Volume dan Kapasitas Paru-paru
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an educational explanation of human lung mechanics, focusing on respiratory volumes and capacities. It details key lung volumes like Tidal Volume (VT), Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV), Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV), and Residual Volume (RV), along with vital and total lung capacities. The video also covers how these values are measured and their importance in respiratory health, helping viewers understand normal breathing mechanics and how the lungs function under different conditions. The information is essential for both medical studies and general knowledge of human physiology.
Takeaways
- 😀 The human respiratory system involves the process of inhaling and exhaling air, with the lungs playing a crucial role in this mechanism.
- 😀 Lung volume and capacity are important aspects of respiration, determined by factors such as lung size, breathing method, and breath strength.
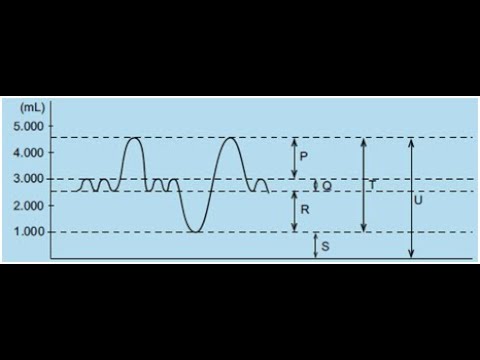
- 😀 The first key volume is called tidal volume (VT), which is the amount of air moved in and out during normal breathing, typically around 500cc or 500 ml.
- 😀 Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) is the maximum air that can be inhaled after a normal breath, with a capacity of approximately 1500cc or 1500 ml.
- 😀 Expiratory reserve volume (ERV) is the maximum air that can be exhaled after a normal breath, also around 1500cc or 1500 ml.
- 😀 Residual volume (RV) refers to the air that remains in the lungs after maximum exhalation, generally about 1000cc or 1000 ml.
- 😀 Vital capacity (VC) refers to the total amount of air that can be exhaled after a maximum inhalation, which includes tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, and expiratory reserve volume.
- 😀 Total lung capacity (TLC) is the maximum air the lungs can hold, which includes all lung volumes such as tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, and residual volume.
- 😀 A formula for vital capacity is: VC = VT + IRV + ERV, with a total volume of approximately 3500cc.
- 😀 Total lung capacity is calculated by the formula: TLC = VT + IRV + ERV + RV, with a total volume of approximately 8500cc.
Q & A
What is tidal volume, and what does it represent in lung function?
-Tidal volume, also known as respiratory volume or air volume, is the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal, relaxed breathing. It typically ranges around 500cc (or 500ml) and is the basic volume of air moved in and out of the lungs with each breath.
What is inspiratory reserve volume (IRV), and how is it defined?
-Inspiratory reserve volume, also called complementary air (UKM), is the amount of additional air that can be inhaled into the lungs after a normal inspiration. This volume can be around 1500cc or 1500ml.
What is expiratory reserve volume (ERV), and what is its function?
-Expiratory reserve volume, also known as supplementary air (USS), is the additional volume of air that can be exhaled after a normal exhalation. It is approximately 1500cc or 1500ml and is the reverse of inspiratory reserve volume.
What is residual volume, and why is it important?
-Residual volume is the amount of air left in the lungs after maximal exhalation. This volume, around 1000cc or 1000ml, ensures that the lungs do not collapse and allows for continuous gas exchange even after forceful exhalation.
What is vital capacity, and how is it calculated?
-Vital capacity is the maximum amount of air that can be exhaled after a full inhalation. It includes tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, and expiratory reserve volume. The formula is: VC = VT + IRV + ERV, and it typically measures around 3500cc.
How is total lung capacity (TLC) defined?
-Total lung capacity (TLC) is the maximum volume of air the lungs can hold. It includes all lung volumes: tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, and residual volume. The total lung capacity is usually around 8500cc.
What is the relationship between inspiratory reserve volume and expiratory reserve volume?
-Inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) and expiratory reserve volume (ERV) are opposite in function. IRV refers to the additional air inhaled after normal inhalation, while ERV refers to the air exhaled after normal exhalation. Both volumes are approximately 1500cc.
How do tidal volume and residual volume differ in lung mechanics?
-Tidal volume is the volume of air moved in and out during normal breathing, while residual volume is the air left in the lungs after a forceful exhalation. Tidal volume is about 500cc, whereas residual volume is around 1000cc.
Why is it important to understand lung volumes and capacities?
-Understanding lung volumes and capacities is crucial for assessing respiratory health. These measurements help identify lung function, diagnose respiratory conditions, and determine how efficiently the lungs can process air during breathing.
Can inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) and expiratory reserve volume (ERV) vary based on physical activity?
-Yes, both inspiratory reserve volume (IRV) and expiratory reserve volume (ERV) can vary based on physical activity. During intense physical activity, individuals may have an increased ability to inhale or exhale more air due to greater lung capacity utilization.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
SISTEM PERNAPASAN MANUSIA PART 2 (Mekanisme, Frekuensi dan Volume Pernapasan)

Mekanisme Pernapasan Manusia, Frekuensi Pernapasan dan Volume Pernapasan
Sistem pernapasan - BIologi kelas 11 SMA

Pulmonary 2 Lung Volumes and Ventilation

IMAT Biology Lesson 6.6 | Anatomy and Physiology | Respiratory System
Kapasitas Paru - paru
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
