Double fertilization| Sexual reproduction in flowering plants | Biology | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the process of fertilization in flowering plants, focusing on the fusion of male and female gametes. It covers key steps, including pollen release, the journey of the male gametes through the pollen tube, and the role of the female gametes in the ovule. The video highlights double fertilization, where one male gamete fertilizes the egg cell (syngamy), while the other combines with polar nuclei to form the primary endosperm nucleus (triple fusion). The process is concluded with a quiz on chromosome numbers, reinforcing the learning of fertilization in plants.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video discusses the process of fertilization in flowering plants, focusing on how male and female gametes fuse.
- 😀 A bisexual flower is used in the example, which contains both male and female reproductive parts and is self-pollinating.
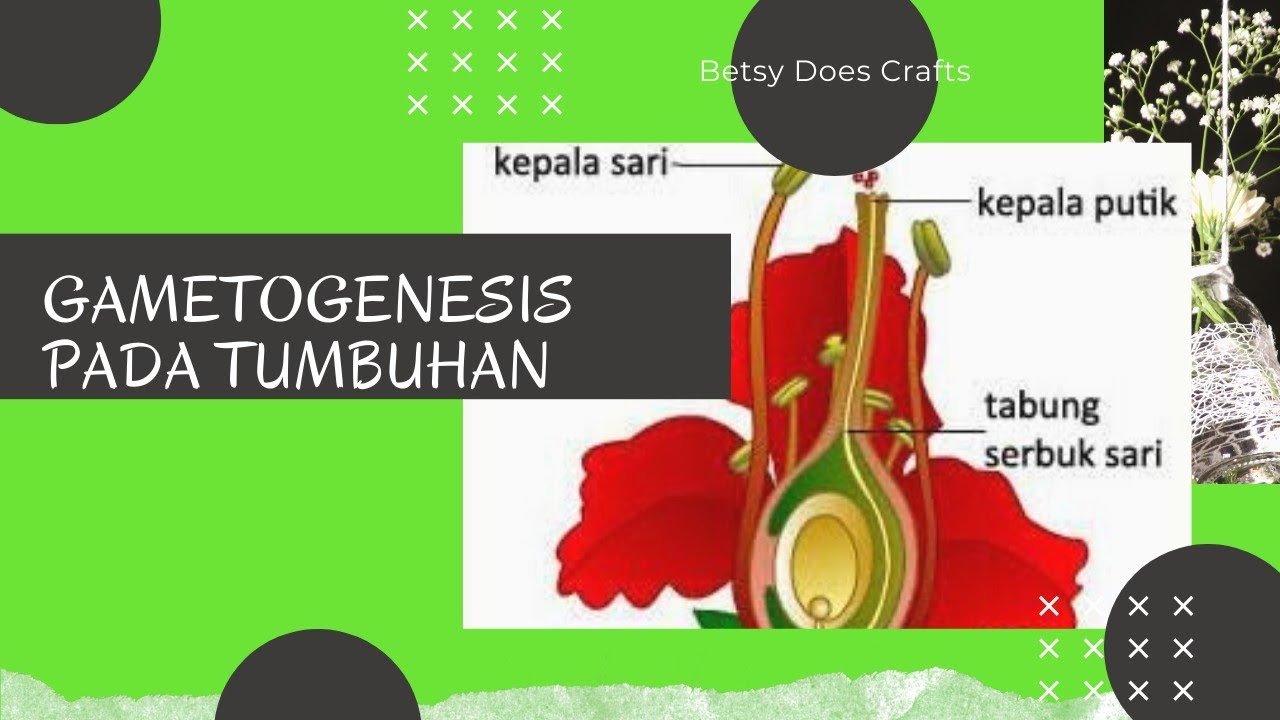
- 😀 Pollen grains, containing male gametes, are released from the anther and travel to the stigma of the flower, sometimes aided by pollinators like bees.
- 😀 Each pollen grain contains two male gametes, both of which are haploid (having half the number of chromosomes).
- 😀 The female gametes, located in the ovule, are also haploid and are enclosed in the embryo sac, which has a distinct structure.
- 😀 The male gametes travel down the style via a pollen tube to reach the ovule where fertilization occurs.
- 😀 The pollen tube is guided to the embryo sac by the synergids, which play a crucial role in directing the male gametes.
- 😀 Fertilization occurs when one male gamete fuses with the egg cell (female gamete), forming a diploid zygote.
- 😀 The second male gamete fuses with two polar nuclei in the embryo sac, creating the primary endosperm nucleus, a triploid structure.
- 😀 This process is called double fertilization, unique to angiospermic plants, involving the formation of both a zygote and primary endosperm.
- 😀 In double fertilization, the primary endosperm nucleus is triploid (3n), containing chromosomes from both male and female gametes, providing nourishment for the developing zygote.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of this video?
-The video explains the process of fertilization in flowering plants, including the fusion of male and female gametes and the process of double fertilization.
What does it mean for a flower to be self-pollinating?
-A self-pollinating flower is one where the male gametes (pollen) from the same flower can fertilize the female gametes (ovules) of that same flower.
How are male gametes transported to the female reproductive part of the flower?
-Male gametes are carried by pollen grains, which can be transferred to the stigma of the female flower part through various agents like wind, bees, or other insects.
What is the role of the pollen tube in fertilization?
-The pollen tube grows from the pollen grain and transports the male gametes through the style to reach the ovule in the ovary, where fertilization occurs.
How many male gametes does each pollen grain contain?
-Each pollen grain contains two male gametes, and both are haploid (having a single set of chromosomes).
What are the antipodal cells in the female gametophyte?
-Antipodal cells are cells located at the opposite end of the female gametophyte, but their exact role in fertilization is unclear. Some research suggests they disintegrate after fertilization.
What are synergies, and what role do they play in fertilization?
-Synergies are two cells in the female gametophyte that guide the pollen tube towards the egg cell. They help direct the male gametes to the egg cell and eventually disintegrate after fertilization.
What is double fertilization in plants?
-Double fertilization is a process unique to angiosperms, where one male gamete fuses with the egg cell to form the zygote, and the other male gamete fuses with the polar nuclei to form the primary endosperm nucleus.
What is the ploidy level of the zygote formed after fertilization?
-The zygote formed after the fusion of a male and female gamete is diploid (2n), meaning it has two sets of chromosomes.
What is the significance of the primary endosperm nucleus in fertilization?
-The primary endosperm nucleus is formed when one male gamete fuses with two polar nuclei. It is triploid (3n) and provides nourishment to the developing zygote, ensuring its growth into an embryo.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

[Sains T1] Bab 4.1 (A) Pembiakan Seks #T1 #KSSM #PT3

Topic 3.5 Angiosperms (Flowering Plants) | Plant Kingdom-11th Class Biology | Handwritten Notes

Fertilisation and Seed Formation

Pembuahan Ganda pada Tumbuhan Berbunga (Angiospermae)

REPRODUÇÃO das PLANTAS 🌱 (Sexuada, Assexuada, com e sem flores)
GAMETOGENESIS PADA TUMBUHAN || MIKROSPOROGENESIS & MEGASPOROGENESIS #biologikelas12 #pembelahansel
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
