Mekanika Fluida FM01 (Lecture3: 1/8). Persamaan Bernoulli (Pengenalan)
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into Bernoulli's equation, a fundamental principle in fluid mechanics that students in engineering should grasp. It explains the concept of streamlines and how Bernoulli’s principle relates to the conservation of energy in a flowing fluid. The script illustrates how fluid flows through different positions, transforming internal pressure into kinetic and potential energy. Using the example of fluid dynamics in a syringe, the script highlights how energy shifts between forms as the fluid moves, applying Bernoulli’s equation to real-life scenarios. This sets the stage for further exploration and practical applications of the equation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Bernoulli's equation is a crucial principle in fluid mechanics that all engineering students should know, even though it simplifies real-world conditions.
- 😀 Streamlines represent the trajectory of a particle in a fluid, such as swimming in a river, where the path forms a line.
- 😀 Bernoulli's equation in its simplified form is expressed as a constant along a streamline, involving pressure, velocity, and height.
- 😀 The equation shows that the sum of the pressure energy, kinetic energy (velocity), and potential energy (height) is constant along a streamline.
- 😀 Bernoulli's principle can be applied in practical scenarios, such as in fluid flow in pipes or devices like syringes.
- 😀 Bernoulli's equation can be derived from the conservation of energy, which is applicable as long as the fluid flow is not too large and energy losses are minimal.
- 😀 The equation can be written in various forms, such as involving the dynamic pressure term and static pressure term.
- 😀 Static pressure refers to the pressure exerted by a fluid at rest, while dynamic pressure involves the velocity of the fluid.
- 😀 In real-life applications like a syringe, Bernoulli’s principle explains the energy transformations from pressure to kinetic energy and then to potential energy as the fluid is expelled.
- 😀 The Bernoulli equation is vital for analyzing energy changes within fluid flow systems, and understanding it is key for practical fluid mechanics applications.
Q & A
What is Bernoulli's equation used for in fluid mechanics?
-Bernoulli's equation is used to describe the conservation of energy in a flowing fluid. It helps relate the pressure, velocity, and elevation in a streamline flow, assuming ideal conditions.
What is a streamline in fluid mechanics?
-A streamline is a line that represents the path a particle follows as it moves through a fluid. In the context of swimming, it's the path traced by a swimmer moving through the water.
How is Bernoulli's equation formulated?
-Bernoulli's equation is formulated as: P/ρg + V²/2g + z = constant, where P is the pressure, ρ is the fluid density, V is the velocity, z is the height, and g is the acceleration due to gravity.
What does the term 'static pressure' mean in Bernoulli's equation?
-Static pressure refers to the pressure in a fluid that is at rest or moving without changing speed, as seen in the form of P + ρgZ in Bernoulli's equation.
What happens to the pressure and velocity as fluid flows through a syringe?
-As fluid moves through a syringe, the pressure at the starting point is high, and the velocity is low. As the fluid exits the syringe, the pressure decreases and the velocity increases.
What does the term 'dynamic pressure' represent in Bernoulli's equation?
-Dynamic pressure represents the kinetic energy per unit volume of a fluid and is expressed as ρV²/2.
How can Bernoulli’s equation be applied to everyday life?
-Bernoulli’s equation can be applied in various real-life scenarios, such as fluid flow in pipes, the functioning of a syringe, and even in weather systems. As long as the fluid flow is not turbulent, Bernoulli’s equation holds.
What does Bernoulli’s equation say about the total energy in a fluid system?
-Bernoulli's equation indicates that the total energy (pressure energy, kinetic energy, and potential energy) remains constant along a streamline in an ideal, incompressible fluid.
How does the concept of energy change in the syringe example?
-In the syringe example, energy transitions from pressure energy (static pressure) to kinetic energy (dynamic pressure) as the fluid accelerates from the syringe’s bottom to the top.
What is the significance of the 'z' term in Bernoulli's equation?
-'z' represents the potential energy per unit weight of the fluid due to gravity, essentially the height of the fluid. It plays a role in determining the energy associated with the fluid’s position in a gravitational field.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

MekFlu #2: Persamaan Bernoulli, Kontinuitas dan Kekekalan Energi

Mekanika Fluida FM01 (Lecture3: 7/8). Static-Pitot Tube

Penerapan Prinsip Bernoulli Dalam Kehidupan Sehari-Hari

Mecánica de fluidos primera parte
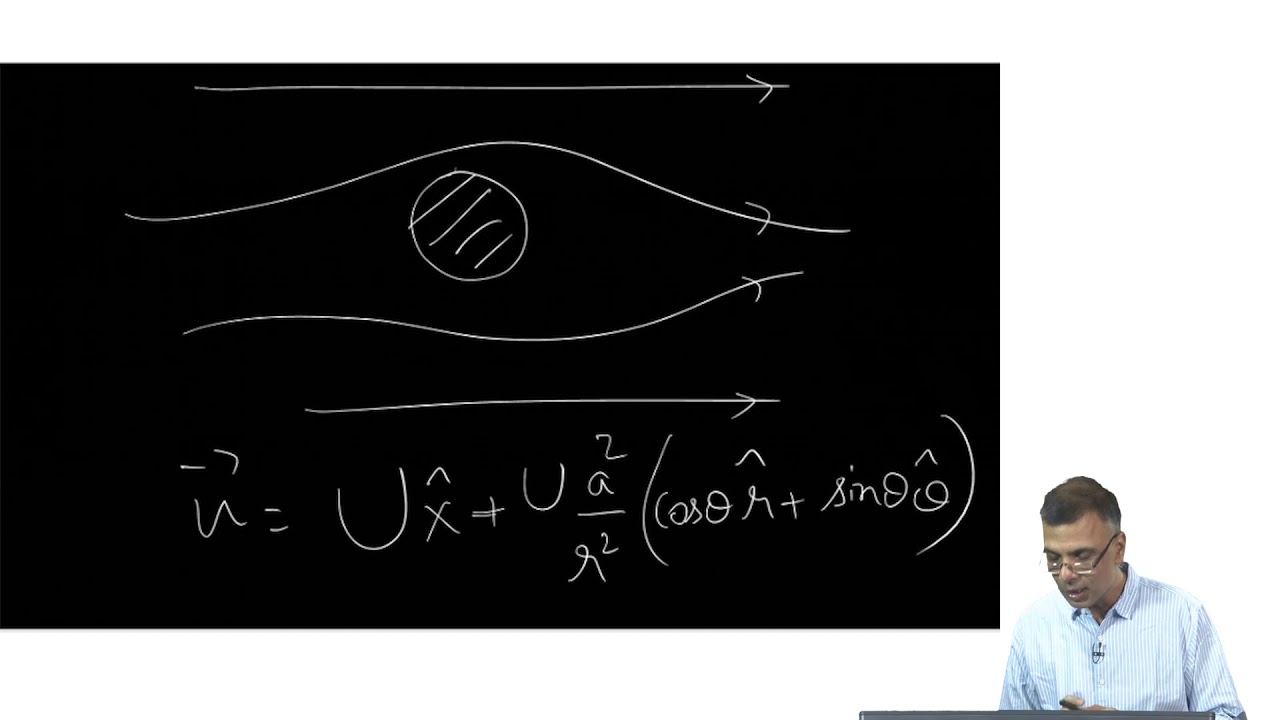
mod03lec11 - Recap - Potential flows, Bernoulli constant and its applications
MekFlu #1: Prinsip Persamaan Bernoulli
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
