How to Calculate a Correlation (and P-Value) in Microsoft Excel
Summary
TLDRThis video tutorial demonstrates how to calculate the significance of a correlation coefficient in Microsoft Excel, which doesn't provide p-values directly through its correlation function. The workaround involves using the regression tool to obtain the p-value. The presenter guides viewers through selecting the correct ranges for input Y and input X, running the regression, and finding the p-value from the ANOVA table. The video concludes with a discussion on interpreting the p-value to determine the statistical significance of the correlation between hours studied and exam grades.
Takeaways
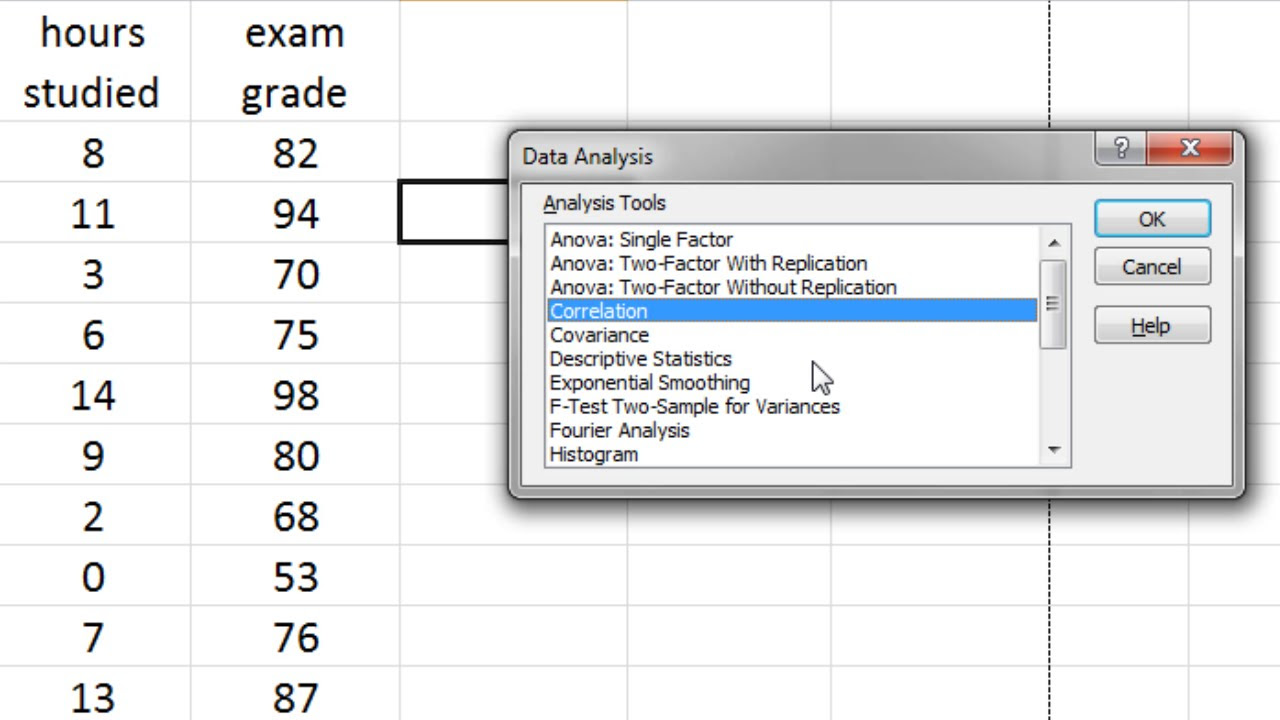
- 😕 Microsoft Excel's Data Analysis Toolpak does not provide a p-value for correlation analysis, making it difficult to assess statistical significance.
- 🔍 A workaround is to use regression analysis in Excel to obtain the p-value, which helps determine the significance of the correlation.
- 📊 For input Y range, select the dependent variable (exam grades), and for input X range, select the independent variable (hours studied), including their labels.
- 📈 In a simple regression with two variables, the multiple R value is equivalent to the Pearson correlation coefficient (r).
- 📉 The p-value can be found in the ANOVA table under 'significance' and is also identical to the p-value under the independent variable in the regression output.
- 🔑 An alpha level of 0.05 is used as the threshold for statistical significance; if the p-value is less than 0.05, the correlation is considered significant.
- 📝 The script demonstrates that a correlation coefficient of .86 is statistically significant, indicating a strong positive relationship between study hours and exam grades.
- 📋 The results are reported with the Pearson's r value, degrees of freedom (df = N - 2), and the p-value (less than .001 or less than .05, depending on the context).
- 📖 The video concludes by showing how to interpret and report the p-value in the context of a correlation analysis using Excel's Data Analysis Toolpak.
Q & A
What is the issue with using Microsoft Excel's Data Analysis Toolpak to calculate correlation?
-The issue is that it does not provide a p-value, which is necessary to assess whether the correlation is statistically significant.
How can we obtain a p-value for correlation in Excel?
-We can obtain a p-value by using the regression feature in Excel, as it provides a p-value that can be used to assess the statistical significance of the correlation.
What are the two boxes in the regression input that need to be filled out?
-The two boxes are 'Input Y range' for the dependent variable and 'Input X range' for the independent variable.
Why is it important to include the variable names when selecting the ranges for regression in Excel?
-Including the variable names ensures that the correct data is being analyzed and helps in interpreting the results accurately.
What is the relationship between 'Multiple R' and 'Pearson r' when there are only two variables?
-When there are only two variables, 'Multiple R' is identical to 'Pearson r', indicating the correlation between the two variables.
Where can the p-value be found in the regression output in Excel?
-The p-value can be found in the ANOVA table under 'significance' and also under the 'p-value' for the independent variable in the regression output.
What is the decision rule for determining statistical significance when using an alpha of .05?
-If the p-value is less than .05, the correlation is considered statistically significant.
What does a p-value of .0001 indicate about the correlation between hours studied and exam grades?
-A p-value of .0001 indicates that there is a statistically significant positive relationship between hours studied and exam grades.
How is the degrees of freedom (df) calculated in this context?
-The degrees of freedom (df) is calculated as N minus 2, where N is the number of observations.
Why is it acceptable to report 'p < .05' even if the actual p-value is less than .001?
-Reporting 'p < .05' is acceptable because the alpha level used for the test is .05, and any p-value below this threshold indicates statistical significance.
What is the practical limit for reporting p-values in written results?
-The practical limit for reporting p-values is typically 'less than .001', as p-values usually do not get reported smaller than this value.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

How To Perform A Pearson Correlation Test In Excel
How to Calculate a Correlation in Microsoft Excel - Pearson's r

Regresi linear, koefisien korelasi dan koefisien determinasi, by Top Mat

La régression linéaire, quelques explications
CORRELATION || MATHEMATICS IN THE MODERN WORLD
[Tagalog] Pearson (r) Product Moment Correlation Coefficient - Computation and Interpretation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
