Prinsip Kerja dan Fungsi LED
Summary
TLDRIn this informative video, Jason Oh explains the principles and functions of Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). He describes their semiconductor construction, the process of photon emission when forward voltage is applied, and how different materials produce various colors. The video highlights the advantages of LEDs, including energy efficiency, long lifespan, and low heat output, as well as their disadvantages such as higher initial costs. Various types of LEDs, including through-hole, bicolor, and SMD LEDs, are discussed, along with their wide-ranging applications in lighting, displays, and indicators, making LEDs a crucial component in modern technology.
Takeaways
- 💡 LEDs (Light Emitting Diodes) emit monochromatic light when forward voltage is applied.
- 🔌 They are made from semiconductor materials, featuring an anode (positive) and a cathode (negative).
- 🌈 Different colors of LEDs depend on the semiconductor materials used, with specific forward voltage requirements for each color.
- ⚡ LEDs are highly energy-efficient, using 80-90% less energy than traditional incandescent bulbs.
- ⏳ The lifespan of LEDs can reach up to 100,000 hours, significantly longer than other light sources.
- 🌡️ High temperatures can cause electrical malfunctions in LEDs.
- 💰 While the initial cost of LEDs can be higher, their long-term savings in energy and replacement make them cost-effective.
- 🔄 LEDs come in various types, including standard, bicolor, RGB, displays, SMD, and COB, each with unique applications.
- 🏠 LEDs are widely used in household lighting, streetlights, electronic displays, indicators, and remote controls.
- 🔍 Understanding the principles and types of LEDs helps consumers and manufacturers make informed decisions in their usage.
Q & A
What is an LED?
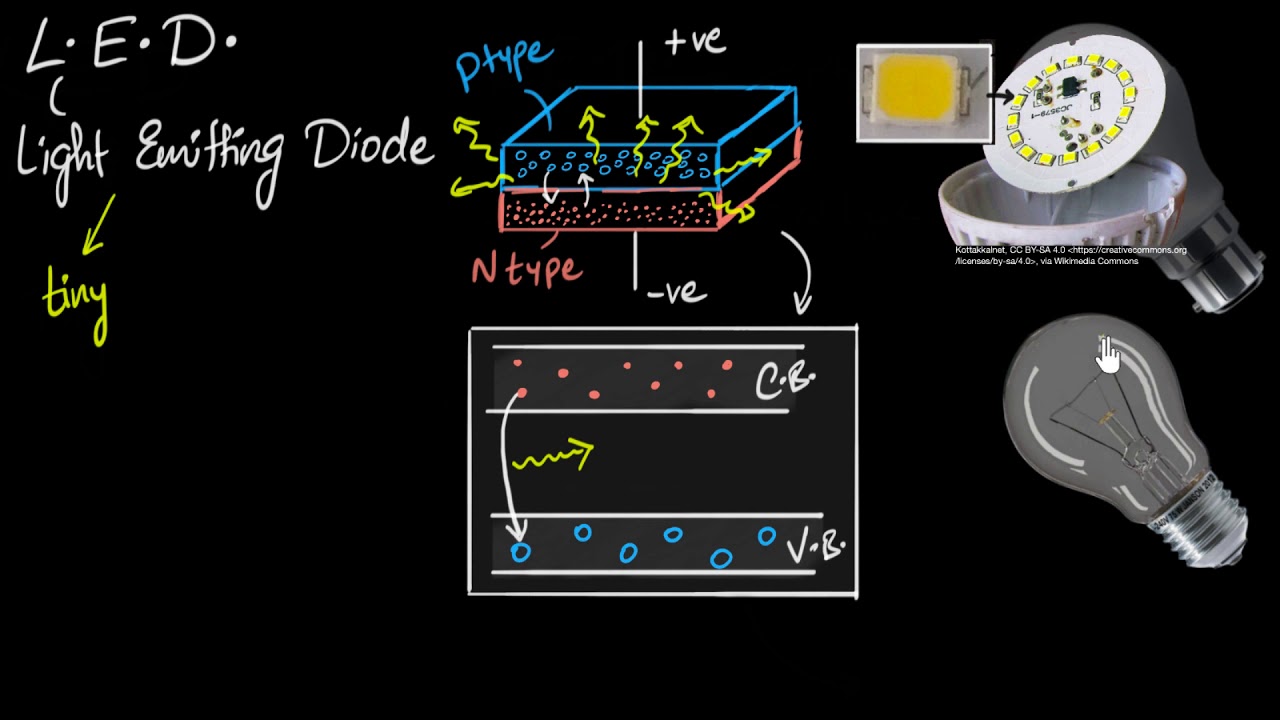
-An LED, or Light Emitting Diode, is an electromagnetic component that emits monochromatic light when a forward voltage is applied.
How does an LED produce light?
-When a forward voltage is applied, electrons move from the n-type semiconductor material to the p-type material, releasing energy in the form of photons when they recombine with holes, resulting in light emission.
What are the main components of an LED?
-An LED consists of two terminals: the anode (positive) and the cathode (negative).
How can you identify the anode and cathode of an LED?
-The anode terminal is usually longer than the cathode, which is often marked with a flat side.
What are some common colors of LEDs, and what materials produce them?
-Common LED colors and their semiconductor materials include infrared (gallium arsenide), red (gallium arsenide phosphide), yellow (gallium phosphide), green (gallium aluminum phosphide), blue (silicon carbide), and white (potassium indium nitride).
What is the typical forward voltage range for different colored LEDs?
-The forward voltage typically ranges from about 1.2 volts for infrared LEDs to around 3.6 volts for blue and white LEDs.
What are the advantages of using LEDs?
-LEDs offer several advantages, including high energy efficiency, long operational life, low operating voltage, minimal heat output, compact size, a variety of colors, and cost-effectiveness.
What are the disadvantages of LEDs?
-Some disadvantages include sensitivity to high temperatures, a higher initial cost compared to traditional lamps, and lower lumen output in some cases.
What types of LEDs are there?
-Types of LEDs include through-hole LEDs, bicolor LEDs, tricolor LEDs, LED displays, surface mount devices (SMD), and chip-on-board (COB) LEDs.
What are some common applications of LEDs in daily life?
-LEDs are used for general lighting, street lighting, advertising boards, LCD backlighting, decorative lighting, indicator lights, and remote control emitters.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

What is LED Light Emitting Diode | How Does LED Works | Electronic Devices & Circuits | Engineering

How LED Works - Unravel the Mysteries of How LEDs Work!
LED working & advantages | Semiconductors | Physics | Khan Academy

LED light Emitting Diode (Unit 3 Special purpose diode and Transistors) in हिन्दी

Light Emitting Diode (LED) Explained (Working, Advantages and Types of LED Explained)

(Nanorush 2024) How LEDs are Made : The Journey from Start to Bright!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
