Understanding Tides and Datums: LAT, HAT, Mean Sea Level, MHWS, MLWS, MHWN, MLWN
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the science behind tides, their causes, and their significance for mariners. It explores how the gravitational pull of the moon and sun creates periodic rises and falls in sea levels, and explains tidal concepts such as high water, low water, spring tides, and neap tides. The video also introduces key reference datums—Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT), Mean Lower Low Water (MLLW), Highest Astronomical Tide (HAT), and Mean Sea Level (MSL)—and shows how they are used for safe navigation, charting depths, and measuring overhead clearances. By understanding tides and datums, mariners and coastal operators can navigate safely and plan effectively.
Takeaways
- 🌊 Tides are the periodic rise and fall of sea level caused mainly by the gravitational pull of the moon and the sun.
- 🌙 The moon has a stronger effect on tides than the sun due to its closer proximity to Earth.
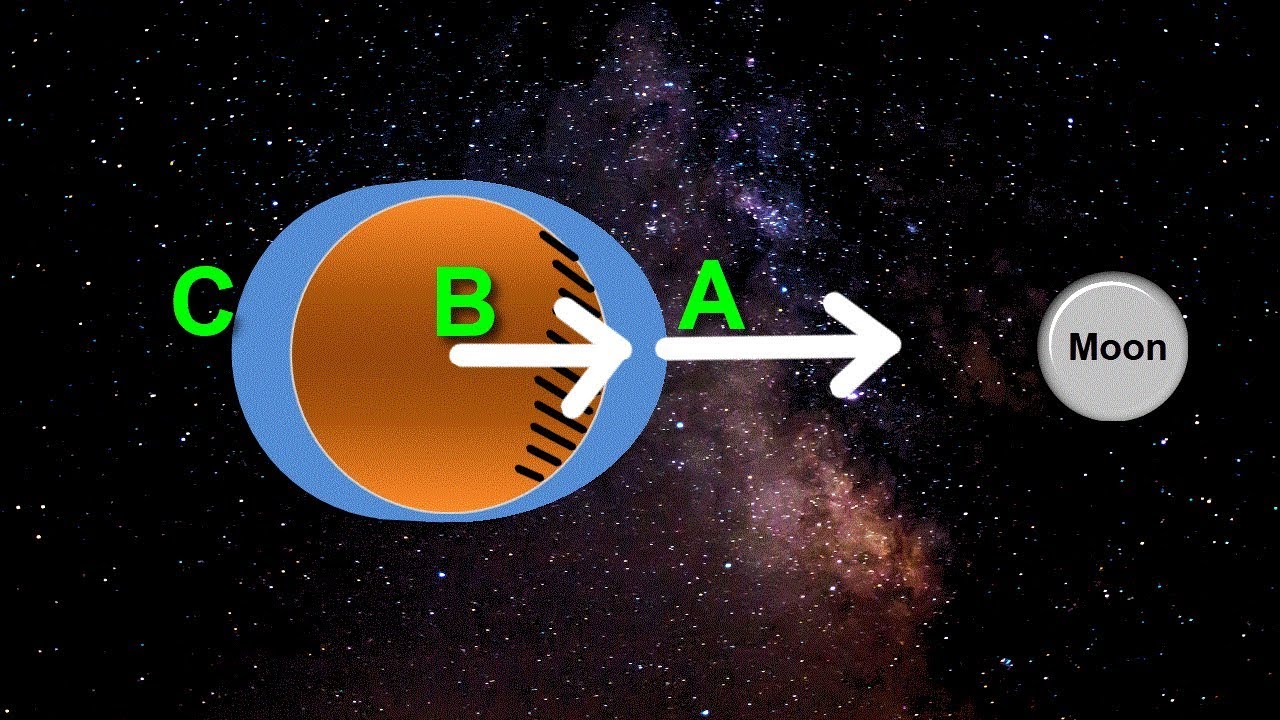
- 🌐 High water occurs at the bulges caused by the moon's gravity, while low water occurs in areas perpendicular to these bulges.
- 📏 Chart datum is a reference water level used for measuring depths, tidal heights, and drying heights on nautical charts.
- ⚓ Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT) represents the lowest predicted tide under normal conditions and is a conservative baseline for navigation.
- 🇺🇸 Mean Lower Low Water (MLLW) is the average of the lower of the two daily low tides over 19 years and is commonly used by NOAA.
- 🌞 Spring tides occur when the sun and moon align, producing the highest high tides and lowest low tides, resulting in the greatest tidal range.
- 🌗 Neap tides occur when the sun and moon are at right angles, producing lower high tides and higher low tides, resulting in the smallest tidal range.
- 🛥️ Highest Astronomical Tide (HAT) is used to measure vertical clearances like bridges and overhead power lines, ensuring safe navigation.
- 📐 Mean Sea Level (MSL) represents the long-term average sea height and serves as a neutral reference point for mapping, engineering, and surveys.
- 🔄 The rotation of Earth causes different locations to experience high and low tides periodically, creating the natural tidal cycle.
- 📊 Nautical charts using LAT show shallower depths for a conservative safety margin, while charts using MLLW display slightly greater depths.
Q & A
What primarily causes tides on Earth?
-Tides are primarily caused by the gravitational pull of the moon, with the sun also contributing to a lesser extent.
Why does the moon have a greater effect on tides than the sun?
-The moon has a greater effect because it is much closer to Earth than the sun, so its gravitational influence on the oceans is stronger.
What is the difference between high high water and low high water?
-High high water refers to the larger ocean bulge closer to the moon, while low high water refers to the smaller bulge on the opposite side of the Earth.
What is a chart datum and why is it important?
-A chart datum is a reference water level used to measure depths, tidal heights, and drying heights on nautical charts. It ensures consistency and safety for navigation.
What is the Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT)?
-LAT is the lowest predicted tide under average meteorological conditions over an 18.6-year period. It serves as a conservative baseline for charting depths.
How does Mean Lower Low Water (MLLW) differ from LAT?
-MLLW is the average of the lower of the two daily low tides over a 19-year period, usually higher than LAT, and is commonly used in U.S. charts by NOAA.
What are spring tides and when do they occur?
-Spring tides occur when the sun and moon's gravitational forces align during the new or full moon, producing higher high tides and lower low tides, resulting in the greatest tidal range.
What are neap tides and when do they occur?
-Neap tides occur when the sun and moon are at right angles during the quarter moon, resulting in lower high tides and higher low tides, producing the smallest tidal range.
What is the Highest Astronomical Tide (HAT) used for?
-HAT represents the highest predicted water level under average conditions and is used to determine safe vertical clearances for bridges, power cables, and other overhead obstructions.
How is Mean Sea Level (MSL) different from LAT and HAT?
-MSL is the long-term average sea surface height, representing a neutral reference point for mapping, engineering, and land surveys, unlike LAT and HAT which represent tidal extremes.
What is a negative surge in tidal terms?
-A negative surge occurs when unusual meteorological conditions, like strong offshore winds or pressure changes, cause sea levels to drop below the Lowest Astronomical Tide.
Why do nautical charts using LAT show shallower depths compared to those using MLLW?
-Because LAT represents a lower baseline than MLLW, charts based on LAT show shallower charted depths, providing a more conservative safety margin for navigation.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)