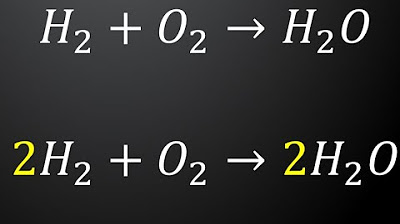Jenis Jenis Reaksi Kimia
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the basics of chemical equations, including their components such as reactants and products. The presenter covers seven types of chemical reactions: composition (synthesis), decomposition, combustion, single replacement, double replacement, neutralization, and endothermic reactions. Examples are provided to illustrate each type, like the formation of water in a composition reaction, or methane burning in a combustion reaction. The video encourages viewers to understand these reactions in detail, with additional topics like neutralization and endothermic reactions to be covered later.
Takeaways
- 😀 Chemical equations represent chemical reactions, where reactants on the left side react to form products on the right side.
- 😀 In a chemical reaction, the left side contains reactants, and the right side contains products, represented by an arrow pointing from reactants to products.
- 😀 The seven types of chemical reactions are composition (synthesis), decomposition, combustion, single replacement, double replacement (metathesis), neutralization, and endothermic reactions.
- 😀 In composition (synthesis) reactions, two or more reactants combine to form a product. An example is the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen to form water.
- 😀 Decomposition reactions involve one reactant breaking down into two or more products. An example is the decomposition of sodium bicarbonate into sodium carbonate, carbon dioxide, and water.
- 😀 Combustion reactions involve the burning of a substance with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water, often releasing energy. For example, methane reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water.
- 😀 Single replacement reactions occur when one element replaces another in a compound, as shown in the reaction between hydrochloric acid and zinc, producing zinc chloride and hydrogen gas.
- 😀 Double replacement (metathesis) reactions involve the exchange of ions between two compounds, forming two new compounds. For example, copper chloride reacts with silver nitrate to produce copper nitrate and silver chloride.
- 😀 Neutralization reactions occur when an acid reacts with a base to form water and a salt, which will be studied after learning about acids and bases.
- 😀 Endothermic reactions absorb heat from their surroundings. This type of reaction will be covered later in the course.
Q & A
What is a chemical equation?
-A chemical equation represents a chemical reaction where reactants are transformed into products. It is written using a chemical formula and is indicated with an arrow rather than an equal sign.
What is the difference between reactants and products in a chemical reaction?
-Reactants are the substances that undergo a chemical change, located on the left side of the chemical equation, while products are the substances formed as a result of the reaction, located on the right side.
What is the first type of chemical reaction mentioned in the script?
-The first type of chemical reaction mentioned is composition (also known as synthesis or combination), where two or more reactants combine to form a single product. An example is the combination of hydrogen and oxygen to form water.
What is a decomposition reaction?
-A decomposition reaction, or breakdown, involves a single reactant breaking down into two or more products. An example is the decomposition of sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) into sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), carbon dioxide (CO2), and water (H2O).
What is the defining feature of combustion reactions?
-Combustion reactions involve the burning of a substance, usually a carbon and hydrogen compound, in the presence of oxygen. The products are typically carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). An example is the combustion of methane (CH4).
How does a single replacement reaction work?
-In a single replacement reaction, one element replaces another in a compound. For example, when zinc (Zn) reacts with hydrochloric acid (HCl), zinc replaces hydrogen to form zinc chloride (ZnCl2) and hydrogen gas (H2).
What happens in a double replacement reaction?
-In a double replacement reaction, two compounds exchange their components to form two new compounds. For example, when copper(II) chloride (CuCl2) reacts with silver nitrate (AgNO3), copper(II) nitrate (Cu(NO3)2) and silver chloride (AgCl) are formed.
What is the difference between a single and double replacement reaction?
-A single replacement reaction involves one element replacing another in a compound, whereas a double replacement reaction involves the exchange of ions between two compounds to form two new products.
What are neutralization reactions, and when will they be studied?
-Neutralization reactions involve the reaction between an acid and a base to form water and a salt. These reactions will be studied after learning about acids and bases.
What is the seventh type of chemical reaction mentioned, and when will it be studied?
-The seventh type of chemical reaction mentioned is endothermic reactions. These will be studied later, after learning about acids and bases.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)