Motherboard Expansion Slots and Bus Speeds - CompTIA A+ 220-801: 1.2
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the complex structure of a motherboard, comparing it to a city with data pathways connecting various components. It covers key expansion slots such as PCI, PCI-X, and PCI Express (PCIe), highlighting their evolution to support higher data throughput. The video also introduces AGP as a legacy interface for graphics cards. Key differences between the various types of expansion slots, including their speeds and functionality, are discussed, with a focus on PCIe as the modern standard for expanding a system’s capabilities. Overall, the video provides a detailed overview of how motherboards facilitate system upgrades and performance.
Takeaways
- 😀 A motherboard can be compared to a city with pathways that connect different components such as the CPU, memory, and expansion cards.
- 😀 Data flows between motherboard components through various independent pathways or buses, including those connecting to adapter cards and bridges like the Northbridge and Southbridge.
- 😀 Modern motherboards allow expansion through built-in slots for additional hardware, such as video cards or network adapters.
- 😀 The bus speed, measured in MHz or GHz, indicates how fast data travels, but it doesn’t necessarily limit the amount of data transferred. The method of data transfer (e.g., DDR3 memory) can increase efficiency.
- 😀 PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) is a legacy standard that includes 32-bit and 64-bit versions, offering throughput speeds ranging from 133 MB/s to 533 MB/s.
- 😀 PCIe (PCI Express) is a more modern standard that uses serial communication, offering greater flexibility and speed through lanes (x1, x2, x4, x16, etc.).
- 😀 PCIe slots come in various sizes depending on the number of lanes, which impacts the data transfer speed and throughput (e.g., x1 offers low speed, x16 offers high speed).
- 😀 The PCIe standard has evolved over time, with version 1.0 offering 250 MB/s per lane and version 4.0 reaching up to 2 GB/s per lane.
- 😀 Mini PCI is a compact version of PCI, designed for mobile devices like laptops, enabling additional features like Wi-Fi or mobile broadband cards.
- 😀 AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port) was a high-bandwidth interface for graphics cards before PCIe became the preferred option for video and graphics processing.
- 😀 Newer PCIe slots have full-duplex communication, allowing data to flow in both directions simultaneously, improving efficiency and speed compared to older PCI systems.
- 😀 Motherboards today feature a mix of legacy and modern slots, including PCIe for high-speed components, while older slots like PCI and AGP are still found in some systems for compatibility with older hardware.
Q & A
What is the analogy used to describe the motherboard's architecture?
-The motherboard is compared to a city seen from 30,000 feet, with pathways resembling streets that connect different components, such as adapter cards, the Northbridge, and Southbridge.
What role do the Northbridge and Southbridge play in a motherboard?
-The Northbridge connects high-speed components like the CPU and memory, while the Southbridge handles slower peripherals and expansion slots.
What does the clock speed of a bus refer to?
-The clock speed of a bus indicates how much data can pass through the bus per second, measured in MHz or GHz, representing the number of cycles per second.
How does the speed of the bus affect the amount of data transmitted?
-The speed of the bus does not always correlate with the amount of data transferred. For example, DDR3 memory can transfer data at 64 times the rate of its clock speed due to efficient data transfer techniques.
What is PCI and why is it important?
-PCI (Peripheral Component Interconnect) is a standard for expansion slots introduced in 1994, allowing users to add peripherals like network cards, sound cards, and video cards to a computer. It is still commonly found in modern motherboards for backward compatibility.
What is the difference between PCI and PCI-X?
-PCI-X (PCI Extended) is an updated version of PCI, offering significantly higher throughput, particularly useful for servers. PCI-X can handle up to 1.064 GB/s, while standard PCI offers lower speeds.
What is PCI Express (PCIe), and how does it differ from PCI?
-PCI Express (PCIe) is the modern standard for expansion slots. Unlike PCI, which uses parallel communication, PCIe uses serial communication and 'lanes' for data transfer, offering much higher bandwidth and flexibility in supporting various devices.
How are PCIe slots categorized, and what do these categories mean?
-PCIe slots are categorized by the number of lanes they support, such as x1, x4, x8, or x16. These represent the number of full-duplex lanes, where x1 has 1 lane, x16 has 16 lanes, and so on. More lanes provide higher data transfer rates.
What is the advantage of PCIe over older PCI and PCI-X slots?
-PCIe offers superior speed and scalability. Unlike PCI and PCI-X, which can slow down if slower cards are added, PCIe allows each card to run at its own optimal speed, ensuring that high-speed devices do not affect slower ones.
What are some legacy interfaces that may still be found on older motherboards?
-Some legacy interfaces include the CNR (Communications and Networking Riser), used for network cards and modems, and AGP (Accelerated Graphics Port), used for high-performance graphics cards before PCIe became the standard.
What was the role of AGP, and why is it less common today?
-AGP was a dedicated slot for graphics cards, designed to provide higher bandwidth for video processing. However, it has been largely replaced by PCIe, which offers greater flexibility, higher speeds, and can support a wider range of devices.
How does the voltage of an expansion card affect its compatibility with a motherboard?
-Expansion cards have specific voltage requirements, and motherboards provide different voltages (3.3V or 5V). The notches on an adapter card ensure it can only be installed in a slot that matches its voltage requirement, ensuring compatibility.
What are mini PCI slots, and how do they differ from standard PCI slots?
-Mini PCI slots are a smaller version of PCI, designed for mobile devices like laptops. They allow users to add components like Wi-Fi or mobile broadband cards but are not easily accessible once installed inside a laptop.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Belajar Komputer Untuk Pemula | Fungsi Motherboard Dan Bagian-Bagiannya

Carte mère

Computer Bus | What Is A Computer Bus ? | Computer Bus Types

Digital Literacy Topic 2 Introduction to computer Hardware Input Devices, Keyboard Basics Urdu H

Arsitektur Sistem Mikroprosesor
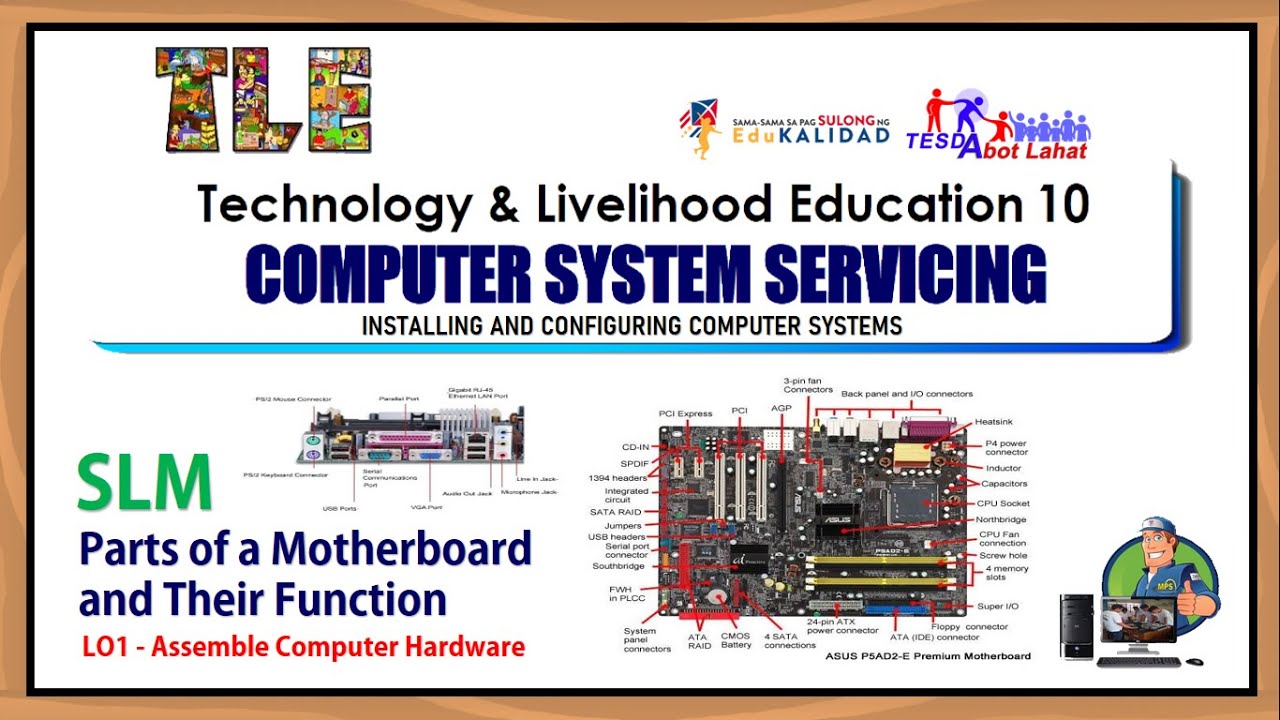
Parts of a Motherboard and Their Function - Part 2 Back Panel Connectors & Ports
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
