Aircraft Navigation Systems
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth look at various aircraft navigation systems, explaining their functions and applications. It covers technologies such as Automatic Direction Finder (ADF), Distance Measuring Equipment (DME), Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range (VOR), and Instrument Landing System (ILS), among others. The video highlights satellite navigation (GPS), Doppler and inertial systems, and introduces advanced tools like Microwave Landing Systems (MLS) and Traffic Collision Avoidance Systems (TCAS). Emphasizing the role of air traffic control and these navigation tools, the video showcases their importance in ensuring flight safety and precision in both routine and challenging conditions.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Automatic Direction Finder (ADF) uses radio signals to provide aircraft with position information, relying on low and medium frequencies.
- 😀 The Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range (VOR) determines the direction of an aircraft relative to a fixed location, forming the basis of current airways and navigation charts.
- 😀 Distance Measuring Equipment (DME) works with VOR to provide accurate navigation fixes and enables communication between aircraft and ground stations.
- 😀 The Instrument Landing System (ILS) is designed for precise aircraft positioning during approaches and landings, especially in poor weather conditions.
- 😀 The Microwave Landing System (MLS) offers wider coverage and more reliable performance compared to ILS, with a variety of channels to avoid interference.
- 😀 Hyperbolic Navigation Systems are ideal for long-range navigation over oceans and undeveloped areas, as they do not rely on external inputs.
- 😀 Doppler Navigation measures speed and position through the Doppler shift principle, providing accuracy for long-distance navigation.
- 😀 Inertial Navigation Systems (INS) calculate an aircraft's position based on speed, heading, and acceleration, even without external signals.
- 😀 Satellite Navigation Systems like GPS use satellites to triangulate the aircraft’s position, providing highly accurate location data and supporting terrain mapping.
- 😀 Air Traffic Control (ATC) systems manage the safe separation of aircraft and the flow of traffic around airports, ensuring safe and efficient operations.
Q & A
What was the significance of the advancements in radio technology for aircraft navigation?
-The advancements in radio technology led to the development of radio navigation systems like the automatic direction finder, which helped pilots determine their position using radio signals. These systems paved the way for the current network of airways and navigational charts.
How does the VHF Omnidirectional Range (VOR) system work?
-The VOR system operates using very high-frequency radio signals. It determines the direction of an aircraft relative to the location of a radio station, helping pilots navigate accurately during enroute phases.
What role does Distance Measuring Equipment (DME) play in navigation?
-DME measures the distance between an aircraft and a ground station, allowing for precise navigation fixes. It also enables communication between the aircraft and ground control, contributing to the safety and accuracy of the flight.
What is the difference between the Instrument Landing System (ILS) and the Microwave Landing System (MLS)?
-The ILS is primarily used for precise landings in low-visibility conditions, while the MLS offers wider coverage and better performance in various weather conditions. The MLS can also avoid interference by using multiple channels.
What is hyperbolic navigation, and where is it commonly used?
-Hyperbolic navigation provides long-range coverage and is often installed along coastlines. It enables reliable navigation over vast distances, especially in areas where other systems are not feasible.
How do dead reckoning systems differ from other navigation systems?
-Dead reckoning systems do not require external inputs or signals, allowing for long-distance navigation over oceans and undeveloped areas. This makes them useful in remote locations where other systems may not be available.
What principle does Doppler Navigation use, and what is its purpose?
-Doppler Navigation relies on the Doppler shift principle, which measures the change in frequency of radio waves to determine an aircraft's speed and position, enabling real-time tracking.
What is the Inertial Navigation System (INS), and how does it work?
-The INS is a self-contained navigation system that tracks an aircraft’s position, heading, and speed using accelerometers and gyroscopes. It computes the navigation data without relying on external signals.
How does satellite navigation, specifically GPS, contribute to air navigation?
-Satellite navigation, such as GPS, determines an aircraft's position by triangulating distances from multiple satellites. GPS has become a vital tool for modern aviation, providing highly accurate position data.
What is the purpose of Air Traffic Control (ATC), and how does it ensure safe airspace management?
-ATC manages the flow of traffic around airports and ensures safe separation of aircraft. It uses secondary surveillance radar and other technologies to track and direct aircraft, preventing collisions and optimizing air traffic efficiency.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
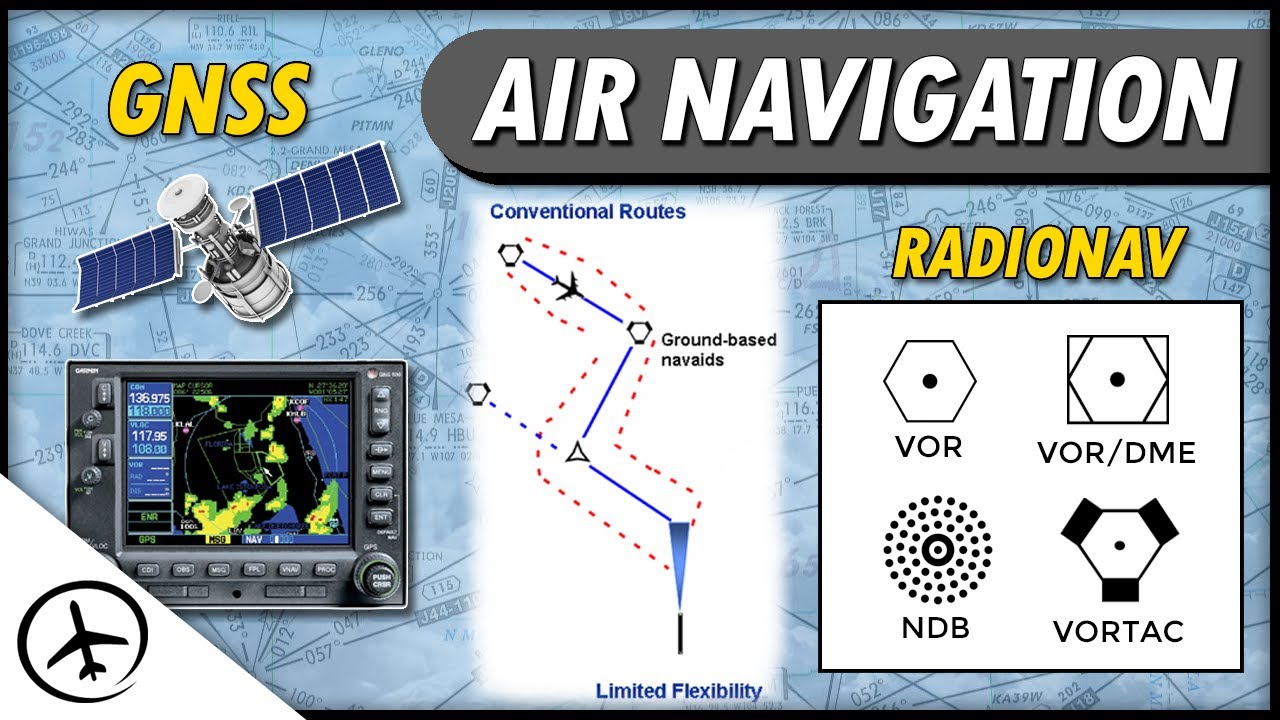
Methods and Systems of Air Navigation

Understanding Aircraft's Communication System | ACARS | Voice & Data | Antennas on an Aircraft!
Centrifugal Pump Basics - How centrifugal pumps work working principle hvacr
Bioreactors | Design, Principle, Parts, Types, Applications, & Limitations | Biotechnology Courses

Airport Secrets: The Mind-Blowing Operation of Qatar Aviation Services

Celbiologie - bouw van de eukaryote cel - HAVO/VWO
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)