Uniform Circular Motion and Centripetal Force
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Professor Dave explains uniform circular motion, focusing on the concepts of tangential speed, centripetal acceleration, and centripetal force. He describes how objects, like Ferris wheel cars, move in circular paths, with tangential speed varying based on distance from the center. The professor clarifies that while tangential speed remains constant, the direction of velocity changes due to centripetal acceleration directed towards the center. Additionally, he discusses the sensation of being pushed outward on rotating objects, attributing it to inertia rather than a real centrifugal force. The lesson emphasizes the importance of these principles in understanding motion in both terrestrial and celestial contexts.
Takeaways
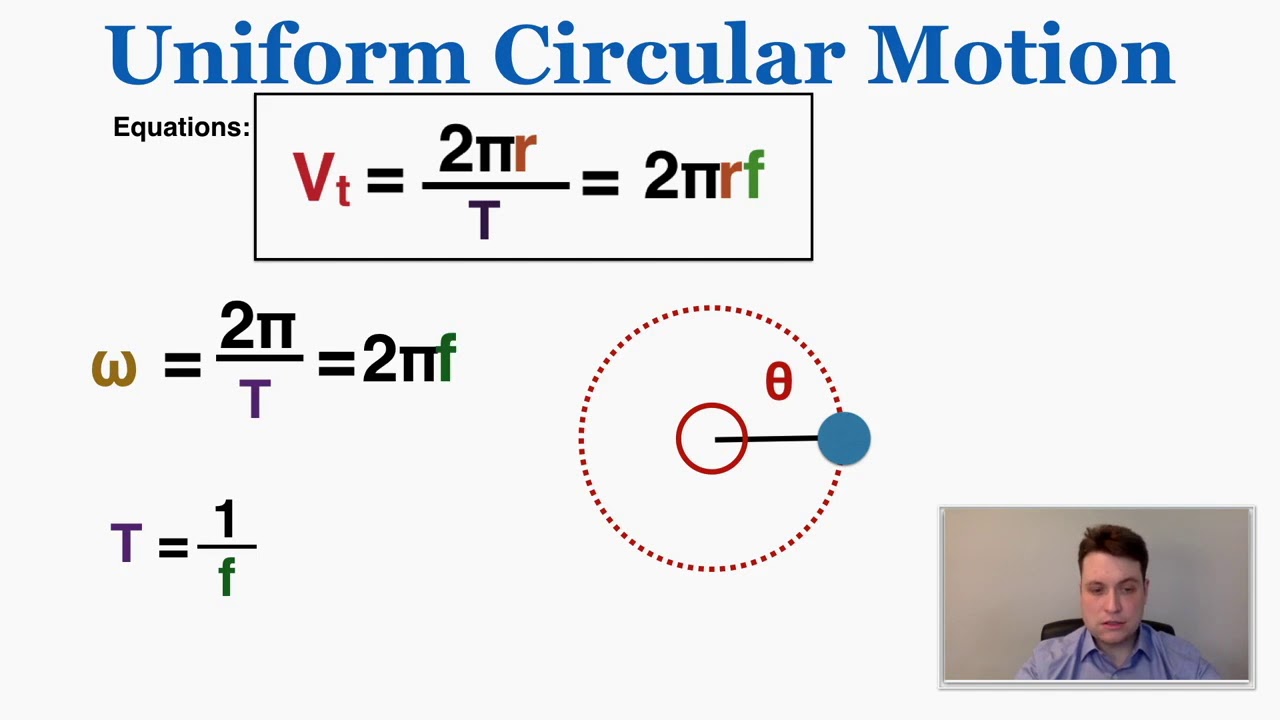
- 😀 Uniform circular motion refers to objects moving along a circular path at a constant speed.
- 🚀 Tangential speed is the speed of an object along the tangent line to its circular path at any moment.
- 🔄 In uniform circular motion, while the speed remains constant, the direction of velocity continuously changes.
- 📏 Centripetal acceleration points toward the center of the circle, enabling circular motion.
- ⚙️ The formula for centripetal acceleration is a_c = v²/r, where v is tangential speed and r is the radius of the circle.
- 💪 Centripetal force is necessary for centripetal acceleration and can be provided by tension, gravity, or friction.
- 📊 Centripetal force can be calculated using F_c = m × a_c = m × (v²/r), where m is the object's mass.
- 🚀 If centripetal force is removed, an object will move in a straight line, following the tangent to the circle at that moment.
- ⚖️ The sensation of being pushed outward on a rotating object is due to inertia, not an actual force called centrifugal force.
- 📚 Understanding uniform circular motion is essential for analyzing various physical phenomena, from planetary motion to everyday circular movements.
Q & A
What is uniform circular motion?
-Uniform circular motion refers to the movement of an object along a circular path at a constant speed. The direction of the object's velocity continuously changes, resulting in a circular trajectory.
What role does tangential speed play in circular motion?
-Tangential speed is the speed of an object moving along the tangent to the circle at any given point. It depends on the distance from the center of the circle; objects further away have higher tangential speeds.
How is centripetal acceleration defined?
-Centripetal acceleration is the acceleration directed towards the center of the circular path, necessary to change the direction of the velocity vector while maintaining a constant speed. It can be calculated using the formula: a_c = v^2 / r.
What is the relationship between centripetal force and mass?
-Centripetal force is directly proportional to the mass of the object and its centripetal acceleration. It can be expressed with the equation: F_c = m * a_c, or F_c = m * (v^2 / r).
What happens to an object if the centripetal force is removed?
-If the centripetal force is removed, the object will move in a straight line along the tangent to the circular path at the moment of release, due to its inertia.
What is the difference between centripetal force and centrifugal force?
-Centripetal force is a real force acting towards the center of the circle, keeping the object in circular motion. In contrast, centrifugal force is not a real force but a perceived effect of inertia, causing objects to appear to be pushed outward when in circular motion.
How does the radius of a circular path affect centripetal acceleration?
-Centripetal acceleration is inversely proportional to the radius of the circular path. A smaller radius results in greater centripetal acceleration for the same tangential speed.
Why is it important to understand angular velocity in circular motion?
-Understanding angular velocity is important because it describes how quickly an object rotates around a circle, providing insight into the relationship between the tangential speed and the radius of the circular path.
What is the significance of inertia in circular motion?
-Inertia is the tendency of an object to maintain its state of motion. In circular motion, inertia causes the sensation of being pushed outward, as the object tries to follow a straight path while being constrained to circular motion.
Can centripetal force take different forms? If so, what are some examples?
-Yes, centripetal force can take various forms, including tension in a string (as in a ball being swung), gravitational force (as for planets in orbit), and static friction (as when a car turns on a curved road).
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)