Development of the Teeth
Summary
TLDROdontogenesis is the intricate process of tooth development, beginning around the 6th week of intrauterine life. It involves the formation of deciduous and permanent teeth, with deciduous teeth starting earlier and permanent teeth continuing to develop for years post-birth. The process begins with the interaction between oral epithelium and dental mesenchyme, leading to the formation of tooth buds, followed by the bud, cap, and bell stages. During these stages, cells differentiate into specialized types like ameloblasts and odontoblasts, responsible for enamel and dentin formation. Root development follows crown formation, and permanent teeth form from the successional lamina or dental lamina.
Takeaways
- 😀 Odontogenesis is the process of teeth development, including both deciduous (milk) and permanent teeth, with deciduous teeth developing between weeks 6-7 of intrauterine life and permanent teeth starting at week 14.
- 😀 The development of teeth is driven by interactions between two tissue components: the oral epithelium (derived from ectoderm) and the dental mesenchyme (derived from craniofacial neural crest cells).
- 😀 Deciduous teeth begin to develop around weeks 6-7, while permanent teeth begin around week 14 of intrauterine life, continuing until about 5 years after birth.
- 😀 Tooth development starts with the thickening of the primitive oral epithelium, forming the primary epithelial bands, which then split into two layers: the dental lamina and vestibular lamina.
- 😀 The dental lamina forms dental placodes, which proliferate and invaginate, starting the morphogenesis process that shapes future teeth.
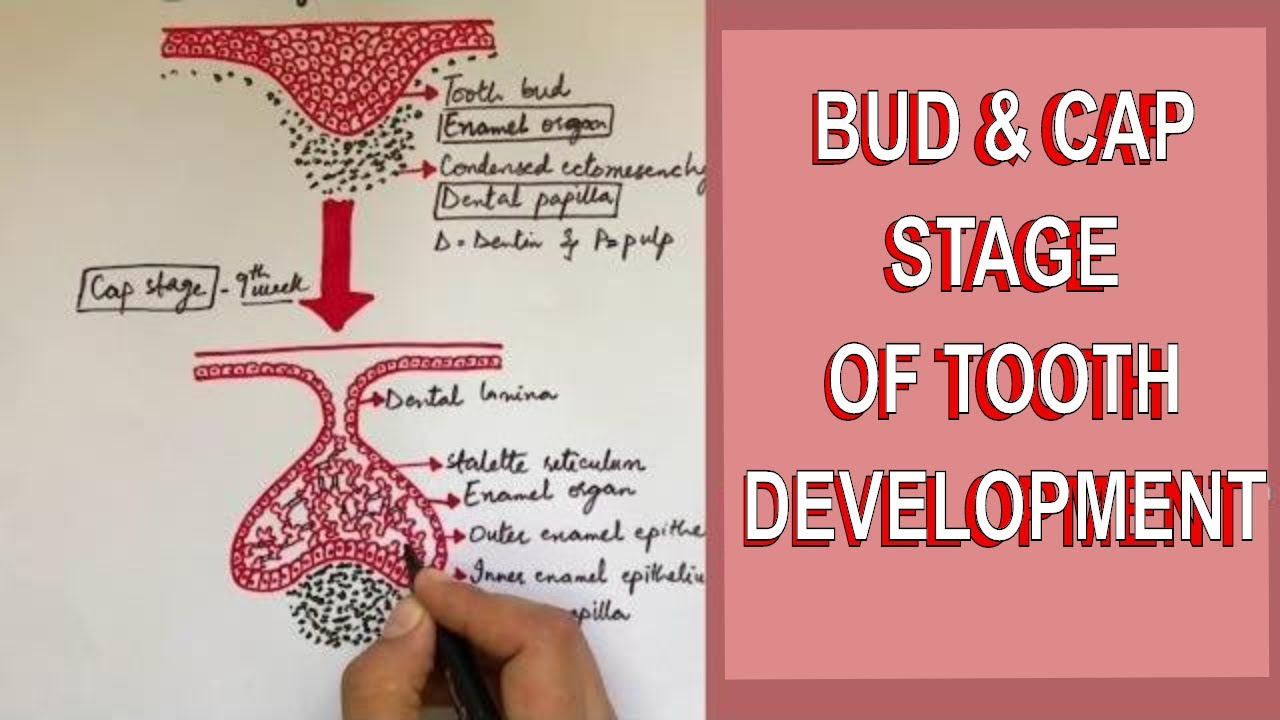
- 😀 During the cap stage, the tooth bud forms a cap-like structure, with three types of epithelial cells in the enamel organ: inner enamel epithelium, outer enamel epithelium, and stellate reticulum.
- 😀 The enamel knot, a cluster of non-dividing cells in the enamel organ, acts as a signaling center to determine the number and shape of the tooth cusps.
- 😀 The bell stage marks histodifferentiation, where the inner enamel epithelium differentiates into ameloblasts (enamel-producing cells) and the dental papilla becomes odontoblasts (dentin-producing cells).
- 😀 Root formation begins after crown development, with the cervical loop cells forming Hertwig's epithelial root sheath (HERS), guiding the root's development and odontoblast differentiation.
- 😀 Supporting structures like the periodontal ligament and alveolar bone develop from the dental follicle cells, providing anchorage and support for the tooth.
Q & A
What is odontogenesis?
-Odontogenesis is the process of tooth development, which includes the formation of both deciduous (baby) teeth and permanent teeth.
When do deciduous teeth begin to develop?
-Deciduous teeth begin to develop during the 6th to 7th week of intrauterine life.
At what stage does the development of permanent teeth begin?
-The development of permanent teeth begins during the 14th week of intrauterine life.
What are the two main tissue components involved in tooth development?
-The two main tissue components involved in tooth development are the primitive oral epithelium (derived from ectoderm) and the underlying ectomesenchyme (dental mesenchyme).
Where do the craniofacial neural crest cells, responsible for the dental mesenchyme, originate?
-The craniofacial neural crest cells migrate from the developing midbrain and the first two rhombomeres into the first branchial arch.
What is the primary epithelial band and what role does it play in tooth development?
-The primary epithelial band is a thickening of the primitive oral epithelium that splits into two parts: the lingual dental lamina and the buccal vestibular lamina. It plays a critical role in initiating the formation of the tooth buds.
What is the significance of dental placodes in tooth development?
-Dental placodes are localized enlargements within the dental lamina that proliferate and invaginate, marking the positions where future teeth will form.
What happens during the cap stage of tooth development?
-During the cap stage, the enamel organ forms three distinct epithelial layers: the inner enamel epithelium, outer enamel epithelium, and stellate reticulum. The enamel knot, a signaling center, regulates cusp formation.
What is histo-differentiation, and when does it occur in tooth development?
-Histo-differentiation is the process in which cells of the dental organ differentiate into specialized cells like ameloblasts (enamel-producing cells) and odontoblasts (dentin-producing cells). This occurs during the late bell stage of tooth development.
How does root formation begin in tooth development?
-Root formation begins when the cervical loop cells proliferate downward to form Hertwig's epithelial root sheath (HERS), which guides root development and induces odontoblasts to form root dentin.
How are permanent teeth different from deciduous teeth in terms of development?
-Permanent teeth develop similarly to deciduous teeth but begin at around the 14th week of intrauterine life, and the development of permanent molars occurs directly from the dental lamina, unlike the successional lamina for other permanent teeth.
What are epithelial pearls, and what role do they play in tooth development?
-Epithelial pearls are nests of epithelial cells left behind after the degeneration of the dental lamina. They can sometimes give rise to dental abnormalities such as supernumerary teeth, odontomas, or eruption cysts.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Development of the Tongue
Development of Tooth - Part 1: Initiation, Bud and Cap stage of Tooth development

Early Tooth Development

EMBRIOLOGIA HUMANA | AULA 06 | PRIMEIRA SEMANA DO DESENVOLVIMENTO EMBRIONÁRIO
Development of EYE : Visual Learning: Easy learning

Sperm Meets Egg: The Journey to Conception -ANIMATION
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
