How Mountains Are Formed
Summary
TLDRThis script explores the fascinating process of mountain formation on Earth. It delves into the role of tectonic plates and their movement over magma, which leads to the creation of mountains. The video outlines three primary types of mountains: volcanic, formed by magma and lava flows; fold, resulting from the bending and warping of the Earth's crust at convergent plate boundaries; and block, created by the uplift and subsidence of Earth's crust along fault lines. The script provides a comprehensive look at how these geological processes shape our planet's landscape.
Takeaways
- ⛰️ Mountains are formed by the movement within the Earth's crust, which is composed of tectonic plates.
- 🌋 Volcanic mountains are created by magma rising to the surface and volcanic eruptions that build up over time.
- 🔥 There are two types of volcanic mountains: cones and shield mountains, formed by different eruption patterns.
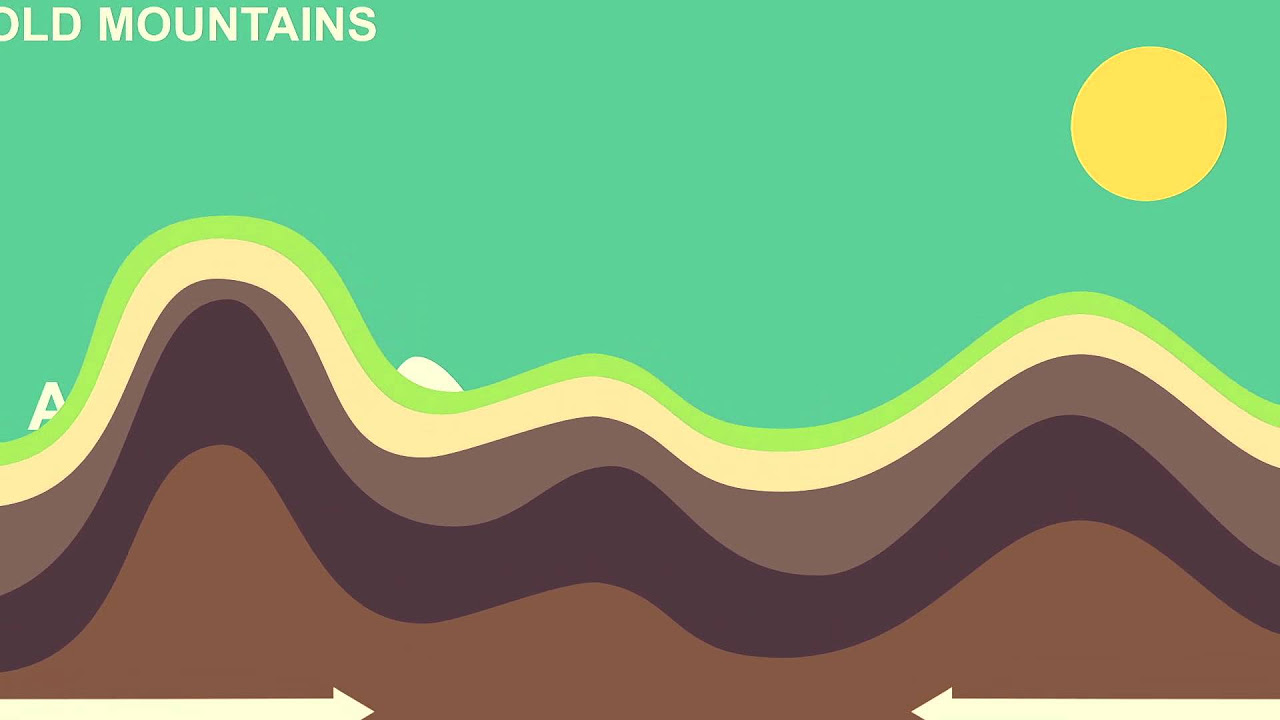
- 🏞️ Fold mountains are formed when tectonic plates meet at convergent boundaries, causing the Earth's crust to bend and fold.
- 📏 Block mountains are formed when tectonic plates create faults, leading to the uplift of one block and the sinking of another.
- 🌌 The Great Rift Valley is a prime example of block mountain formation, stretching from Lebanon to Mozambique.
- 🌍 The movement of tectonic plates, although slow and often imperceptible to humans, has significant impacts on the Earth's surface.
- 🌋 Volcanic activity is characterized by magma rising and lava flows, which contribute to mountain formation.
- 🏔️ The three types of mountain ranges are volcanic, fold, and block, each with distinct formation processes.
- ⏳ Mountain formation is a gradual process that can occur over thousands to millions of years due to continuous tectonic activity.
Q & A
What causes the formation of mountains?
-Mountains are formed by the movement within the Earth's crust, specifically by the movement of tectonic plates which shift and collide over time.
What are tectonic plates?
-Tectonic plates are large, free-floating chunks of the Earth's crust that move within molten rock called magma.
How do humans typically experience the movement of tectonic plates?
-Humans usually do not feel the movement of tectonic plates as they are very slow and the plates are so large.
What are the three types of mountains that can be formed by the movement of tectonic plates?
-The three types of mountains are volcanic, fold, and block mountains.
How are volcanic mountains formed?
-Volcanic mountains are formed in areas of volcanic activity where magma rises to the surface and erupts, creating lava flows and debris that build up around the volcano.
What are the two different ways in which volcanoes form mountains?
-Volcanoes form mountains as either cones or shield mountains, depending on the type of eruption and the way lava flows.
In what type of areas are fold mountains created?
-Fold mountains are created in areas where tectonic plates meet, known as convergent plate boundaries, where the pressure and friction cause the Earth's crust to bend and fold.
How do block mountains form?
-Block mountains form along fault lines or edges of tectonic plates where extreme pressure or gaps cause blocks of earth to move upward or downward, creating rift valleys.
What is the Great Rift Valley, and how is it related to block mountain formation?
-The Great Rift Valley is a geological formation that runs from Lebanon to Mozambique and is an example of block mountain formation, specifically a rift valley.
What is magma and why does it rise to the surface in volcanic mountains?
-Magma is molten rock found beneath the Earth's surface. It is lighter than the solid rock around it, which causes it to rise to the surface, contributing to volcanic mountain formation.
How long does it typically take for mountains to form through tectonic plate movement?
-Mountain formation through tectonic plate movement can take thousands to millions of years, depending on the type of mountain and the rate of plate movement.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)