The Heart and Circulatory System - How They Work
Summary
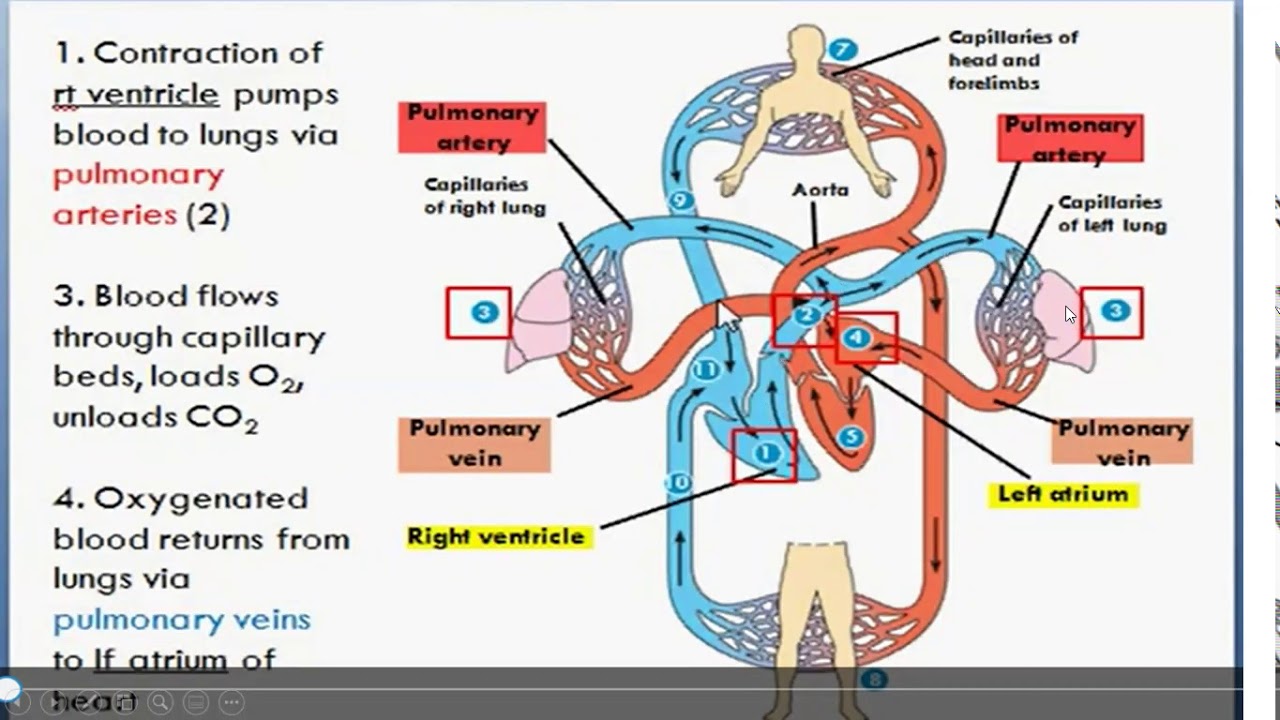
TLDRThe script explains the heart as a muscular pump, roughly the size of a fist, that powers the cardiovascular system. It details the heart's division into right and left sides, ensuring oxygen-rich and poor blood don't mix. The heart pumps about 35 million times a year, with four valves ensuring proper blood flow. Blood nourishes the heart through coronary arteries, and an electrical conduction system coordinates heartbeats, maintaining life-sustaining oxygen exchange.
Takeaways
- 💓 The heart is a muscular organ about the size of a fist, located slightly left of the chest's center.
- 🔄 It is divided into right and left sides to prevent the mixing of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood.
- 🔁 The heart and blood vessels form the cardiovascular system, responsible for circulating blood and oxygen throughout the body.
- 🚀 The heart pumps approximately five quarts of blood every minute and beats around 100,000 times per day.
- 🔴 Oxygen-poor blood returns to the heart and is sent to the lungs to be refreshed with oxygen, turning it red.
- 💧 The left side of the heart, consisting of the left atrium and ventricle, pumps oxygen-rich blood to the body via the aorta.
- 🚪 Four valves within the heart—tricuspid, mitral, pulmonary, and aortic—ensure unidirectional blood flow.
- 🔄 These valves open and close once per heartbeat, allowing blood to flow in the correct direction.
- 📈 The right ventricle contracts slightly before the left, initiating the blood flow to the lungs and body.
- 🌱 The heart is nourished by blood from the coronary arteries, which branch into capillaries to supply oxygen-rich blood.
- ⚡ The heart's electrical system, starting in the right atrium, sends impulses through specialized pathways to coordinate the heartbeat and maintain rhythm.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the heart?
-The primary function of the heart is to pump blood throughout the body, ensuring the circulation of oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs.
How is the heart's size typically described in relation to the human body?
-The heart is a muscular organ about the size of a person's fist, located slightly left of center in the chest.
What does the division of the heart into right and left sides prevent?
-The division of the heart into right and left sides prevents oxygen-rich blood from mixing with oxygen-poor blood, ensuring efficient circulation.
How much blood does the human heart pump every minute on average?
-The human heart pumps about five quarts of blood every minute.
How many times does the heart beat in a day and in a year?
-The heart beats about 100,000 times in one day and approximately 35 million times in a year.
What happens to the blood after it has circulated through the body?
-Oxygen-poor blood, often referred to as 'blue blood,' returns to the heart where it is then sent to the lungs to be oxygenated.
Which side of the heart is responsible for pumping blood to the lungs?
-The right side of the heart, composed of the right atrium and ventricle, is responsible for pumping blood to the lungs.
What is the role of the aorta in the circulatory system?
-The aorta is responsible for carrying oxygen-rich blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the rest of the body.
How many valves are there within the heart, and what is their function?
-There are four valves within the heart: the tricuspid, mitral, pulmonary, and aortic valves. They function like one-way gates to ensure blood flows in the correct direction.
What is the term for the heart's contraction phase, and what happens during this phase?
-The contraction phase is called systole. During systole, the ventricles contract, forcing blood into the vessels going to the lungs and body.
How does the heart's electrical system contribute to its function?
-The heart's electrical system initiates and coordinates the heartbeat, ensuring a normal rhythm and efficient blood circulation.
How is the heart nourished with oxygen-rich blood?
-The heart is nourished by blood vessels called coronary arteries, which extend over the surface of the heart and branch into smaller capillaries.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)