Isotopes Explained in Simple Words with Real-life Examples
Summary
TLDRThis engaging script explains the concept of isotopes by using a fun James Bond analogy. It introduces isotopes as different forms of an element that share the same number of protons but differ in neutrons. The script discusses how isotopes are formed, either through radioactive decay or human-driven processes like particle accelerators. Examples like hydrogen and carbon isotopes are highlighted, including the use of Carbon-14 in dating organic materials. It also covers how isotopes are used in various fields, from medical research to security, illustrating their importance in everyday life and scientific discovery.
Takeaways
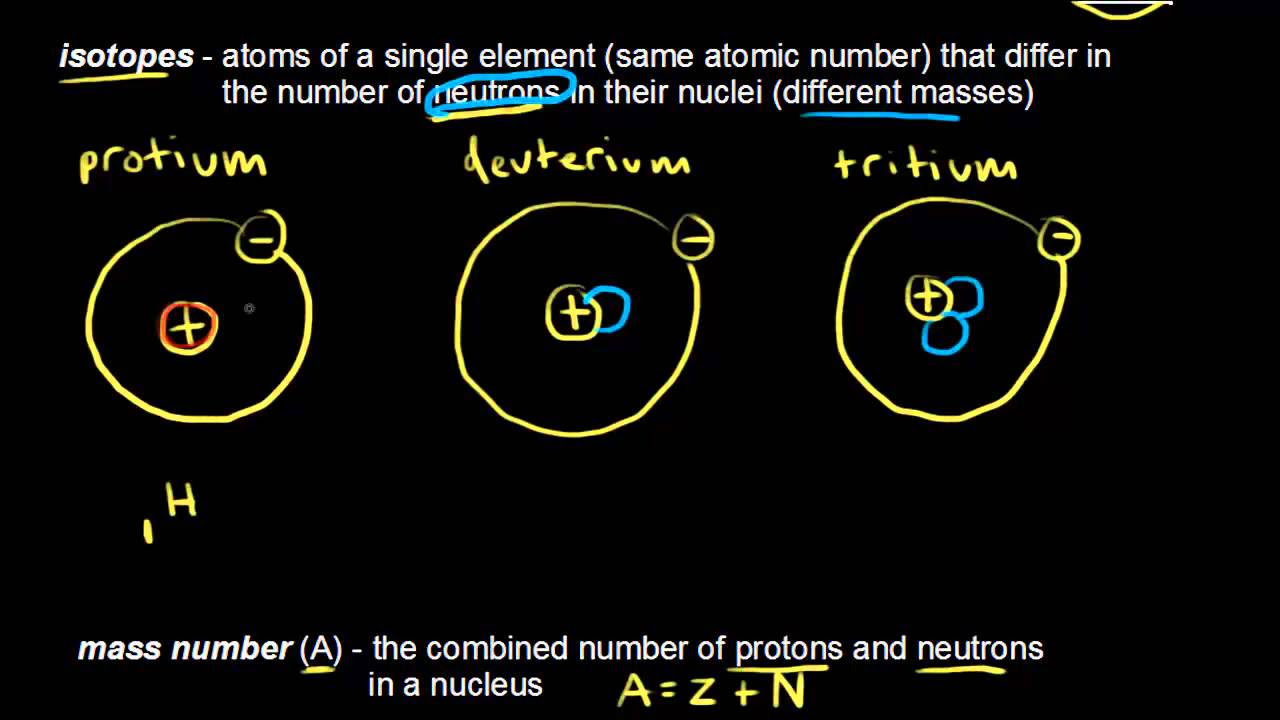
- 😀 Isotopes are forms of elements with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons.
- 😀 An analogy comparing isotopes to secret agents, with the same mission but different identities, helps explain the concept.
- 😀 The atomic number of an element is determined by the number of protons, while the mass number is determined by the number of neutrons.
- 😀 Isotopes are created when neutrons are added or removed from an atom's nucleus while keeping the number of electrons the same.
- 😀 Isotopes can be formed through natural radioactive decay or by human-driven processes like particle bombardment in accelerators.
- 😀 Elements on the periodic table, like hydrogen and carbon, have multiple isotopes with varying numbers of neutrons.
- 😀 Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope used in carbon dating, which helps estimate the age of organic materials up to 60,000 years old.
- 😀 Isotopes play a significant role in various industries, such as medical research, diagnostic imaging, and disease treatment.
- 😀 Specific isotopes like selenium-75 and Americium-241 have applications in non-destructive testing, smoke detectors, and climate research.
- 😀 Isotopes are crucial in national security and defense, helping detect explosives and hazardous materials, and supporting nuclear reactors.
Q & A
What are isotopes?
-Isotopes are forms of the same element that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons, leading to different mass numbers. Although they belong to the same element family, they can have different properties.
How are isotopes formed?
-Isotopes form in two main ways: naturally, through radioactive decay of unstable atomic nuclei, or artificially, by bombarding a stable nucleus with charged particles in a particle accelerator.
What is the difference between atomic number and mass number?
-The atomic number of an element is determined by the number of protons in its nucleus, while the mass number is determined by the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
What is transmutation in the context of isotopes?
-Transmutation refers to the process by which a stable nucleus is bombarded with particles to create an isotope, or even change the element entirely.
Can you explain the significance of Carbon-14 in dating organic materials?
-Carbon-14 is a radioactive isotope that decays over time. It is used in carbon dating to estimate the age of organic materials by measuring the remaining amount of Carbon-14, which decreases as the material ages.
What role do isotopes play in medical applications?
-Isotopes are used in medical research, diagnostic imaging, and the treatment of diseases. They help in procedures like non-destructive testing, as well as in the detection and treatment of various conditions.
How does selenium-75 contribute to industrial processes?
-Selenium-75 is used in gamma radiography to examine thinner-walled steel surfaces non-destructively, helping in industrial inspections and ensuring safety.
What is the role of isotopes in national security?
-Isotopes play a crucial role in national defense by aiding in the detection of explosives, hazardous chemicals, and nuclear materials. For instance, Nickel-63 is used in airport security to detect dangerous substances.
Why is Carbon-12 the most abundant carbon isotope?
-Carbon-12 is the most abundant isotope of carbon, with 99% of Earth's carbon being in this form. It has 6 protons and 6 neutrons, making it stable and the primary form found in nature.
How do isotopes affect global climate research?
-Isotopes like Silicon-32 are used in oceanographic research to model and better understand the global climate. Their unique properties allow researchers to track environmental changes over time.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

What are Isotopes?

Easy equilibrium – demonstrating Le Chatelier's principle
Atomic number, mass number, and isotopes | Chemistry | Khan Academy

Calculating Enthalpy Changes from Bond Enthalpies

What are Isotopes? | Properties of Matter | Chemistry | FuseSchool

Metabolism & Nutrition, Part 2: Crash Course Anatomy & Physiology #37
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
