Kapasitas Paru - paru
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, Widyaningsih explains the various lung capacities, including tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, residual volume, and vital capacity. She provides a breakdown of each lung capacity, detailing the volumes in milliliters and their respective functions, such as tidal breathing and maximum exhalation. Additionally, she discusses total lung capacity and its components. The video also includes a multiple-choice question to test viewers' understanding, followed by a preview of the next topic: the factors influencing respiratory rate.
Takeaways
- 😀 The topic of the video is lung capacity, specifically for class 11 students studying the respiratory system.
- 😀 Lung capacity refers to the total volume of air the lungs can hold.
- 😀 The video explains different components of lung capacity, such as tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, residual volume, and vital capacity.
- 😀 Tidal volume is the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal breathing, approximately 500 ml.
- 😀 Inspiratory reserve volume is the additional volume of air that can be inhaled after a normal inspiration, about 1500 ml.
- 😀 Expiratory reserve volume is the additional volume of air that can be exhaled after a normal exhalation, also around 1500 ml.
- 😀 Residual volume is the amount of air left in the lungs after maximal exhalation, around 1000 ml.
- 😀 Inspiratory capacity is the sum of tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume, totaling about 2000 ml.
- 😀 Functional residual capacity is the sum of residual volume and expiratory reserve volume, approximately 2500 ml.
- 😀 Vital capacity is the maximum amount of air that can be exhaled after a maximal inhalation, roughly 3500 ml, and is calculated using a specific formula.
- 😀 Total lung capacity is the sum of vital capacity and residual volume, approximately 4000 ml.
- 😀 The video ends with a quiz based on the diagram of lung capacity and factors affecting respiratory frequency.
Q & A
What is lung capacity?
-Lung capacity refers to the total volume of air the lungs can hold. It includes several components such as tidal volume, inspiratory reserve volume, expiratory reserve volume, residual volume, and vital capacity.
What is tidal volume?
-Tidal volume is the amount of air inhaled or exhaled during normal, relaxed breathing, which is approximately 500 ml.
What is inspiratory reserve volume?
-Inspiratory reserve volume is the additional volume of air that can be inhaled after a normal inhalation, typically about 1500 ml.
What is expiratory reserve volume?
-Expiratory reserve volume is the additional volume of air that can be exhaled after a normal exhalation, also approximately 1500 ml.
What is residual volume?
-Residual volume is the volume of air that remains in the lungs after a full exhalation, which is about 1000 ml and cannot be voluntarily exhaled.
What is inspiratory capacity?
-Inspiratory capacity is the total volume of air that can be inhaled, which is the sum of tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume. It is approximately 2000 ml.
What is functional residual capacity?
-Functional residual capacity is the sum of residual volume and expiratory reserve volume, totaling approximately 2500 ml.
What is vital capacity?
-Vital capacity is the maximum amount of air that can be exhaled after taking a deep breath. It is typically about 3500 ml.
What is total lung capacity?
-Total lung capacity is the sum of vital capacity and residual volume, which equals about 4500 to 6000 ml depending on the individual.
What is the correct answer to the lung capacity question in the script?
-The correct answer is option C: Vital capacity of the lungs is 3500 ml, as shown in the diagram.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

VOLUME PERNAPASAN | SISTEM PERNAPASAN MANUSIA

Volume dan Kapasitas Paru-paru

Respiratory | Spirometry: Lung Volumes & Capacities

IPA Kelas 8 : Sistem Pernapasan 3 (Frekuensi dan Volume Pernapasan)
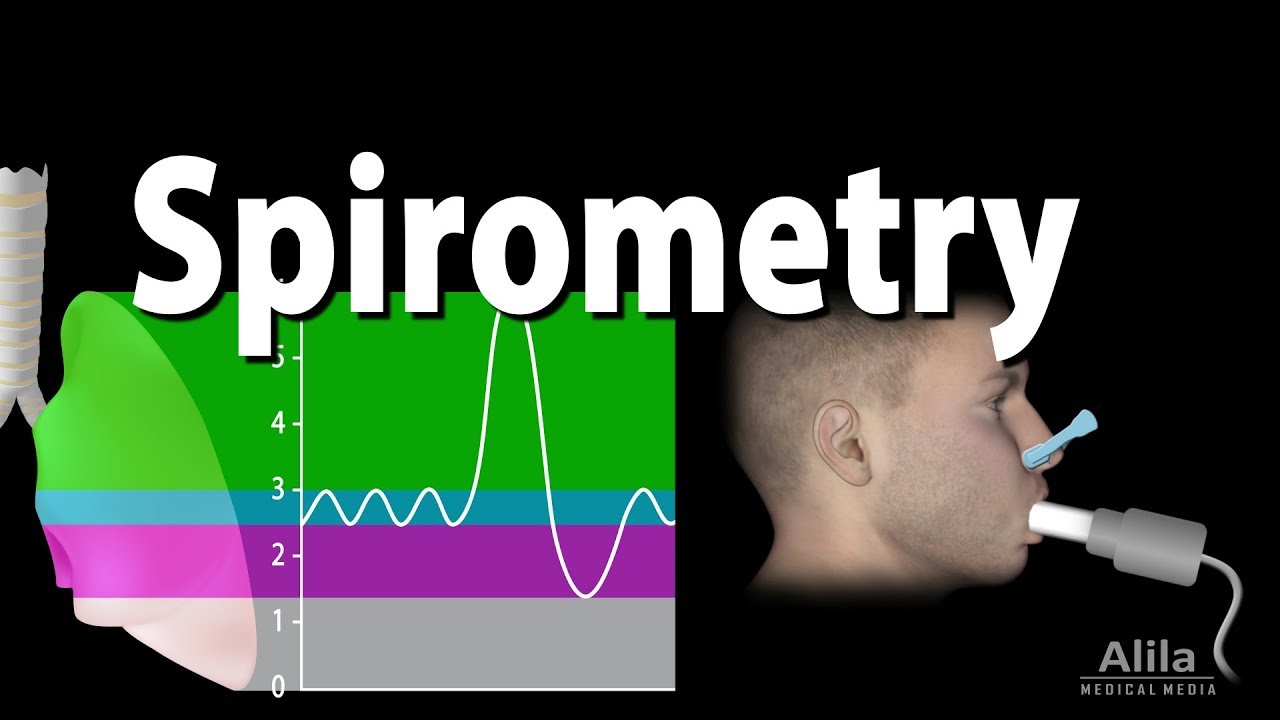
Spirometry, Lung Volumes & Capacities, Restrictive & Obstructive Diseases, Animation.

Praktikum Fisiologi - Spirometri Final
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)