Química: Metais e Ligações Metálicas
Summary
TLDRThe video explains the unique properties of metals, such as their brilliance, malleability, ductility, and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. It highlights the structure of metals, where positive ions are surrounded by a sea of mobile electrons, explaining their properties like conductivity and shine. It contrasts metallic bonds with ionic and covalent bonds, noting the strength differences. The video also discusses how metals respond to force, with metals like gold being more malleable and platinum being highly ductile. Finally, it mentions mercury as the only liquid metal at room temperature and others that melt close to it.
Takeaways
- 😀 Metals are shiny, malleable, ductile, and excellent conductors of heat and electricity.
- 😀 The structure of metals and the nature of metallic bonds explain their unique properties.
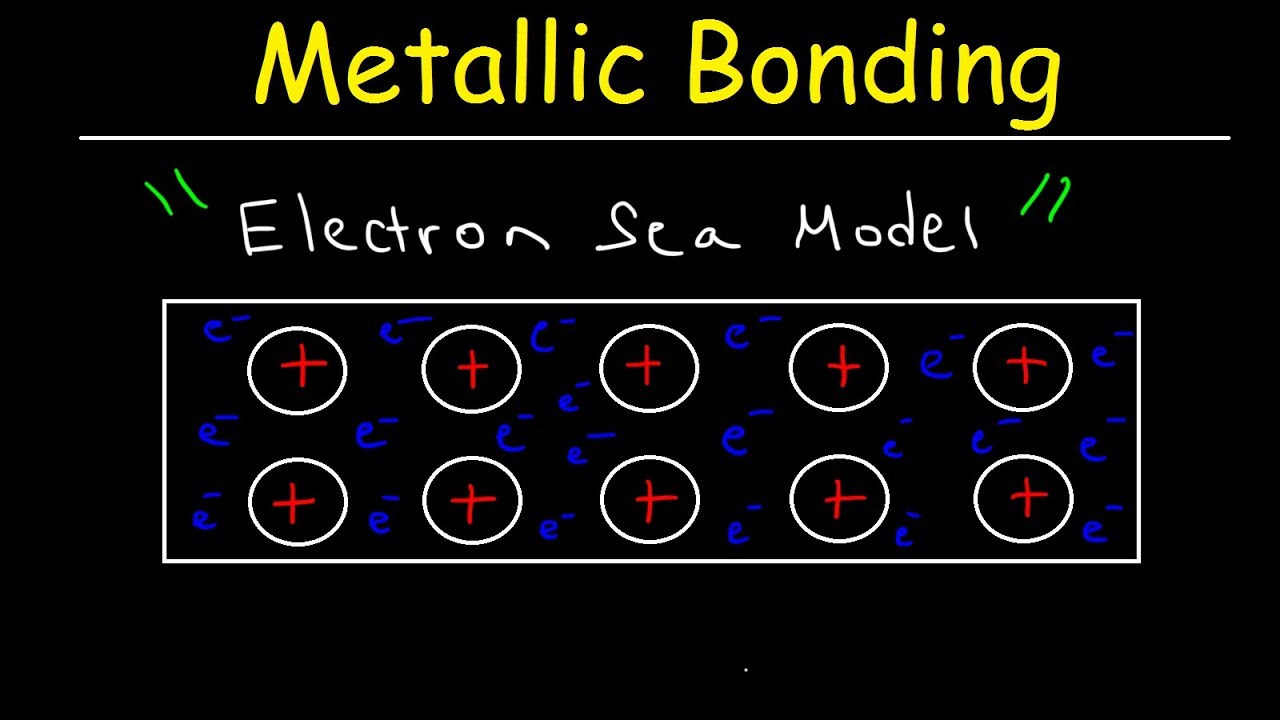
- 😀 Metals consist of positive ions closely packed in crystal structures, surrounded by a sea of free-moving valence electrons.
- 😀 Metallic bonds are weaker than ionic or covalent bonds, but the mobility of electrons contributes to the properties of metals.
- 😀 The shine of metals is due to the ability of free electrons to absorb light photons and reemit them as light, determining the metal's color.
- 😀 The mobility of electrons also explains metals' ability to conduct heat and electricity efficiently.
- 😀 When a metal is heated, its free electrons vibrate, causing an increase in kinetic energy and temperature.
- 😀 Metals can deform under applied force, which is why they are malleable. The free electrons prevent repulsion between the ions.
- 😀 Unlike ionic crystals, which break when struck, metals don't break easily due to the protective nature of the free electron sea.
- 😀 Ductility in metals allows them to be drawn into long wires without breaking, a property that ionic bonds lack due to their inability to be shaped.
- 😀 Most metals are solid at room temperature, but mercury is an exception, as it is liquid at room temperature. A few metals like francium, cesium, gallium, and rubidium melt near room temperature.
Q & A
What are the main properties of metals mentioned in the script?
-The main properties of metals discussed are that they are shiny, malleable, ductile, and excellent conductors of heat and electricity.
What explains the typical characteristics of metals?
-The typical characteristics of metals are explained by their atomic structure and the nature of metallic bonds. In metals, positive ions are surrounded by a 'sea' of free-moving valence electrons.
How do metallic bonds work?
-In metallic bonds, free-moving electrons from valence shells move between atoms. When one electron moves away due to electrostatic attraction, another takes its place, creating a bond that holds the metal together.
How does the behavior of free electrons explain the shine of metals?
-The shine of metals is due to the mobility of free electrons. When light photons are absorbed, free electrons easily jump to higher energy levels and reemit the energy as light, contributing to the metal's brightness.
What makes metals good conductors of heat and electricity?
-Metals conduct heat and electricity well due to the mobility of their free electrons. When heat or an electric current is applied, these electrons quickly move, transferring energy through the metal.
Why are metals malleable and ductile?
-Metals are malleable and ductile because their free-moving electrons allow the metal atoms to shift without causing repulsion. This makes the metal change shape without breaking or cracking.
What happens when an ionic crystal is hit with a hammer?
-When an ionic crystal is hit with a hammer, it shatters. This happens because the applied force pushes similarly charged ions together, causing them to repel and break the crystal.
How do metals respond to being hammered compared to ionic crystals?
-Metals do not shatter when hammered. Instead, they deform because their free electrons protect the metal ions from repulsion, allowing the metal to change shape without breaking.
What is ductility, and which metal is considered the most ductile?
-Ductility is the ability of a metal to be drawn into long, thin wires without breaking. The most ductile metal is platinum.
Why are ionic bonds not ductile?
-Ionic bonds are not ductile because if an ionic crystal is shaped or pulled, the like-charged ions repel each other, causing the structure to break instead of stretch.
Which metal is the only liquid at room temperature, and which metals melt near room temperature?
-Mercury is the only metal that is liquid at room temperature. Other metals that melt near room temperature include francium, cesium, gallium, and rubidium.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Química Simples #58 - Ligações Metálicas

Grade 10 Classification of Matter: Properties of materials

IKATAN KIMIA : IKATAN LOGAM ( KIMIA SMA KELAS 10 )
Metallic Bonding and the Electron Sea Model, Electrical Conductivity - Basic Introduction

What Are Metallic Bonds | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool

Alloy & their Properties | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
