Light Emitting Diode (LED) Explained (Working, Advantages and Types of LED Explained)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, viewers will explore the fascinating world of Light Emitting Diodes (LEDs). The video covers the advantages of LEDs, including energy efficiency, long lifespan, and fast switching capabilities. It also dives into how LEDs work, using a PN junction to emit light when current flows through. Different types of LEDs such as through-hole, SMD, high-power, COB, and RGB are explained. Additionally, the video discusses LED specifications like forward voltage, luminous intensity, and viewing angle. This comprehensive guide will help viewers understand how LEDs work, their various types, and their applications in everyday technology.
Takeaways
- 😀 LEDs are widely used in electronic devices like smartphone displays, cameras, LED TVs, streetlights, and traffic signals.
- 😀 LEDs are more energy-efficient and have a longer lifespan compared to conventional bulbs.
- 😀 LEDs can operate in fast-switching applications and their brightness can be easily controlled.
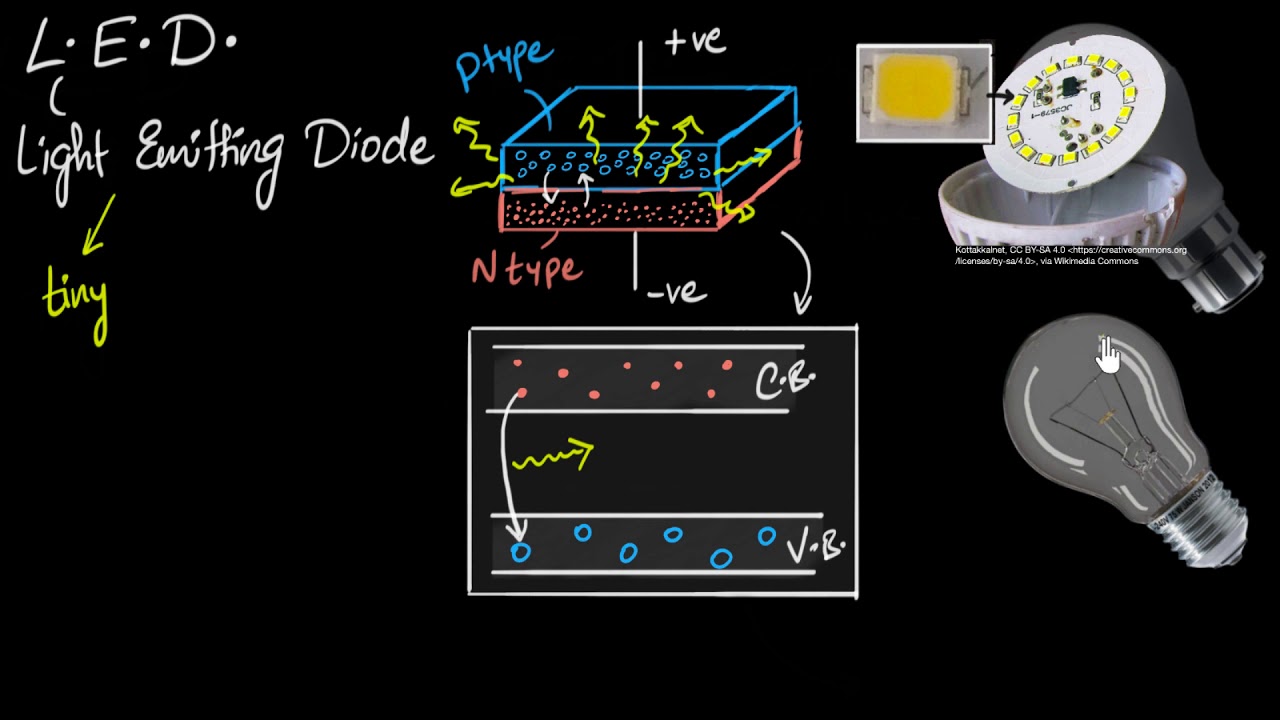
- 😀 LEDs work by emitting light when current flows through them in the forward direction, similar to a PN junction diode.
- 😀 The energy released during electron-hole recombination in LEDs is emitted as light, unlike regular diodes where energy is released as heat.
- 😀 The color of the emitted light in an LED is determined by the bandgap of the semiconductor material used.
- 😀 The forward voltage drop of an LED is higher than that of a regular PN junction diode, ranging from 1.8V to 3.5V.
- 😀 A series resistor is essential to limit the current through an LED to prevent damage.
- 😀 Important LED specifications include current, forward voltage, wavelength, luminous intensity, and viewing angle.
- 😀 Different types of LEDs include through-hole LEDs, SMD LEDs, high-power LEDs, COB LEDs, RGB LEDs, and alphanumeric LEDs.
Q & A
What are some common uses of LEDs in electronic devices?
-LEDs are commonly used in smartphone displays, camera flashlights, LED TVs, lighting for homes and offices, street lights, traffic signals, and display boards.
What are the main advantages of using LEDs for lighting?
-LEDs are more energy-efficient than conventional bulbs, have a longer lifespan, can operate in fast switching applications, are smaller in size, and offer better controllability, including easy brightness adjustment.
How does an LED emit light?
-When current flows through an LED in the forward direction, electrons and holes recombine, releasing energy in the form of light instead of heat, which is different from a typical PN junction diode.
What is the difference in energy release between a normal PN junction diode and an LED?
-In a normal PN junction diode, energy is released in the form of heat, while in an LED, energy is released as light (photons) due to the use of different semiconductor materials like GaAs and GaP.
How does the energy band gap affect the color of light emitted by an LED?
-The energy band gap determines the wavelength of the emitted light, and by modifying the band gap through engineering, the color of the emitted light can be changed. The energy of the photon emitted is directly related to the band gap.
What are the key electrical characteristics of an LED?
-The key electrical characteristics of an LED are similar to a PN junction diode but with a larger forward voltage drop, which can range from 1.8V to 3.5V depending on the LED's emitted color.
Why is a series resistor necessary when using an LED?
-A series resistor is necessary to limit the current flowing through the LED, preventing it from being damaged by excessive current, as the current flowing through the LED can become very high without one.
What does the 'Luminous Intensity' specification in an LED datasheet mean?
-Luminous Intensity defines the brightness of the LED at a specific current, measured in millicandela (mcd). It is an important specification when selecting an LED for specific applications.
What is the significance of the viewing angle in an LED?
-The viewing angle defines the spread of light emitted from the LED. It indicates the angle at which the light intensity drops to 50% of its maximum value, helping to understand the directionality of the LED's emission.
What are the different types of LEDs mentioned in the video?
-The video mentions several types of LEDs, including through-hole LEDs, SMD (Surface Mount Devices) LEDs, high-power LEDs, COB (Chip On Board) LEDs, RGB LEDs, and alphanumeric LEDs.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

What is LED Light Emitting Diode | How Does LED Works | Electronic Devices & Circuits | Engineering

(Nanorush 2024) How LEDs are Made : The Journey from Start to Bright!
LED working & advantages | Semiconductors | Physics | Khan Academy

How LED Works - Unravel the Mysteries of How LEDs Work!

LED light Emitting Diode (Unit 3 Special purpose diode and Transistors) in हिन्दी

Prinsip Kerja dan Fungsi LED
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)