Ginjal: Anatomi dan Fisiologi | Ilmu Biomedik Dasar | Brainy Panda
Summary
TLDRThis educational script offers a detailed exploration of the kidneys' role in filtering blood. It explains how the kidneys remove excess substances and toxins through a complex process involving the nephrons, the functional units of the kidney. The script delves into the anatomy of the kidney, highlighting structures like the renal cortex, medulla, and the nephron itself. It describes the filtration process in the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule, where blood is filtered into the renal tubules. The journey of the filtrate through the tubules, including the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, and collecting duct, is outlined, detailing the reabsorption of essential substances and the concentration of urine. The script concludes with the final product—urine—being transported out of the body, emphasizing the kidney's vital function in maintaining homeostasis.
Takeaways
- 💧 The primary function of the kidneys is to filter the blood and remove unnecessary or excess substances.
- 🌀 Kidneys maintain the balance of substances in the blood by filtering out waste and retaining necessary components.
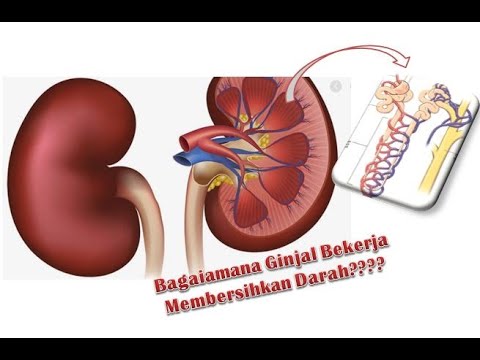
- 🔎 The outer layer of the kidney is called the renal capsule, which resembles a thin medicine capsule.
- 🏗️ Beneath the renal capsule, the kidney is divided into the renal cortex and the renal medulla.
- 🔬 The basic functional unit of the kidney is the nephron, which performs all the essential functions of the kidney.
- 🧐 Each kidney contains approximately one million nephrons, distributed throughout the cortex and medulla.
- 🌐 Blood enters the nephron through the afferent arteriole and is filtered in the glomerulus.
- 🩸 The filtration process in the glomerulus allows small molecules to pass through while retaining larger molecules like proteins and blood cells.
- 💧 The filtrate, which is the fluid that has passed through the glomerulus, contains small molecules that will eventually form urine if not reabsorbed.
- 🔄 The proximal convoluted tubule is where most of the reabsorption of useful substances like glucose and amino acids back into the bloodstream occurs.
- 🌡️ The loop of Henle plays a crucial role in concentrating the urine by adjusting the medulla's salt concentration, which affects water reabsorption.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the kidneys?
-The primary function of the kidneys is to filter the blood and remove unnecessary or excess substances, maintaining the balance of chemicals in the body.
How does the kidney filter blood?
-Blood is filtered by the kidneys through a process involving the glomerulus, where high pressure pushes blood towards the Bowman's capsule, allowing small components to pass through while retaining larger molecules like blood cells and proteins.
What is the Bowman's capsule and its role in the kidney?
-The Bowman's capsule is a cup-shaped structure surrounding the glomerulus. It collects the filtered fluid, known as the filtrate, which then moves through the nephron for further processing.
What are nephrons and how many are there in a kidney?
-Nephrons are the functional units of the kidney, each performing the task of filtering blood and producing urine. There are approximately one to two million nephrons in each kidney.
What is the role of the renal cortex and medulla in the kidney?
-The renal cortex is the outer layer of the kidney where filtration begins, while the renal medulla is the inner part where the concentration of urine takes place. The medulla is crucial for the reabsorption of water and the concentration of urine.
What is the function of the proximal convoluted tubule in the nephron?
-The proximal convoluted tubule is responsible for the reabsorption of important substances such as glucose and amino acids back into the bloodstream, ensuring they are not lost in the urine.
Can you explain the role of the loop of Henle?
-The loop of Henle plays a critical role in the concentration of urine. It has an ascending limb that removes salt from the filtrate, making the medulla hypertonic, and a descending limb that allows water to be reabsorbed, helping to concentrate the urine.
What substances are filtered out of the blood by the glomerulus?
-The glomerulus filters out small molecules such as water, ions, glucose, and urea from the blood, while retaining larger molecules like proteins and blood cells.
How does the kidney maintain the body's electrolyte balance?
-The kidney maintains electrolyte balance by selectively reabsorbing or secreting ions like sodium, potassium, and chloride through various segments of the nephron, adjusting the concentration in the blood.
What is the final product of the nephron and where does it go?
-The final product of the nephron is urine, which contains waste products and excess substances. Urine travels through the collecting duct, into the renal pelvis, then the ureter, bladder, and finally exits the body through the urethra.
Why is the kidney's function critical for overall body health?
-The kidney's function is critical for overall body health because it filters waste products and excess substances from the blood, regulates electrolyte balance, maintains acid-base balance, and produces hormones that help control blood pressure and stimulate red blood cell production.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Urinary System | Structure, Function, Plastinated Kidney and Bladder, 3D Model

Fungsi dan Struktur Ginjal (Animasi)

Excretory Products & Elimination FAST One SHOT!🔥 | Full Revision in 20 Min | NCERT | Class 11 | NEET
Bagaimana cara kerja ginjal dalam menyaring darah???

The Human Kidney: Anatomy and Physiology

Metabolism | Gluconeogenesis
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
