Power Diode Recovered Charge(Qr) & Reverse Recovery Time(trr) || Diode Switching Loss Explanation
Summary
TLDRIn this educational lecture, the presenter delves into the concept of stored charge and reverse recovery in diodes. They explain the functioning of a diode under forward and reverse bias, highlighting the role of minority charge carriers and junction capacitance. The lecture further discusses the process of removing stored charges and the significance of reverse recovery time (tRR). It explores power loss in diodes due to stored charges and reverse recovery, and contrasts different types of diodes, such as the IN4007 and SBD, in terms of their reverse recovery characteristics.
Takeaways
- 🔌 Diodes function by allowing current flow when forward-biased and blocking current when reverse-biased.
- 🌊 The depletion region in a diode expands when reverse-biased, which helps to block current flow.
- ⚡ The process of removing stored charges in a diode's junction capacitance is crucial for its operation.
- 🕒 Reverse recovery time (tRR) is the time it takes for a diode to remove all stored charges and become capable of blocking reverse voltage.
- 📉 The waveform of voltage and current across a diode can illustrate the diode's behavior during forward and reverse bias conditions.
- 🔋 The stored charge in the junction capacitance affects the diode's ability to block reverse voltage, which is significant for its performance.
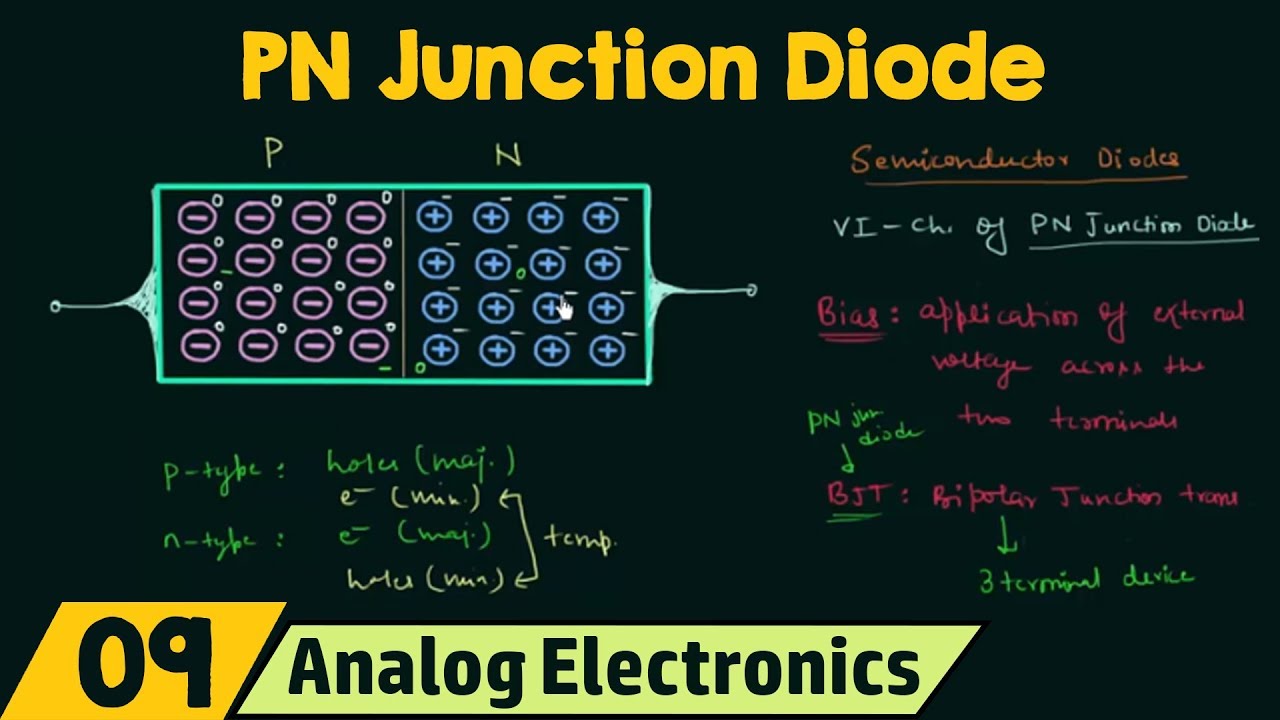
- 💡 The minority charge carriers' diffusion from the P-region to the N-region and vice versa is key to the diode's conduction.
- 🔗 The slope of the current during the diode's operation influences the diode's charge and discharge dynamics.
- 🛑 The removal of stored charges is achieved by applying a reverse voltage, which initiates the reverse recovery process.
- 📚 Different types of diodes, such as Schottky or standard silicon diodes, have varying reverse recovery times and stored charge characteristics.
Q & A
What is the main topic of the lecture?
-The main topic of the lecture is the stored charge and reverse recovery in diodes, including power loss due to stored charges and the concept of reverse recovery time (t_rr) in diodes.
What happens when a diode is forward biased?
-When a diode is forward biased, the depletion region reduces, allowing current to flow through it due to the diffusion of minority charge carriers from the P region to the N region and vice versa.
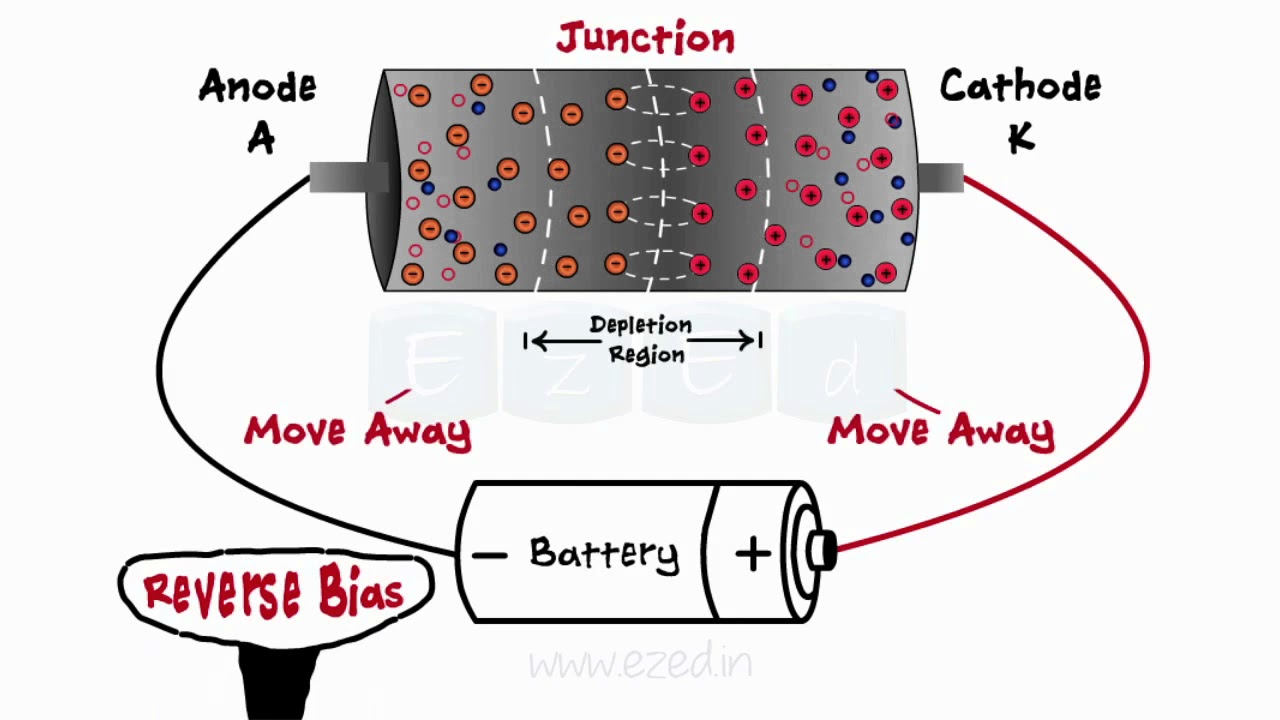
How does the depletion region change when a diode is reverse biased?
-When a diode is reverse biased, the depletion region spreads towards the PN junction, and the minority carrier charges are pulled out, preventing current flow until the diode is capable of blocking the reverse voltage.
What is meant by stored charge in a diode?
-Stored charge in a diode refers to the minority charge carriers that accumulate at the junction capacitance when the diode is forward biased.
What is reverse recovery?
-Reverse recovery is the process of removing the stored charges from the junction capacitance when the diode transitions from forward bias to reverse bias.
How is the reverse recovery time (t_rr) defined?
-The reverse recovery time (t_rr) is the time required for a diode to remove all stored charges and block the applied reverse voltage after transitioning from forward bias to reverse bias.
What is the significance of the current slope during reverse recovery?
-The current slope during reverse recovery is significant as it determines the rate at which the stored charges are removed and the diode's ability to block the reverse voltage.
What are the power losses in a diode during reverse recovery?
-Power losses in a diode during reverse recovery include conduction losses when the diode is forward biased and switching losses when the diode transitions to reverse bias.
Why is it important to know the reverse recovery time for diodes?
-Knowing the reverse recovery time is important because it affects the efficiency and performance of circuits, especially in applications involving fast switching.
How do different types of diodes compare in terms of reverse recovery time?
-Different types of diodes have different reverse recovery times. For example, Schottky diodes typically have faster reverse recovery times compared to silicon diodes, which is an important consideration in high-speed switching applications.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)