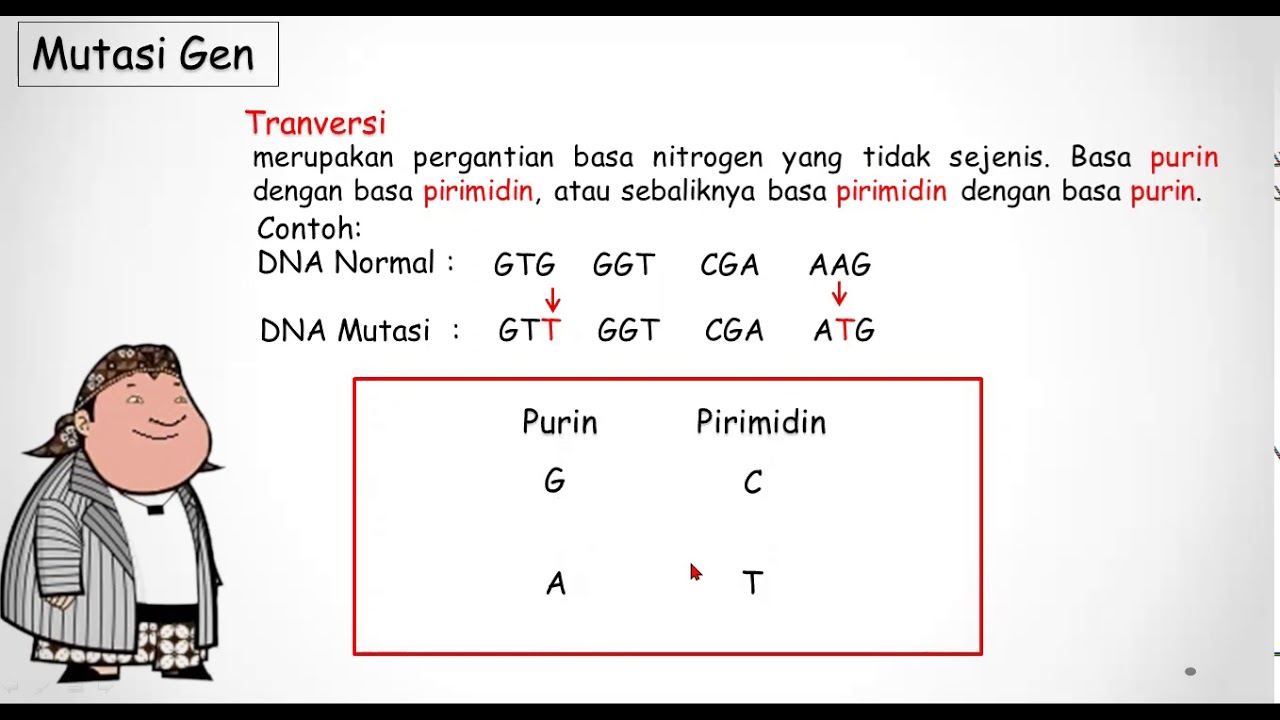
BIOLOGI Kelas 12 - Pengaruh Mutasi pada Makhluk Hidup | GIA Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful discussion on the effects of mutations in living organisms. It explores both beneficial and harmful mutations, highlighting real-life examples such as seedless fruits and Sansevieria plants, as well as their genetic implications. The video delves into medical applications like cancer treatments through radiation and discusses genetic disorders like Down syndrome and Turner syndrome. It also explains how mutations contribute to genetic diversity, evolution, and agricultural advancements. By breaking down complex scientific concepts, the video makes understanding mutations accessible and engaging for viewers.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mutations can have both beneficial and harmful effects on living organisms.
- 😀 An example of a beneficial mutation is seen in the Sansevieria plant, which exhibits variation in leaf shape, size, and color due to mutations.
- 😀 Seedless watermelon is another example of a beneficial mutation, resulting from the use of colchicine to prevent spindle fibers from forming during mitosis, leading to triploid (3N) watermelons.
- 😀 Mutations in crops like sorghum can lead to better homozigot plant varieties, contributing to agricultural improvements.
- 😀 Mutations are used in medicine, such as in radiotherapy for cancer treatment, where radioactive rays kill cancer cells by inducing ionization and the formation of free radicals.
- 😀 Mutations play a key role in evolution and genetic diversity, providing variations that can improve crops and other organisms.
- 😀 Mutations can improve antibiotic production in fungi like Penicillium.
- 😀 On the negative side, mutations can lead to genetic diseases like cancer, sickle cell anemia, and various chromosome-related syndromes.
- 😀 Down syndrome is caused by an extra chromosome 21, leading to intellectual disabilities and physical traits like a round face and upward-slanted eyes.
- 😀 Mutations in chromosomes can also cause syndromes like Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, and Edward syndrome, each with its own specific physical and developmental characteristics.
Q & A
What is the impact of mutation on living organisms?
-Mutations can have both beneficial and harmful effects. While most mutations are harmful, some can be advantageous, leading to new variations and characteristics that benefit the organism, such as in agriculture and medicine.
How can mutations be beneficial for plants?
-Mutations can lead to desirable characteristics in plants, such as non-seedless fruits or variations in the appearance of ornamental plants like Sansevieria. These mutations can help improve crop yields or provide environmental benefits like pollution absorption.
What is a specific example of a beneficial mutation in plants?
-An example of a beneficial mutation is the seedless watermelon, which results from treating watermelon plants with colchicine to prevent spindle formation during cell division, leading to triploid (3N) plants without seeds.
How does gamma radiation help in plant mutation?
-Gamma radiation can be used to induce mutations in plants, such as in sorghum. This radiation causes genetic changes, leading to the creation of homozygous plants with desirable traits, helping in plant breeding and improvement.
How is mutation used in cancer treatment?
-In cancer treatment, radioactive radiation, such as X-rays or gamma rays, is used in radiotherapy. This radiation kills cancer cells by ionizing water molecules in the cells, leading to the formation of free radicals that damage and kill the cancer cells.
What are some examples of genetic disorders caused by mutations in humans?
-Genetic disorders caused by mutations include sickle cell anemia, where a single base change causes abnormal hemoglobin, and various types of cancer that arise from mutations in specific genes.
What is Down syndrome, and how is it related to mutations?
-Down syndrome is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21, leading to a total of 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. This mutation results in intellectual disabilities and physical characteristics like a broad face and short stature.
What are some chromosomal mutations that affect human health?
-Chromosomal mutations in humans can lead to disorders such as Turner syndrome (45,XO), Klinefelter syndrome (47,XXY), and Jacob syndrome (47,XYY), each with its own set of physical and cognitive symptoms.
How does mutation contribute to genetic diversity and evolution?
-Mutations introduce genetic variation by altering the DNA sequence. This genetic diversity is crucial for evolution, as it provides the raw material for natural selection to act upon, leading to the adaptation of species to changing environments.
Why is seedless fruit a disadvantage for plants?
-Seedless fruit, while beneficial to humans, is disadvantageous to the plant because seeds are necessary for the plant's natural reproduction. Seedless fruit results from mutations that prevent the formation of seeds, hindering the plant's ability to propagate sexually.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)