106. OCR A Level (H446) SLR15 - 1.4 D-type flip flops
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the purpose and principles of D-type flip-flops, fundamental components in digital electronics used for memory storage. It describes how D-type flip-flops store one bit of data, triggered by a clock pulse at the rising edge, and how they synchronize components in a computer. The video highlights both basic and advanced configurations, such as the master-slave D-type flip-flop, and introduces concepts like edge triggering and glitch prevention. While simplifying the core ideas for A-level exams, the video also provides deeper insights for those interested in further understanding the underlying electronics.
Takeaways
- 😀 D-type flip-flops are fundamental memory devices used to store one bit of data in digital circuits.
- 😀 A D-type flip-flop captures the value of its data input (D) only at the rising edge of the clock signal.
- 😀 The output of a D-type flip-flop (Q) follows the input (D) at the rising edge of the clock, and holds the value when the clock is not at the rising edge.
- 😀 D-type flip-flops are edge-triggered, meaning they only respond to changes in the clock signal at the rising or positive edge.
- 😀 The clock pulse is used to synchronize the state changes in D-type flip-flops, enabling precise timing in memory operations.
- 😀 A clocked D-latch is often confused with a D-type flip-flop, but it lacks the master-slave configuration that prevents glitches.
- 😀 NAND gates, which are universal logic gates, are used internally in D-type flip-flops, but exam focus is on the functionality rather than the specific gate design.
- 😀 D-type flip-flops are used in important digital systems such as memory circuits, counters, and shift registers.
- 😀 The D-type flip-flop ensures stable memory storage and synchronization, preventing issues like glitches or incorrect data transfers.
- 😀 A master-slave D-type flip-flop design uses two latches (master and slave) to ensure data is correctly stored and transferred without conflict.
- 😀 Understanding the basic operation of a D-type flip-flop, including its behavior at the clock's rising edge, is key for exam success in digital electronics.
Q & A
What is a D-type flip-flop and how is it used in computers?
-A D-type flip-flop is a fundamental memory device that stores one bit of data and changes its state based on clock pulses. It is used in computers for memory circuits, counters, and shift registers, where it helps synchronize components and store data.
What are the main components of a D-type flip-flop?
-A D-type flip-flop has two main inputs: a data input (D) and a clock input (C). It also has two outputs: a data output (Q) and its inverse (not-Q).
What does it mean for a flip-flop to be 'edge-triggered'?
-An edge-triggered flip-flop updates its output only at specific points in the clock cycle, typically the rising edge (when the clock signal transitions from low to high). The output changes only at this precise moment, regardless of the state of the data input at other times.
What is the difference between a D-type flip-flop and a D-latch?
-A D-latch, also called a gated D-latch, is a simpler circuit that allows the output to follow the data input whenever the clock is high. In contrast, a D-type flip-flop is a more precise circuit that only updates its output at the rising edge of the clock pulse.
What is the significance of the clock signal in a D-type flip-flop?
-The clock signal controls when the D-type flip-flop updates its output. The flip-flop only changes its output at the rising edge of the clock pulse, ensuring that data is captured at specific intervals, synchronized with other components.
How does a D-type flip-flop behave when the clock signal is not at the rising edge?
-When the clock signal is not at the rising edge, the output of the D-type flip-flop remains unchanged, even if the data input (D) changes. The output only reflects the data input when the clock signal rises from low to high.
What does the term 'Q follows D at the rising edge' mean?
-This phrase means that the output (Q) of the D-type flip-flop will take on the value of the data input (D) exactly at the rising edge of the clock pulse. The output only updates at this specific moment in time.
What is the purpose of the 'master-slave' configuration in a D-type flip-flop?
-The master-slave configuration in a D-type flip-flop uses two latches to prevent glitches and ensure more precise control over data transfer. The master latch captures the input at the rising edge, and the slave latch outputs the data when the clock signal falls.
How does the clocked D-latch prevent data glitches?
-The clocked D-latch prevents data glitches by only allowing the output to change at the rising edge of the clock signal, reducing the chance of incorrect data being passed through due to signal noise or timing issues.
What is the role of edge detection in a D-type flip-flop circuit?
-Edge detection is used to convert the clock signal into a series of short, sharp pulses. This ensures that the flip-flop responds precisely to the rising edge of the clock signal and avoids any issues related to signal delays or incorrect timing.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Part 5.2 #Latches and #FlipFlops #SequentialCircuits in Digital Electronics in Hindi
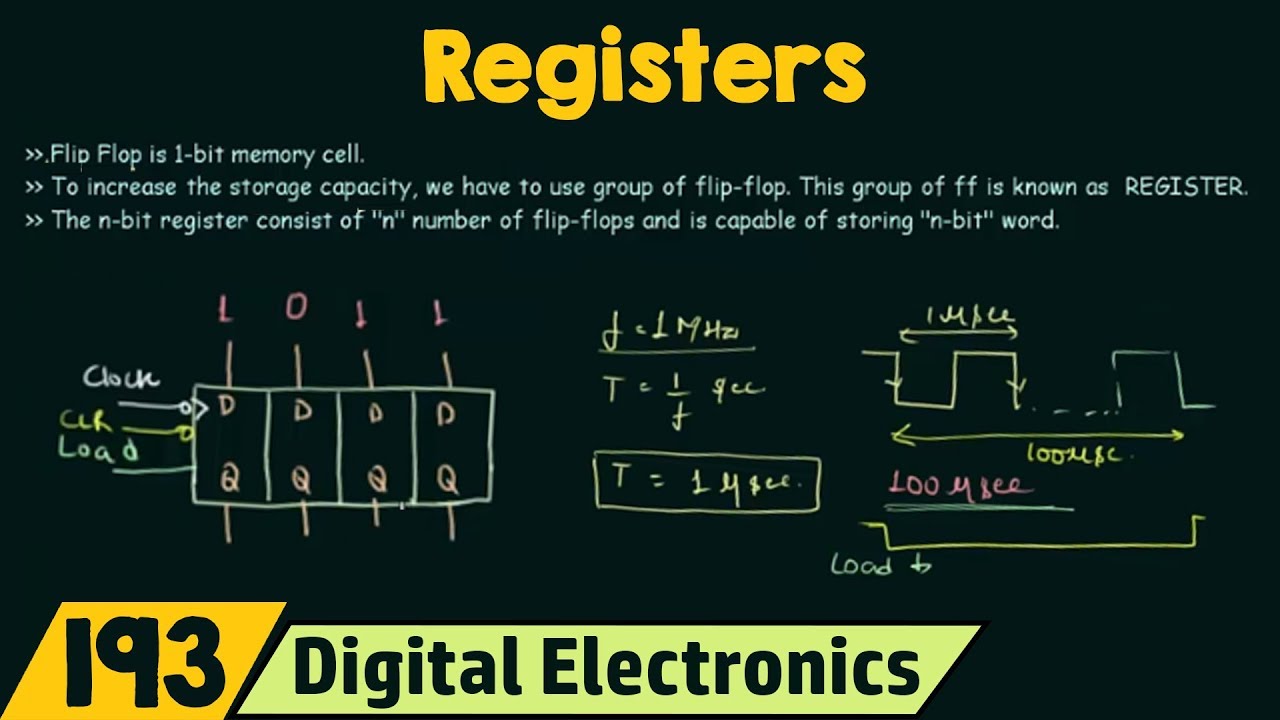
Introduction to Registers

Introduction to Sequential Circuits | Important

Digital Logic Basics Review - Sequential Logic

Sistem Digital - Flip Flop D, JK dan T
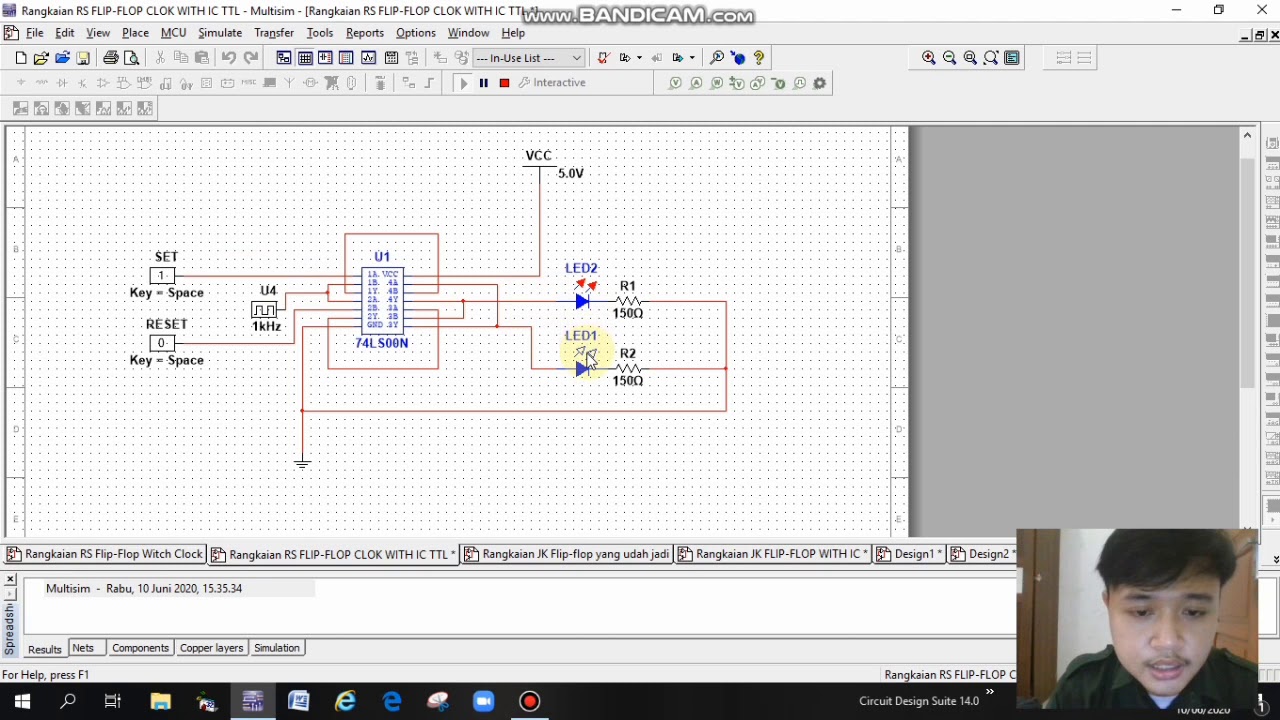
Simulasi Rangkaian JK Flip-flop, RS Flip-flop, dan D Flip-flop ( Faishal Satria G 2211181006 )
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)