Fisika Kelas 11 | Konsep Pembiasan Cahaya pada Lensa Cembung
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the teacher, Aris Kurniawan, explains the concept of light refraction, particularly through convex lenses. He introduces the basic properties and types of lenses, emphasizing the behavior of light as it passes through convex lenses. The lesson includes the classification of convex lenses, the anatomy of the lens, and how light focuses. It also explains the calculation of image magnification and focal length using specific formulas. The teacher provides examples of problems involving real-world applications of convex lenses, such as magnifying glasses, eyeglasses, and microscopes. The lesson concludes with practice problems to enhance understanding.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lenses are transparent objects that bend light, commonly made of glass or plastic, and are used in optical devices like glasses, magnifying glasses, cameras, telescopes, and microscopes.
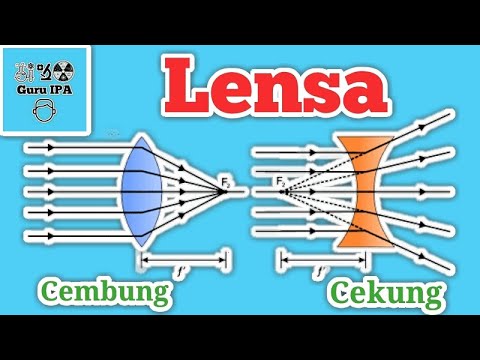
- 😀 A convex lens (also known as a converging lens) has a thicker center and bends light rays to converge at a focal point behind the lens.
- 😀 The focal point of a convex lens is where parallel light rays converge, and this point is called the true focus. The focal length of the lens is positive.
- 😀 Convex lenses are referred to as converging lenses because they focus light rays, and they can be used for applications such as magnification or focusing light.
- 😀 There are three types of convex lenses: biconvex (both surfaces curved), plano-convex (one flat surface and one curved), and concave-convex (one curved surface and one concave).
- 😀 The convex lens has two focal points: the active focal point (behind the lens) and the passive focal point (in front of the lens). These are symmetric with respect to the lens.
- 😀 When a convex lens focuses light, such as sunlight, at a single point, it can create enough heat to burn a piece of paper, demonstrating the lens's ability to concentrate light.
- 😀 Three special rays for convex lenses include: (1) rays parallel to the principal axis converge at the focal point, (2) rays through the focal point in front of the lens become parallel after passing through, and (3) rays passing through the optical center remain unaffected.
- 😀 To draw an image formed by a convex lens, two special rays should be used to locate the image's position and determine its size and orientation.
- 😀 The image's properties (real or virtual, upright or inverted, magnified or reduced) depend on the object's position relative to the lens. Real images are inverted, while virtual images are upright.
- 😀 The lens formula (1/f = 1/s + 1/s') and magnification formula (M = |s'| / |s|) are used to calculate image properties, with 'f' being the focal length, 's' the object distance, and 's'' the image distance.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the video?
-The main topic of the video is about the refraction of light in lenses, specifically focusing on convex lenses and their properties.
What is a lens, and where are they commonly used?
-A lens is a transparent object that refracts light. Lenses are commonly used in eyeglasses, magnifying glasses, cameras, telescopes, and microscopes.
What are the two types of lenses discussed in the video?
-The two types of lenses discussed are convex lenses and concave lenses.
How does a convex lens work?
-A convex lens is thicker in the middle and causes light rays to converge or meet at a focal point behind the lens. This property allows it to form real or virtual images depending on the object's position relative to the lens.
What is the difference between the focal points F1 and F2 in a convex lens?
-F1, the active focal point, is located behind the lens and is used to converge light rays. F2, the passive focal point, is in front of the lens and serves as a reference point for determining the behavior of light rays.
What is the significance of the 'focus' in a convex lens?
-The focus of a convex lens is the point where light rays converge after passing through the lens. This focus is crucial for forming sharp and clear images in optical devices like cameras and microscopes.
How do you calculate magnification in a lens system?
-Magnification (M) can be calculated using the formula M = S' / S, where S' is the image distance and S is the object distance from the lens. Alternatively, magnification can also be calculated using the heights of the image and object.
What happens to the image when the object is placed closer to the lens than the focal point?
-When the object is placed closer to the lens than the focal point, the image formed is virtual, upright, and magnified, and it appears in front of the lens.
What formula is used to find the relationship between object distance, image distance, and focal length in a lens?
-The formula used is 1/f = 1/S + 1/S', where f is the focal length, S is the object distance, and S' is the image distance.
How does the curvature of the lens affect its focal length?
-The curvature of a lens affects its focal length. A lens with a greater curvature will have a shorter focal length, while a lens with a flatter curvature will have a longer focal length.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
Lensa Cekung dan Lensa Cembung

Pemantulan dan Pembiasan Cahaya dengan KIT OPTIK
Why Does Light Bend? | Concave & Convex Lenses | The Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz
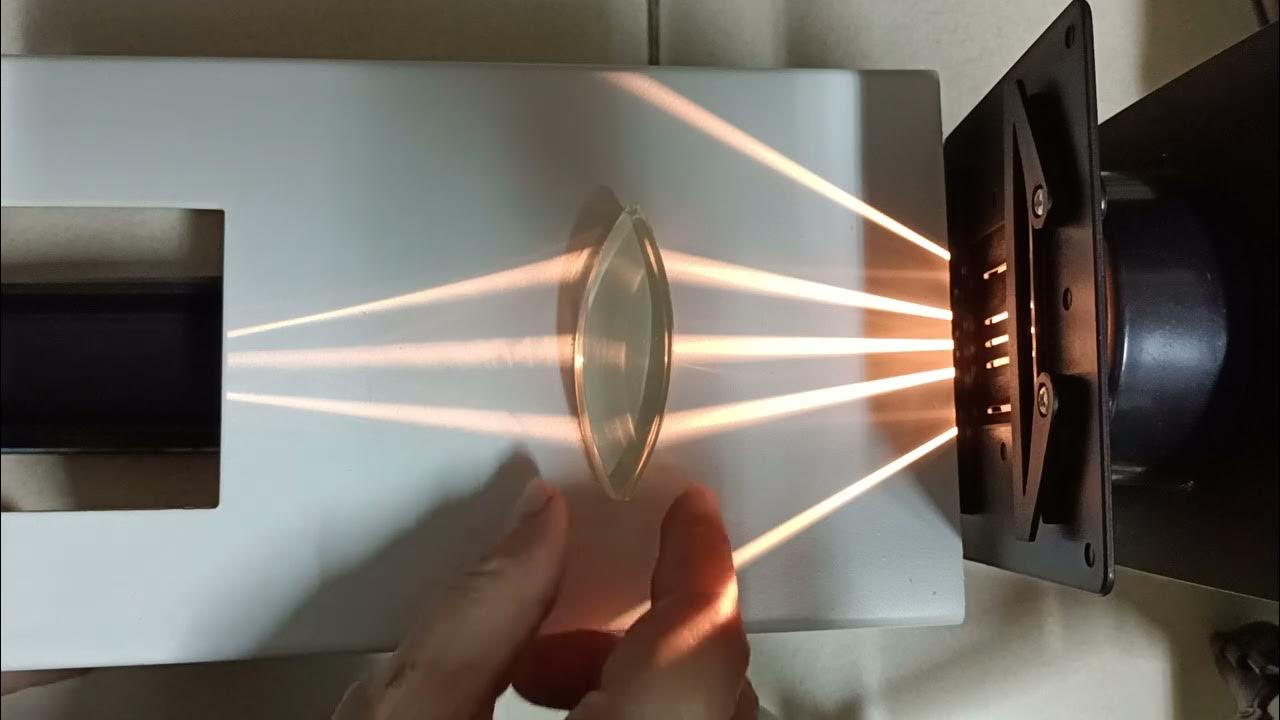

Pembiasan Cahaya Lensa Cembung dan Lensa Cekung

Grade 10 SCIENCE | Quarter 2 Module 7 | Refraction in Lenses • Ray Diagrams • Lens Equation

Light - Reflection & Refraction FULL CHAPTER in Animation | NCERT Science | CBSE Class 10 Chapter 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
