What Your Brain Is Really Doing When Doing 'Nothing'
Summary
TLDRThe script delves into the default mode network (DMN), a mysterious brain region active during 'rest', which may hold the key to individual identity. It discusses the DMN's role in memory, self-awareness, and social cognition, and its disruption in psychiatric disorders. The script also explores psilocybin's potential in treating neuropsychiatric disorders by altering the DMN, suggesting it contributes to a unified sense of self.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The Default Mode Network (DMN) is a set of brain regions that become active when the brain is 'at rest', comprising about 20% of the brain.
- 🔍 The DMN was discovered through neuroimaging studies, which revealed a pattern of brain activity when subjects were not engaged in active tasks.
- 🧐 The DMN includes regions like the medial prefrontal cortices, posterior cingulate cortex, and angular gyrus, which are associated with emotion, language, and memory.
- 🤔 The network's function was initially mysterious, but research has since implicated it in key cognitive areas, such as memory and self-awareness.
- 📚 The DMN is connected to the hippocampus for the formation and recall of episodic memories, which are autobiographical memories about past experiences.
- 🌐 It also plays a role in semantic memory, which involves general knowledge and the processing of facts, concepts, and language.
- 💭 The network is linked to self-reflection, daydreaming, and mind-wandering, which often involve recalling personal experiences and envisioning the future.
- 🤝 The DMN is connected to social cognition, including thinking about others' thoughts and feelings, which is crucial for social interaction.
- 🔄 The network does not function in isolation but interacts with other brain systems, such as the salience network, which is responsible for attention.
- 🛑 Disruptions in the DMN's normal functioning are implicated in various psychiatric disorders, suggesting a role in mental health conditions.
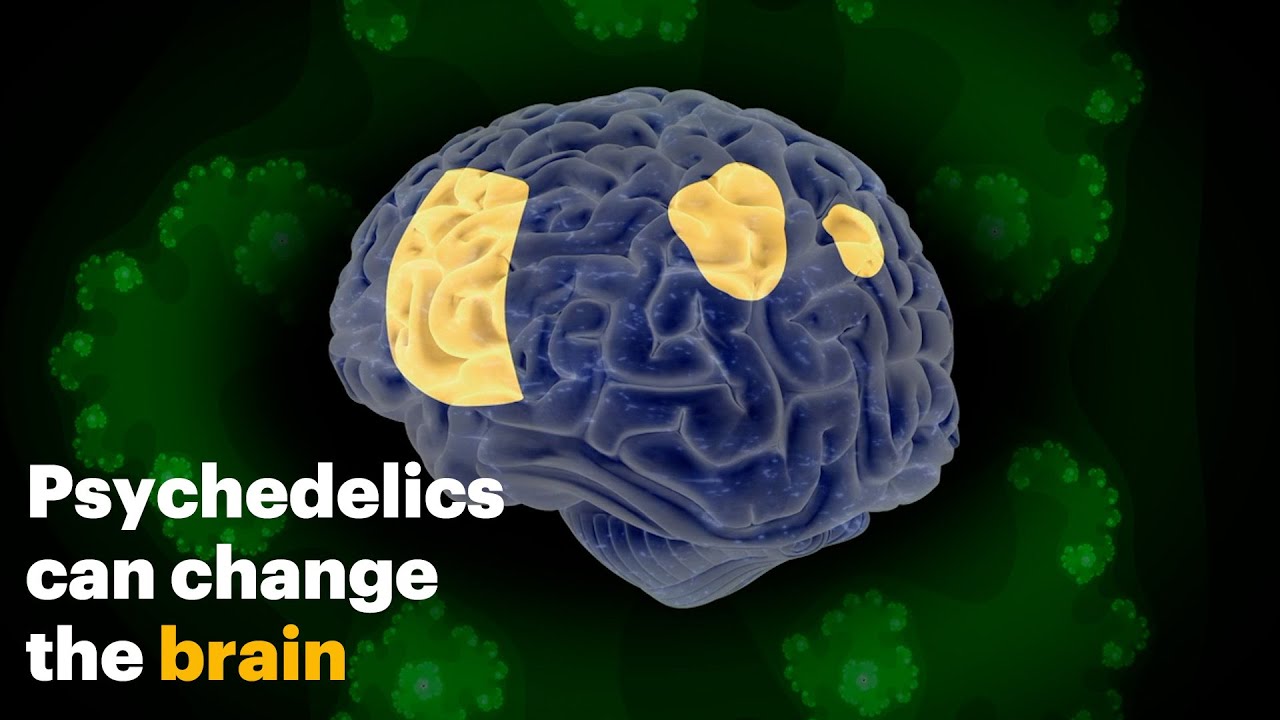
- 🍄 Research on psilocybin, the active component in magic mushrooms, has shown its potential in treating neuropsychiatric disorders possibly by affecting the DMN.
- 🧬 The DMN is thought to contribute to a unifying sense of self by weaving together an internal narrative that shapes self-perception and social interaction.
Q & A
What is the default mode network and why is it significant in understanding the human brain?
-The default mode network (DMN) is a set of brain regions that become active when a person is not focused on the outside world and the mind is at rest. It's significant because it indicates that the so-called resting brain is not idle but engaged in complex internal processes, which may be key to understanding individual uniqueness.
Who invented the electroencephalogram (EEG) and what did it reveal about the brain's activity at rest?
-German psychiatrist Hans Berger invented the EEG in the 1920s. It revealed that even when subjects were at rest, the brainwave patterns changed but did not stop, suggesting that the human brain is never truly inactive.
What did the neuroimaging studies at Washington University discover about the brain's activity during active tasks?
-The studies found a common pattern of deactivated regions, including the medial prefrontal cortices, posterior cingulate cortex, and angular gyrus, when subjects were engaged in active tasks. These regions became active when the mind was at rest, indicating the presence of the default mode network.
How did the term 'default mode' come to describe the resting activity of the brain?
-The term 'default mode' was coined after neuroimaging studies showed that certain brain areas became engaged during rest and disengaged during focused tasks, doing the opposite of what most of the brain does.
What role does the default mode network play in memory processes?
-The DMN is involved in memory processes, particularly episodic memory, which includes the formation and recall of autobiographical memories about past experiences, and prospective memory, which involves thinking about future intentions.
What is semantic memory and how is it related to the default mode network?
-Semantic memory is the general knowledge and understanding of facts, concepts, and language that we have acquired. It is related to the DMN as the network is involved in the processing of this type of long-term memory.
How is the default mode network connected to self-awareness and social cognition?
-The DMN is connected to self-awareness and social cognition through its involvement in thinking about oneself, one's place in society, and the mental states of others, which requires an internal theory of mind.
What happens to the default mode network when the mind is wandering?
-During mind wandering, the DMN turns inward and engages in internally focused thought processes, such as self-reflection, daydreaming, and recalling personal experiences or envisioning the future.
How does the default mode network interact with other brain networks, and what can disruptions in this interaction lead to?
-The DMN interacts with other systems, such as the salience network, which is responsible for switching attention. Disruptions in the normal push and pull between the DMN and other networks can lead to abnormal brain function and may be implicated in psychiatric disorders.
What is the potential therapeutic effect of psilocybin on the default mode network, and how has it been observed in fMRI studies?
-Psilocybin, the active component of magic mushrooms, has shown promise in treating depression and other neuropsychiatric disorders, likely by boosting neuroplasticity. fMRI studies have revealed that psilocybin causes a desynchronization or scrambling of the DMN, leading to temporary changes in brain organization.
What larger question remains about the default mode network, and what is one theory about its overall function?
-The larger question is what the entire default mode network accomplishes. One theory suggests that the DMN is where critical components come together to create a unifying sense of self, enabling us to weave an internal narrative that shapes our perception and interaction with others.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Psychiatrist reacts to: "I have too much self-awareness"

Mastering Your Mind: Controlling the Default Mode Network for Better Mental Health

Neuroscience of Mindfulness Meditation in 4 minutes

How to Rest Your Brain Even When You’re Busy 😮💨

The benefits of daydreaming - Elizabeth Cox
How Psychedelics Change the Brain
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
