Regni romano-barbarici (+ Regno dei Franchi e Ostrogoti) - età tardo antica
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the decline of the Western Roman Empire, marked by the deposition of the last emperor in 476 CE, and the subsequent rise of Barbarian Kingdoms in Europe. It highlights the invasion and settlement of tribes like the Franks, Visigoths, and Ostrogoths, and the resulting cultural, economic, and social shifts. The Barbarians, though militarily strong, relied on Roman administrators for governance, leading to a blending of Roman and Barbarian cultures. Key figures such as Clovis and Theoderic shaped these new kingdoms, and the growing influence of Christianity played a significant role in this transformative period leading to the early Middle Ages.
Takeaways
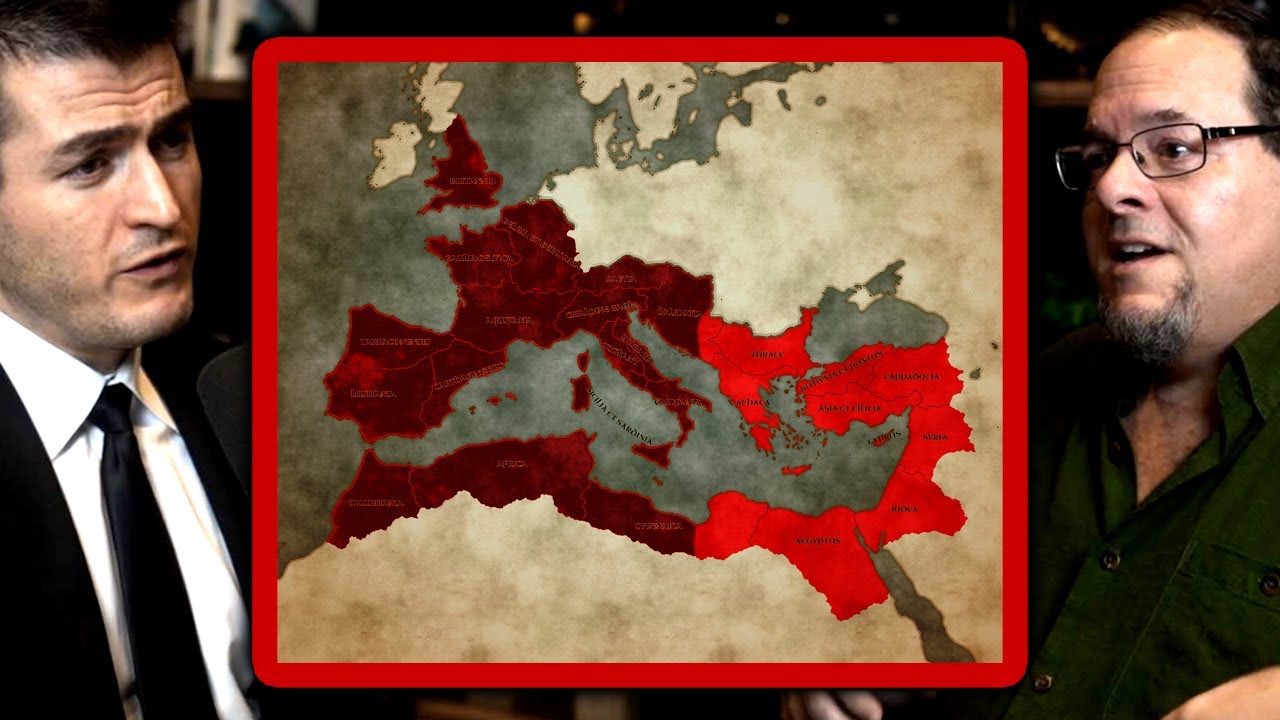
- 😀 The Western Roman Empire officially fell in 476 AD when the last Roman emperor was deposed by the barbarian Odoacer, marking the end of the Empire.
- 😀 By 476 AD, several Germanic tribes (Franks, Swabians, Visigoths, Vandals, and Anglo-Saxons) had already invaded and occupied significant parts of the Western Roman Empire.
- 😀 Despite the fall of the Western Roman Empire, the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) continued to survive and play a key role in European politics.
- 😀 The period between the 5th and 6th centuries, known as 'Late Antiquity,' saw a demographic collapse in Italy due to warfare, invasions, and plundering.
- 😀 Major cities and rural areas were abandoned, leading to a significant decrease in agricultural productivity and the collapse of infrastructure like roads and aqueducts.
- 😀 Barbarian groups established kingdoms in the former Western Roman territories, blending their military power with Roman administrative functions.
- 😀 Barbarian societies were initially smaller and less complex than the Romans, which led to a division of responsibilities: barbarians controlled military power, while Romans handled administration.
- 😀 There were cultural and religious tensions between barbarians and Romans, especially regarding differences in language, laws, and religion (Arianism vs. Catholicism).
- 😀 The Franks, led by Clovis I, successfully integrated with the Gallo-Roman population, adopted Catholicism, and expanded their kingdom, which remained influential in Europe for centuries.
- 😀 The Ostrogoths, led by Theodoric the Great, established a kingdom in Italy in 488 AD and attempted a policy of integration with the Roman population, though religious differences eventually led to failure.
- 😀 After Theodoric's death, the Byzantine Empire under Justinian reconquered Italy, but this control was short-lived due to the Lombard invasion in 569 AD, marking the beginning of the High Middle Ages.
Q & A
What event in 476 AD is considered the fall of the Western Roman Empire?
-In 476 AD, the last Roman emperor of the West, Romulus Augustulus, was deposed by the barbarian Odoacer. This is traditionally considered the end of the Western Roman Empire.
What characterized the 'Late Antiquity' period and how did it lead to the Middle Ages?
-The Late Antiquity period, spanning the 5th and 6th centuries, was marked by significant demographic decline, particularly in Italy, due to wars, invasions, and sackings. This transition led to the establishment of 'barbarian' kingdoms and eventually paved the way for the Middle Ages.
What impact did the barbarian invasions have on the Roman Empire's infrastructure?
-The barbarian invasions led to a collapse in infrastructure. Cities and villages were abandoned, lands left uncultivated, and the transportation and communication systems were severely disrupted. The lack of maintenance caused rivers to overflow, and forests and swamps replaced cultivated lands.
What was the structure of power in the Roman barbarian kingdoms?
-In the Roman barbarian kingdoms, power was shared between the barbarians and the Romans. The barbarians controlled military and political power, while the Romans handled administrative tasks like managing infrastructure, taxes, and agriculture.
Why did the barbarians respect Roman infrastructure and culture?
-Although the barbarians had a military focus, they admired and respected Roman infrastructure such as aqueducts, roads, and amphitheaters. They maintained these structures because they saw their practical value, preferring to preserve them rather than destroy them.
How did the legal systems differ between the Romans and the barbarians?
-The Romans had a written legal system, while the barbarians followed oral traditions. Over time, the barbarians began adopting written laws, and the Visigoths in Spain established the first written laws in the 7th century.
What were the religious differences between the Romans and the barbarians?
-Initially, the barbarians practiced their own polytheistic beliefs. Some later converted to Christianity but followed Arianism, which was deemed heretical by the Catholic Church. The Franks were among the first to convert to Catholicism, while others took longer to do so.
How did the Franks integrate with the Gallo-Roman population?
-The Franks, led by Clovis, integrated with the Gallo-Roman population through a series of strategic actions, including adopting Catholicism, promoting intermarriage, and appointing Romans to important positions, even in the military.
What significant military victory did Charles Martel achieve in 732?
-In 732, Charles Martel defeated the advancing Arab forces in the Battle of Poitiers, stopping their expansion into Europe. This victory was crucial in preserving Christian Europe from Muslim control.
What role did Theodoric the Great play in the Ostrogothic Kingdom in Italy?
-Theodoric the Great, sent by the Eastern Roman Emperor Zeno in 488, established the Ostrogothic Kingdom in Italy. He governed with respect for Roman culture and legal systems but faced tensions due to religious differences, as he followed Arianism while the Romans were Catholic.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

¿Cómo fue la caída del Imperio romano de occidente?

👑 I REGNI ROMANO BARBARICI e gli OSTROGOTI in ITALIA ⚔ Inizia il MEDIOEVO 📚 (Storia)

Why Did Rome Fall?

The Fall of Rome Explained In 13 Minutes
How the Roman Empire split into Western and Eastern empires | Gregory Aldrete and Lex Fridman

El Imperio Romano en 10 minutos
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
