Why Did Rome Fall?
Summary
TLDRThe fall of the Roman Empire was not a single event but a complex process marked by internal strife and external pressures. Key moments include the 'crisis of the third century' and the 476 AD deposition of the last Western Roman Emperor by Odoacer. Despite the Western Empire's collapse, the Eastern Empire, or Byzantium, thrived until 1453. Factors contributing to the fall included barbarian invasions, economic troubles, and climate change. The Roman legacy, however, persisted through the Byzantine Empire and the Catholic Church, influencing future civilizations.
Takeaways
- 🏛 The fall of Rome was not a single event but a complex process with no exact date, highlighting the gradual decline of the Western Roman Empire.
- 👑 The symbolic end of Western Rome is marked by the deposition of the last Emperor by Odoacer in 476 AD, signifying the end of Roman rule in Rome.
- 🌐 The Roman Empire had split into Eastern and Western halves before the fall of Rome, with the Eastern Empire lasting until 1453, suggesting a longer legacy of Roman rule.
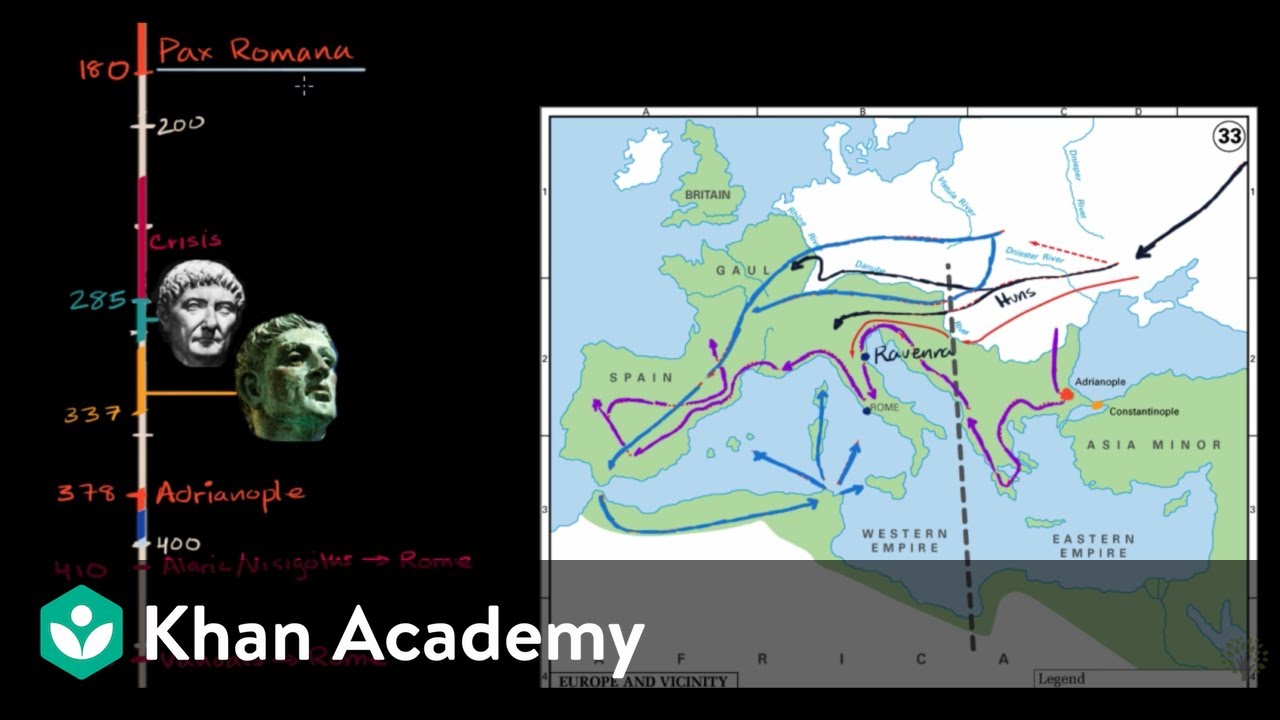
- 🛡 The 'crisis of the third century' was characterized by civil wars, rebellions, and economic strife, which weakened the Empire's structure.
- 🗡 The invasions by 'barbarians,' primarily Germanic tribes, were a significant factor in the fall of the Western Roman Empire, challenging Roman control.
- 🌍 Climate change and the Great Migration forced tribes like the Huns to move westward, leading to increased pressure on the Roman borders.
- 💸 Economic troubles, including high military spending and oppressive taxation, contributed to the Empire's decline and the rise of poverty among the populace.
- 🏛️ The policy of granting citizenship to immigrants and conquered peoples led to a labor shortage as the traditional slave economy was impacted.
- 🏴☠️ The Vandals' takeover of North African provinces and piracy in the Mediterranean severely damaged the Roman economy and trade.
- 🏺 The sack of Rome by the Visigoths under Alaric was a psychological blow to the Empire, demonstrating Rome's vulnerability despite the lack of widespread destruction.
- ⚔️ The final annexation of Rome by the barbarian Kingdom of Italy in 476 AD was almost anticlimactic, reflecting the long-term decline of Roman power.
Q & A
What is the symbolic date often associated with the fall of the Western Roman Empire?
-The symbolic date often associated with the fall of the Western Roman Empire is 476 AD, when Odoacer deposed the last Emperor of Western Rome.
Why is the division of the Roman Empire into two parts significant?
-The division of the Roman Empire into two parts is significant because it led to the Eastern Empire outliving the Western Roman Empire by almost 1000 years, suggesting that the Roman Empire in a broader sense only fell in 1453 with the fall of Constantinople.
What were the main groups of 'barbarians' that troubled the Western Roman Empire?
-The main groups of 'barbarians' that troubled the Western Roman Empire were Germanic tribes, who began to pass through the frontier and settle on Roman territory.
Why did the Romans fail to keep the barbarian tribes out of their territory?
-The Romans failed to keep the barbarian tribes out because the tribes and political systems had been around the border area for generations, and many of their leaders were client kings who paid tribute to Rome regularly and were considered friends of Rome.
How did climate change contribute to the fall of the Western Roman Empire?
-Climate change pushed several groups, including the nomadic Huns, away from the steppes of central Asia eastward, causing the barbarians to move further inland into the Empire, a movement known as the Great Migration.
What economic troubles did the Roman Empire face that contributed to its decline?
-The Roman Empire faced severe economic troubles including overextension, excessive spending on military campaigns and administration of rebellious provinces, leading to oppressive taxation and a labor shortage.
How did the policy of granting citizenship to immigrants and those in occupied areas affect the Roman Empire?
-Granting citizenship to immigrants and those in occupied areas caused a severe problem by lowering the ready supply of slaves that had previously fueled economic growth, leading to a labor shortage.
What was the impact of the Vandals taking over the North African provinces on the Roman Empire?
-The Vandals taking over the North African provinces was a significant blow to the economy and structure of the Empire, as it disrupted trade and reduced the Empire's ability to collect taxes.
How did the sack of Rome by the Visigoths under Alaric differ from earlier invasions?
-The sack of Rome by the Visigoths under Alaric differed from earlier invasions in that they had great respect for Rome and did not intend to destroy it. Instead, they sought to leverage the capture for land and left the city relatively unharmed.
In what ways did the concept of the Roman Empire endure after the fall of the Western Roman Empire?
-The concept of the Roman Empire endured through the continuation of the Eastern Roman Empire, future leaders like Charlemagne and Peter the Great claiming authority derived from Roman Emperors, and the global influence of the Catholic Church.
What is the significance of the Catholic Church in the legacy of the Roman Empire?
-The Catholic Church grew in stature and wielded significant influence globally, becoming a major player in many parts of the world, thus preserving and extending the legacy of the Roman Empire.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

O Império Bizantino: Os Herdeiros de Roma - Grandes Civilizações da História - Foca na História

MENGAPA MUGHAL HARUS RUNTUH? | Sejarah India dari Mughal menuju Kolonialisme Inggris - Episode 2

¿Cómo fue la caída del Imperio romano de occidente?
Fall of the Roman Empire | World History | Khan Academy

How the Roman Republic Became the Roman Empire?

Eps 285 | MAJAPAHIT BUKAN KERAJAAN HINDU!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)