Grade 10 SCIENCE | Quarter 2 Module 7 | Refraction in Lenses • Ray Diagrams • Lens Equation
Summary
TLDRIn this educational session, students learn about lenses, specifically focusing on converging (convex) and diverging (concave) lenses. The instructor explains the principles of light refraction, ray diagrams, and how different object placements affect image characteristics. Key concepts include real versus virtual images, sign conventions for focal lengths, and calculations using the lens equation. Through examples and problem-solving, students gain a deeper understanding of how lenses manipulate light to form images, highlighting the importance of these concepts in optics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Lenses are transparent objects with curved surfaces that refract light.
- 😀 There are two main types of lenses: converging (convex) and diverging (concave).
- 😀 Converging lenses are thicker in the center and focus light rays towards a focal point.
- 😀 Diverging lenses are thicker at the edges and cause light rays to spread apart.
- 😀 Ray diagrams for converging lenses show how image characteristics change based on object distance.
- 😀 Real images are formed on the opposite side of the lens from the object, while virtual images are formed on the same side.
- 😀 The lens equation is expressed as 1/f = 1/do + 1/di, relating focal length, object distance, and image distance.
- 😀 Sign conventions indicate that the focal length is positive for converging lenses and negative for diverging lenses.
- 😀 Magnification is calculated as m = hi/ho = -di/do, indicating the size and orientation of the image.
- 😀 Understanding lenses involves both qualitative descriptions and quantitative calculations using ray diagrams and equations.
Q & A
What are lenses and how do they function?
-Lenses are pieces of clear plastic or glass with curved surfaces that refract light, bending the light rays as they pass through.
What are the two main types of lenses?
-The two main types of lenses are converging (convex) lenses, which are thicker at the center, and diverging (concave) lenses, which are thicker at the edges.
How do converging lenses affect light rays?
-Converging lenses converge light rays towards a focal point, allowing them to meet on the opposite side of the lens.
What happens to light rays passing through diverging lenses?
-Diverging lenses cause light rays to spread apart, diverging from a focal point on the same side as the object.
What are the key characteristics of images formed by converging lenses?
-Images formed by converging lenses can be real or virtual, inverted or upright, and their size can vary depending on the object's distance from the lens.
What is the lens equation, and what does it represent?
-The lens equation is 1/f = 1/do + 1/di, where f is the focal length, do is the object distance, and di is the image distance. It describes the relationship between these distances.
How is magnification calculated in lens systems?
-Magnification (m) is calculated using the formula m = hi/ho = -di/do, where hi is the height of the image and ho is the height of the object.
What is the significance of the sign conventions in lens equations?
-Sign conventions indicate whether the focal length and image distance are positive or negative, which helps determine the nature of the lens and image. For example, focal lengths for converging lenses are positive.
Can you explain how to determine if an image is real or virtual using ray diagrams?
-If the image is formed on the opposite side of the lens from the object, it is real. If it is on the same side as the object, it is virtual.
What can be inferred about an image's nature when its magnification is greater than 1?
-A magnification greater than 1 indicates that the image is larger than the object and is upright.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
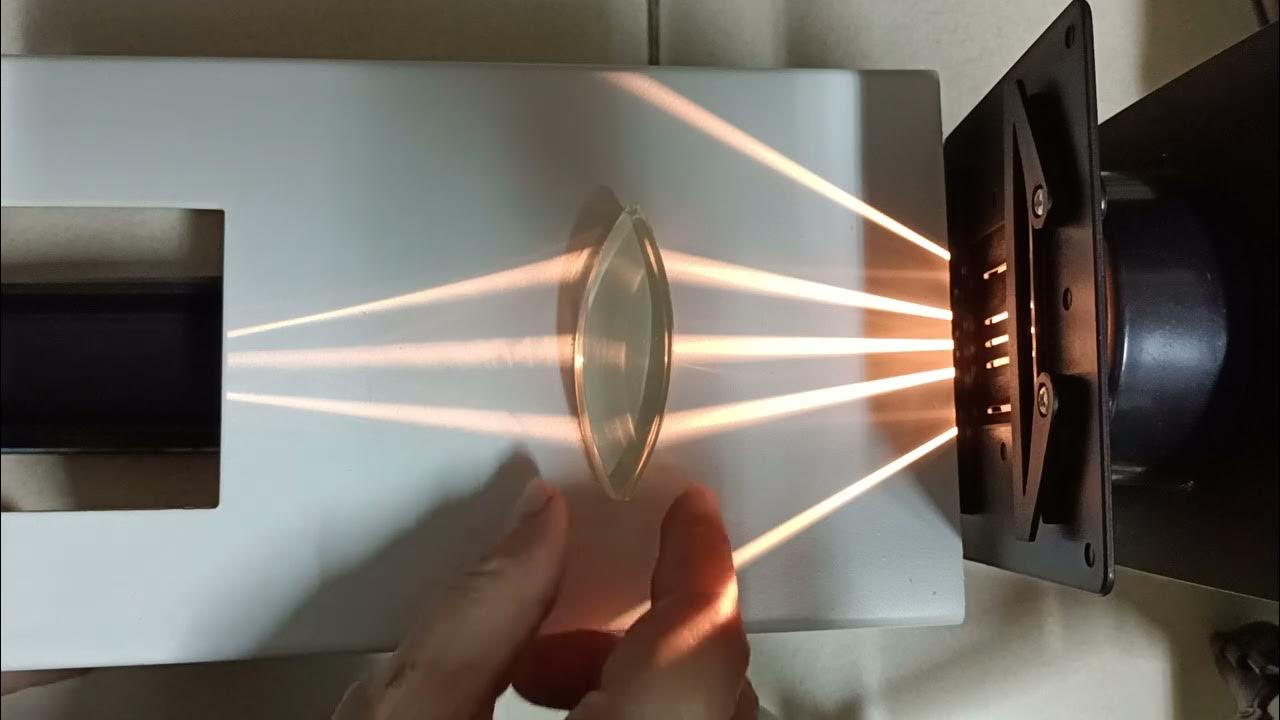

Pembiasan Cahaya Lensa Cembung dan Lensa Cekung

Qualitative Characteristics (Orientation, Types, and Magnification) of Images Formed by Lenses

GCSE Physics - How Lenses Work #69
Myopia and Hypermetropia

Lesson 7: Types of Lenses (Convex and Concave)
Why Does Light Bend? | Concave & Convex Lenses | The Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)