What Are Metallic Bonds | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the unique properties of metals, such as their ability to conduct heat and electricity, their high melting and boiling points, and their malleability and ductility. These properties are linked to metallic bonding, where metal ions are arranged in a lattice structure, surrounded by free-floating electrons. This 'sea of electrons' creates a strong electrostatic attraction, making metals useful in everyday objects like pots, kettles, and wiring. The video also compares metallic bonding to ionic lattices, highlighting the versatility of metals in various applications.
Takeaways
- 🔩 Metals are used in many everyday objects due to their useful properties.
- 🍳 Metals are good conductors of heat, which is why they're used in cookware like pots and heating elements.
- ⚡ Metals are also good conductors of electricity, as seen in copper wires inside electrical cords.
- 🔧 Metals are malleable, meaning they can be shaped into different forms like pots and wires.
- 🧵 Metals are ductile, allowing them to be stretched into thin wires, such as those used in electronics.
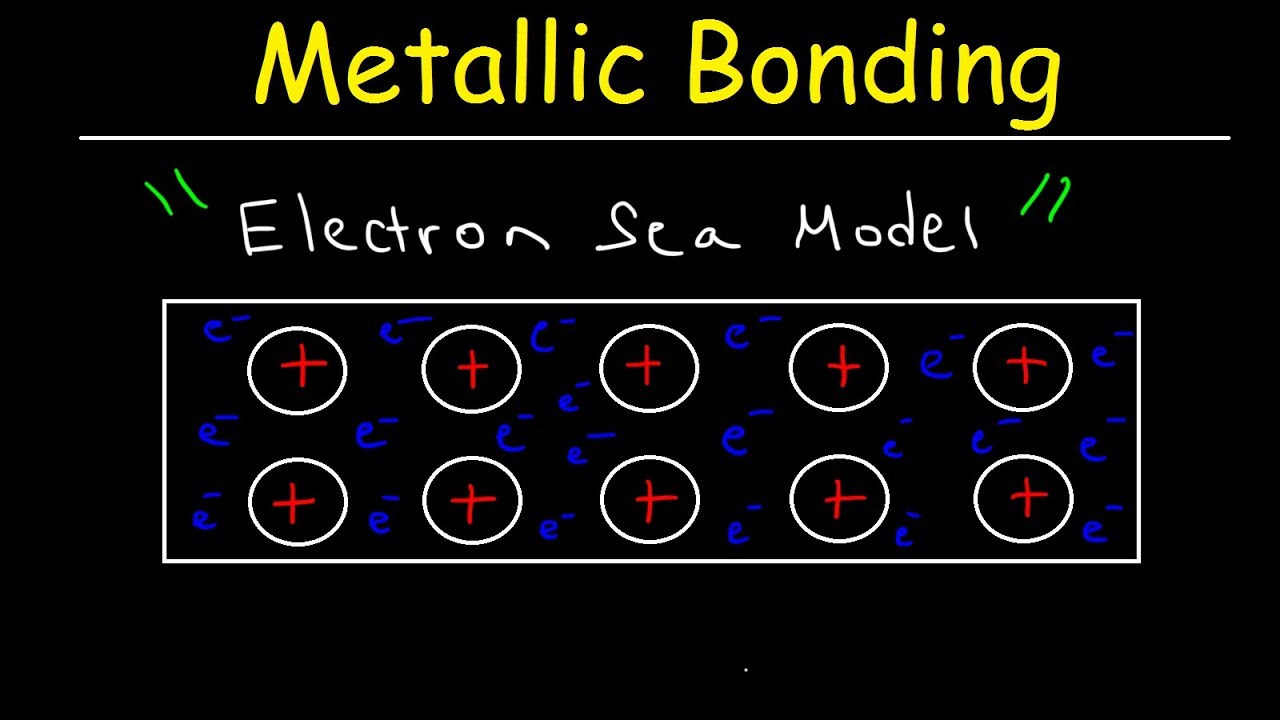
- 🔒 Metallic bonding involves the electrostatic attraction between metal ions arranged in a lattice structure and free-floating electrons.
- 🌊 The 'sea of electrons' in metallic bonding allows these electrons to move freely, contributing to the properties of metals.
- 📏 A lattice structure refers to a regular, repeating pattern found in metallic and ionic structures.
- 🔥 The strong attraction between metal ions and free electrons explains metals' high melting and boiling points.
- 🛠️ Metals retain their structure when shaped because the free-floating electrons adjust to the new form while maintaining a strong bond.
Q & A
What are some everyday objects made of metals mentioned in the script?
-Everyday objects made of metals mentioned in the script include a pot, the heating element inside a kettle, and copper wires.
Why are metals used in objects like pots and heating elements?
-Metals are used in these objects because they are good conductors of heat, allowing efficient heat transfer.
Why wouldn’t you see a pot made of wood or a heating element made of plastic?
-Wood and plastic are not good conductors of heat, making them unsuitable for such applications where heat transfer is necessary.
What property of metals allows them to be stretched into wires?
-Metals are ductile, which means they can be stretched into wires without breaking.
What term describes the ability of metals to be shaped into different forms?
-The term 'malleable' describes the ability of metals to be shaped or molded into different forms.
What is metallic bonding?
-Metallic bonding is the electrostatic attraction between metal ions arranged in a lattice structure and free-floating electrons around them.
What role do free-floating electrons play in metallic structures?
-Free-floating electrons act like glue, holding the metal ions in place within the lattice structure. They also allow metals to conduct heat and electricity.
How does the lattice structure in metallic bonding differ from ionic lattices?
-In metallic lattices, only metal ions are present, whereas ionic lattices have alternating metal and nonmetal ions.
Why do metals have high melting and boiling points?
-Metals have high melting and boiling points because a lot of heat energy is needed to overcome the strong electrostatic attraction between the metal ions and free-floating electrons.
What are some common uses of metals due to their properties?
-Common uses of metals include making cars, bicycles, trains, planes, buildings, cutlery, spectacles, and furniture due to their malleability, ductility, and conductivity.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
Metallic Bonding and the Electron Sea Model, Electrical Conductivity - Basic Introduction

Ikatan Logam: Pengertian, Sifat, dan Contoh dalam Kehidupan Sehari-hari

GCSE Chemistry - Metals & Non-metals: Electron Arrangement & Properties

Grade 10 Classification of Matter: Properties of materials

GCSE Chemistry - What is an Ionic Compound? Ionic Compounds Explained #15

IKATAN LOGAM ADALAH
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)