Penyetaraan Persamaan Reaksi Kimia dengan Cepat- Kimia Kelas 10
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial provides an in-depth explanation on how to balance chemical reactions. It covers the basics of chemical reactions, including reactants, products, and the significance of coefficients in equations. The video emphasizes the importance of keeping the number of atoms equal on both sides of the equation. Through various examples, viewers learn how to balance equations step by step by adjusting coefficients without altering chemical formulas. The tutorial also highlights key rules for proper balancing, making it an essential guide for students learning this fundamental chemistry skill.
Takeaways
- 😀 Reactions in chemistry involve a change from reactants to products, as seen in the example of iron rusting.
- 😀 A chemical reaction equation represents the reactants and products, including their states (solid, liquid, gas, or aqueous).
- 😀 The coefficients in a chemical equation indicate the number of molecules or atoms involved in the reaction.
- 😀 States of matter are represented as 'S' (solid), 'L' (liquid), 'G' (gas), and 'aq' (aqueous) in a reaction equation.
- 😀 Dalton's atomic theory states that atoms are neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction, only rearranged.
- 😀 To balance a chemical reaction, the number of atoms on the left side must equal the number of atoms on the right side.
- 😀 When balancing equations, only the coefficients (numbers in front of molecules) should be changed, not the subscripts (small numbers in molecular formulas).
- 😀 An example is provided with the reaction of magnesium (Mg) and oxygen (O2), where balancing is done by adjusting the coefficients to match the number of atoms on both sides.
- 😀 The script emphasizes that when balancing equations, no additional reactants or products should be added that aren't already part of the equation.
- 😀 The video also demonstrates balancing equations through multiple examples, like MnO2 + HCl producing MnCl2, H2O, and Cl2, ensuring the atom count is equal on both sides.
Q & A
What is a chemical reaction?
-A chemical reaction is a process where substances called reactants undergo a transformation to form new substances called products. This involves a change in the chemical structure, resulting in different properties.
What are the four states of matter commonly indicated in chemical equations?
-The four states of matter commonly used in chemical equations are: (s) for solid, (l) for liquid, (g) for gas, and (aq) for aqueous (dissolved in water).
What is the importance of balancing chemical equations?
-Balancing chemical equations ensures that the law of conservation of mass is followed, meaning the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
Can the subscripts in chemical formulas be changed when balancing reactions?
-No, subscripts (the small numbers within chemical formulas) should not be changed, as this would alter the identity of the substances. Only the coefficients (numbers in front of molecules) should be adjusted.
What is the role of coefficients in a balanced chemical equation?
-Coefficients indicate the number of molecules or moles of a substance involved in the reaction. They ensure that the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides of the equation.
Why is it important to check the final balanced equation?
-It is important to check the final balanced equation to ensure that all atoms are accounted for and that the equation follows the law of conservation of mass, with no atoms added or lost.
What does it mean for a chemical reaction to be 'balanced'?
-A chemical reaction is balanced when the number of atoms of each element on the left side (reactants) equals the number of atoms of that same element on the right side (products).
In the reaction Mg + O₂ → MgO, how do you balance it?
-To balance the equation, add a coefficient of 2 to MgO on the right side to match the number of oxygen atoms. Then, adjust the number of magnesium atoms by adding a coefficient of 2 to Mg on the left side: 2Mg + O₂ → 2MgO.
How do you balance the reaction MnO₂ + HCl → MnCl₂ + H₂O + Cl₂?
-To balance this reaction, adjust the coefficients of HCl and Cl₂ to match the chlorine atoms on both sides. Then, balance the hydrogen atoms by adding the correct coefficient to H₂O, ensuring all atoms are equal on both sides.
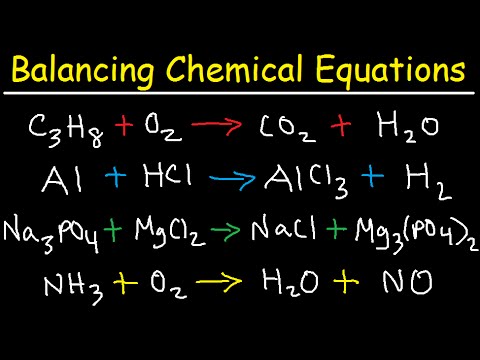
What is the process for balancing a combustion reaction, like C₃H₆ + O₂ → CO₂ + H₂O?
-To balance a combustion reaction, start by balancing the carbon (C) and hydrogen (H) atoms, then balance the oxygen (O) atoms last. In this case, you would first balance carbon by adding a coefficient to CO₂, then balance hydrogen by adjusting H₂O, and finally balance oxygen.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

REAKSI REDOKS DAN ELEKTROKIMIA - MATERI KIMIA KELAS 12 | Edcent.id

Alkohol dan Eter | Senyawa Turunan Alkana | KIMIA KELAS 12

Persamaan Reaksi || Kimia kelas X

Chemical reactions and equations Full chapter in animation | CBSE Class 10 | NCERT Science ch -1

Silver oxide battery | Working Animation | Anode(Zn) Cathode Ag2O | Electrochemistry | Chemistryask
Introduction to Balancing Chemical Equations
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)