Penjelasan D Flip Flop
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker explains the D flip-flop, a memory element in digital electronics that operates using a rising-edge clock signal. The D flip-flop stores and updates a single bit of data based on input values at the clock's active edge. The explanation covers key concepts such as the truth table, state diagram, and timing diagram, demonstrating how the flip-flop's output responds to inputs and clock signals. Through clear visuals and step-by-step breakdowns, the video helps viewers understand the D flip-flop’s role in storing and retaining data in digital circuits.
Takeaways
- 😀 The D flip-flop is a type of memory circuit used in digital electronics to store or delay data.
- 😀 The 'D' in D flip-flop stands for 'data' or 'delay,' reflecting its function to store or delay information.
- 😀 The D flip-flop operates based on a clock signal, specifically triggered by the rising edge (clock naik).
- 😀 The truth table of the D flip-flop defines the relationship between the input (D) and output (Q), where the next output is determined by the current output and input values.
- 😀 If the current output is 0 and the input is 0, the next output remains 0. If the current output is 1 and the input is 0, the next output becomes 0.
- 😀 If the current output is 0 and the input is 1, the next output becomes 1. If the current output is 1 and the input is 1, the next output remains 1.
- 😀 The state diagram of the D flip-flop visually represents the transitions between states based on the input values.
- 😀 The timing diagram shows that the D flip-flop updates its output only when the clock signal is active (rising edge).
- 😀 When the clock is inactive, the D flip-flop retains its current output value, regardless of changes in the input.
- 😀 The D flip-flop functions as a memory element, storing logical values (0 or 1) until the next active clock signal.
- 😀 The video encourages viewers to watch more tutorials to understand other flip-flop types and the concept of clock signals in greater depth.
Q & A
What is a D flip-flop in digital electronics?
-A D flip-flop is a type of memory element used in digital circuits that stores a single bit of data. It can either store data or delay it based on the clock signal.
Why is it called a 'D flip-flop'?
-It is called a 'D flip-flop' because of the 'Data' input, denoted by 'D', which is where the information to be stored is provided.
What are the two main functions of a D flip-flop?
-The two main functions of a D flip-flop are storing data and delaying data, acting as a memory element in digital circuits.
How does a D flip-flop respond to the clock signal?
-A D flip-flop updates its output based on the input data only when a clock signal is received, typically at the rising edge of the clock.
What is the truth table for a D flip-flop?
-The truth table for a D flip-flop shows how the output (Q) changes based on the current output and the input (D). If the current output is 0 and the input is 0, the next output is 0. If the input is 1, the next output becomes 1.
Can the output of a D flip-flop change without a clock signal?
-No, the output of a D flip-flop can only change when the clock signal is active, regardless of any changes in the input.
What is a state diagram in the context of D flip-flops?
-A state diagram is a graphical representation showing how the output of the D flip-flop transitions between different states based on the current input and the clock signal.
How does the timing diagram of a D flip-flop work?
-In the timing diagram, the output of the D flip-flop is updated only when the clock signal is active. The diagram shows how the flip-flop holds its output even when the input changes, until the next clock pulse.
What happens when the clock signal is inactive in a D flip-flop?
-When the clock signal is inactive, the output of the D flip-flop does not change, even if the input (D) changes. This behavior allows the D flip-flop to store data.
What is the significance of the clock rise edge in a D flip-flop?
-The clock's rising edge triggers the D flip-flop to capture the input data (D) and update the output (Q). This edge ensures that the data is stored and updated in a controlled manner.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

106. OCR A Level (H446) SLR15 - 1.4 D-type flip flops
Simulasi Rangkaian JK Flip-flop, RS Flip-flop, dan D Flip-flop ( Faishal Satria G 2211181006 )
Clocked SR Flip Flop using NAND Gates with Truth Table and Circuit Diagram

Part 5.2 #Latches and #FlipFlops #SequentialCircuits in Digital Electronics in Hindi
Latches and Flip-Flops 6 - The JK Flip Flop
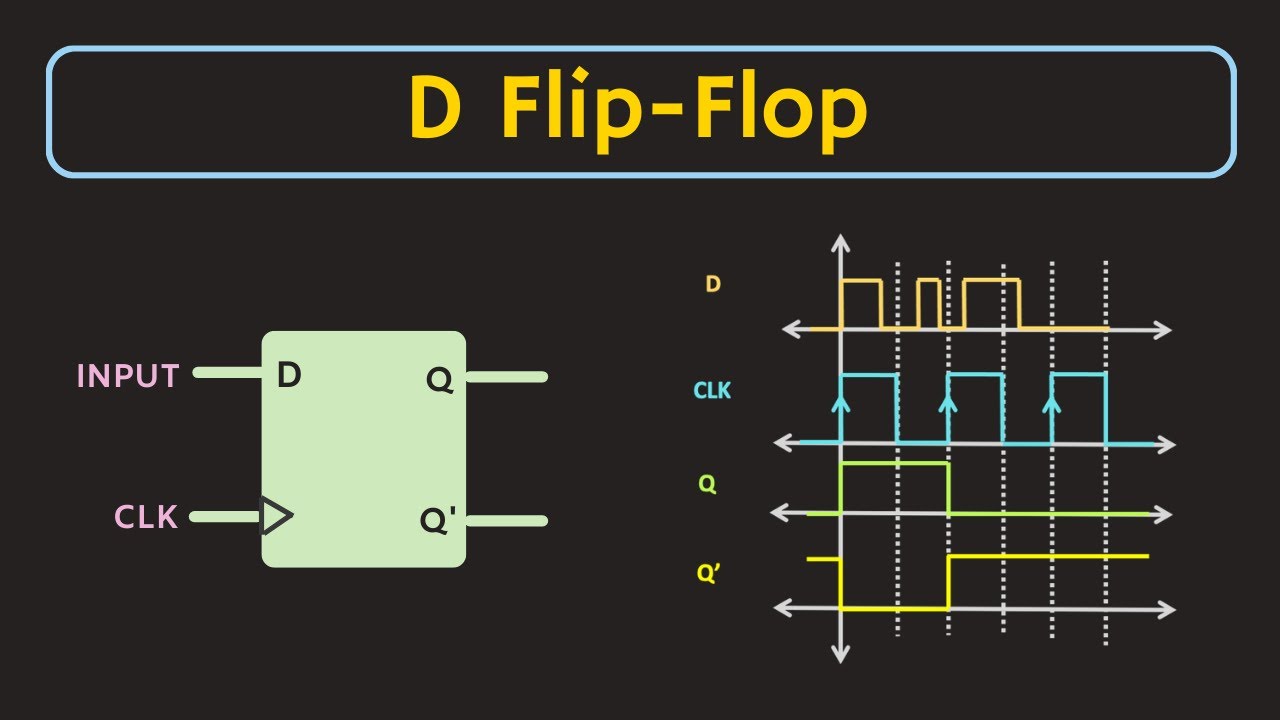
D Flip-Flop Explained | Truth Table and Excitation Table of D Flip-Flop
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
