to ensure stable output without interference from race-around conditions.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
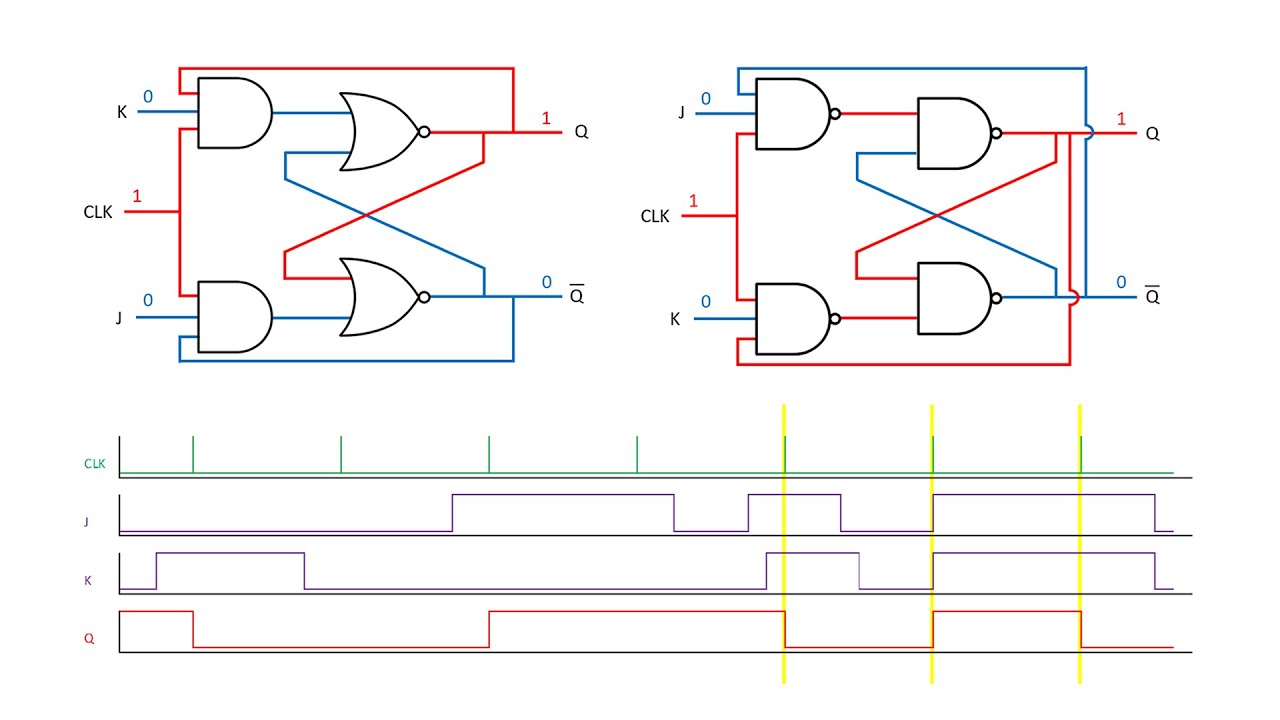
Latches and Flip-Flops 6 - The JK Flip Flop

SAYISAL ELEKTRONİK DERSLERİ: JK Flip Flop
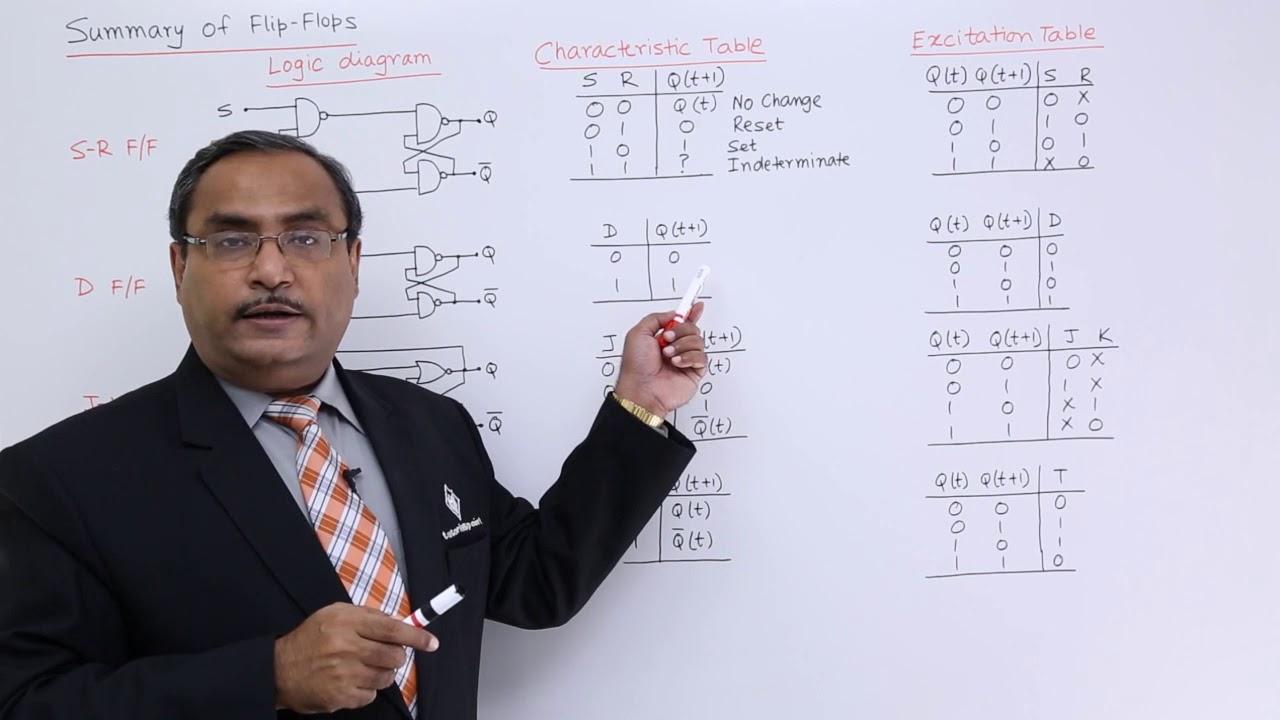
Summary of all Flip-Flops

Introduction to JK Flip Flop | JK flip flop full explanation | Digital Electronics

FLIP-FLOP - Jenis dan tabel kebenaran

Part 5.2 #Latches and #FlipFlops #SequentialCircuits in Digital Electronics in Hindi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
