Methods and Systems of Air Navigation
Summary
TLDRThe video provides an in-depth overview of air navigation, detailing its definition as the method of guiding aircraft from one location to another while monitoring position. It explores various navigation techniques, including pilotage, dead reckoning, radio navigation, GNSS, INS, LORAN, ARNAV, and RNP, each with its own applications and limitations. The video emphasizes the importance of understanding different flight rules, navigation systems, and the impact of external factors on navigation effectiveness. By the end, viewers gain insights into how modern navigation methods enhance safety and efficiency in aviation.
Takeaways
- ✈️ Air navigation is defined as a set of techniques used to determine the position of an aircraft and navigate along a predetermined route.
- 🗺️ The main objectives of air navigation include determining the aircraft's current position, identifying the destination, and calculating the most suitable route, including time and fuel considerations.
- 🌤️ Factors affecting navigation include weather conditions, airspace structure, aircraft performance, terrain, obstacles, and applicable regulations.
- 👀 Visual Flight Rules (VFR) require pilots to navigate using visual references, while Instrument Flight Rules (IFR) allow navigation by cockpit instruments in low visibility.
- 📍 Pilotage is the oldest navigation method, relying on visual landmarks, while dead reckoning calculates position using heading, distance, and time.
- 📻 Radio navigation utilizes ground-based navaids like VOR, DME, NDB, and ILS, and is essential for IFR flights.
- 🌐 Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS), including GPS, GLONASS, and others, provide precise positioning using satellite signals.
- 🌀 Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) operate independently of external signals, using gyroscopes and accelerometers to calculate the aircraft's position.
- 📊 Area Navigation (ARNAV) combines multiple navigation systems to enhance accuracy, while Required Navigation Performance (RNP) allows for curved flight paths.
- ⚙️ Performance-Based Navigation (PBN) sets the standards for ARNAV and RNP operations, focusing on accuracy and integrity in navigation systems.
Q & A
What is air navigation?
-Air navigation is defined as a set of techniques used to determine the position of an aircraft, allowing it to move along a predetermined trajectory, or route.
What are the basic objectives of air navigation?
-The basic objectives are to determine the aircraft's current location, the desired destination, the most suitable route, and the estimated time and fuel required for the journey.
What are the two types of flight rules and how do they differ?
-The two types of flight rules are Visual Flight Rules (VFR), where pilots navigate using visual references, and Instrument Flight Rules (IFR), where navigation is conducted using instruments in the cockpit.
What is pilotage in the context of air navigation?
-Pilotage is the simplest and oldest form of air navigation, relying on the observation of visual landmarks such as cities, rivers, and highways to navigate.
How does dead reckoning complement pilotage?
-Dead reckoning uses calculations of heading, distance, and time between visual reference points to navigate, often employed alongside pilotage during VFR flights.
What is the significance of radio navigation in IFR flights?
-Radio navigation uses ground-based radio navigation aids (NAVAIDs) to assist IFR pilots in determining their positions and navigating routes effectively.
What role does GNSS play in modern air navigation?
-Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) is widely used for both IFR and VFR navigation, relying on satellite signals to determine an aircraft's position accurately.
What are the main components of an Inertial Navigation System (INS)?
-An INS uses gyroscopes and accelerometers to measure the aircraft's acceleration and rotation, allowing it to estimate its position without needing external signals.
What is the purpose of Required Navigation Performance (RNP)?
-RNP is a navigation system that incorporates performance monitoring to ensure accurate navigation and allows aircraft to follow curved paths during flight.
How does Performance-Based Navigation (PBN) enhance air navigation standards?
-PBN establishes specifications and standards regulating the accuracy, integrity, availability, continuity, and functionality requirements of ARNAV and RNP systems, improving overall navigation performance.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
AIR TRAFFIC SERVICES THEORY [ANNEX 11]

Training Module 1 COMPRESSED AIR (FULL)
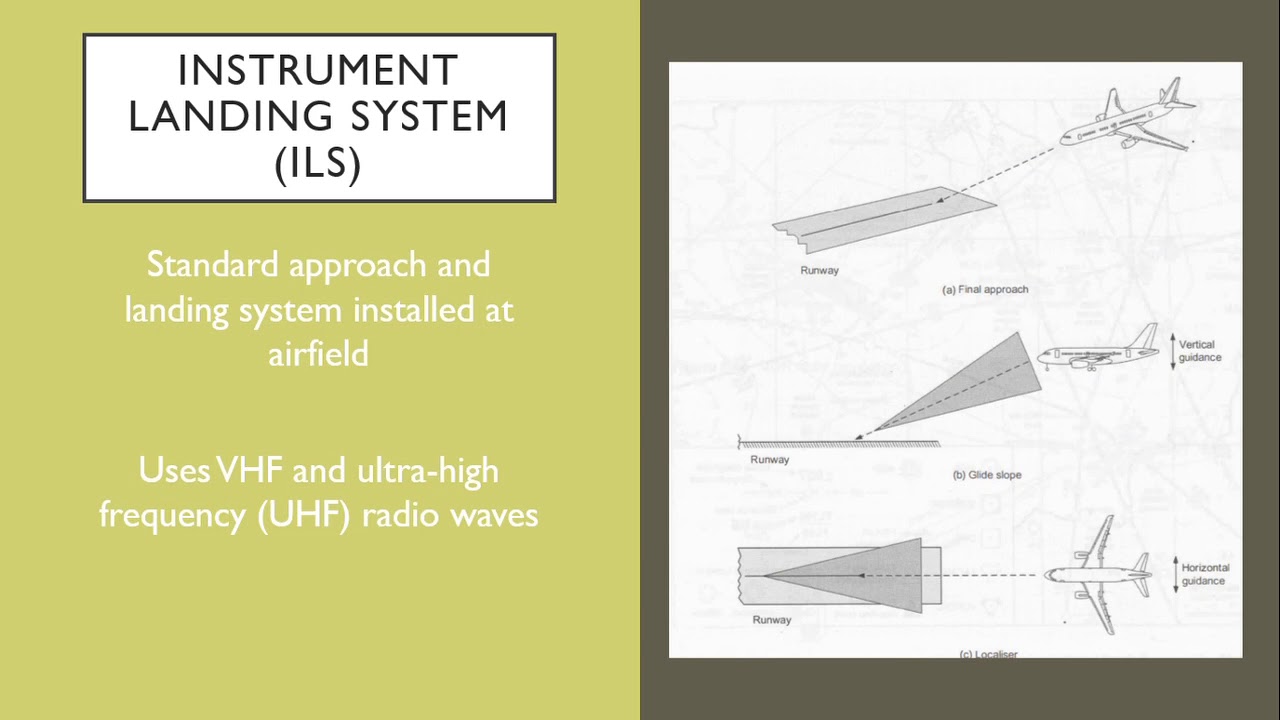
Aircraft Navigation Systems

ATPL Radio Navigation - Class 13: Satellite Augmentation.

BAB 2 PENGINDRAAN JAUH | GEOGRAFI KELAS X| KURIKULUM MERDEKA

Economics | Foreign Trade in India | Chapter 10 | Types of Foreign Trade | Class 12th | Jay Sir |
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
