GCSE Biology Revision "Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes"
Summary
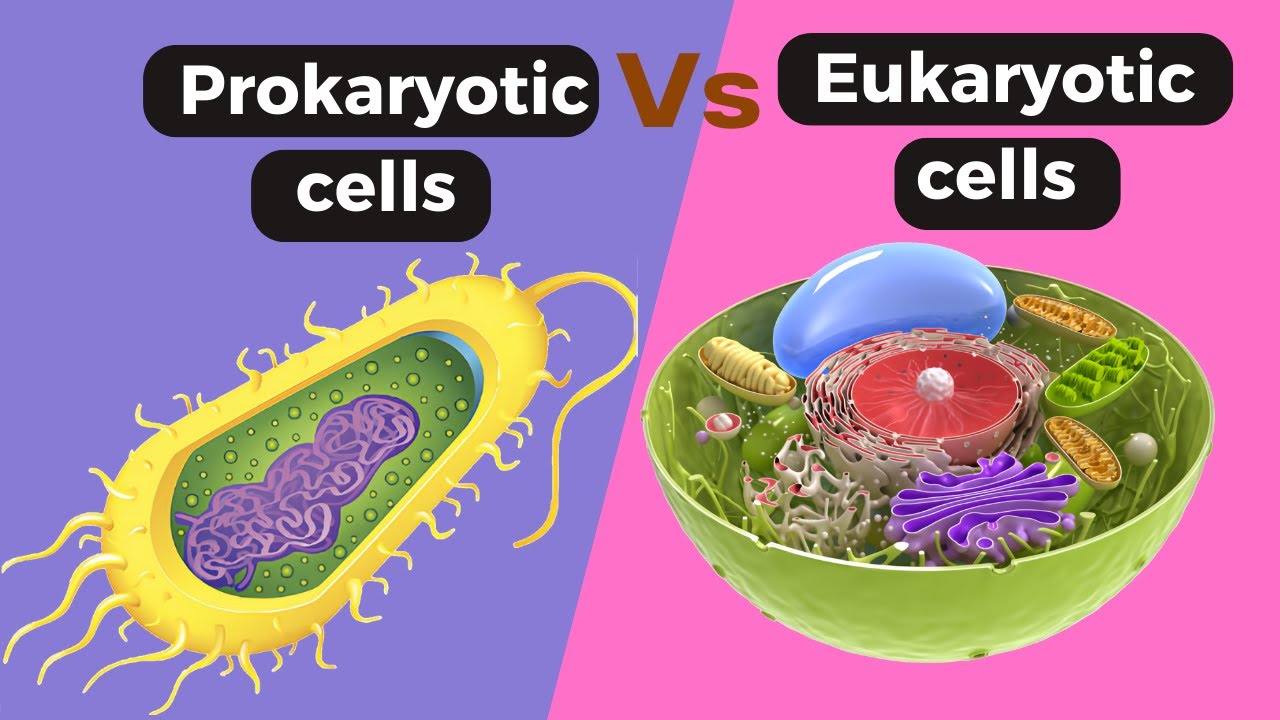
TLDRThis educational video from three sighs lessons introduces the fundamental differences between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. It highlights that eukaryotic cells, such as animal and plant cells, have a nucleus containing DNA, a cell membrane, and cytoplasm. In contrast, prokaryotic cells, like bacteria, lack a nucleus and have their DNA in a single loop, often accompanied by plasmids. They also possess a cell membrane and a cell wall, which is distinct from that of plant cells. The video aims to clarify these distinctions and encourages viewers to explore further through a provided workbook.
Takeaways
- 🧬 The primary distinction between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is the presence of a nucleus in eukaryotic cells, which encloses the genetic material (DNA).
- 📚 Eukaryotic cells are characterized by having their genetic material within a nucleus, a key definition to remember.
- 🔬 Both animal and plant cells are examples of eukaryotic cells, featuring a nucleus, cell membrane, and cytoplasm.
- 🌱 Unlike eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, do not have a nucleus; their genetic material is a single loop of DNA.
- 📏 Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller in size compared to eukaryotic cells.
- 🔬 Bacterial cells, a type of prokaryotic cell, may contain additional small loops of DNA known as plasmids.
- 🏛 Prokaryotic cells possess a cell membrane and a cell wall, which is distinct from the cell wall found in plant cells.
- 🧪 The cell membrane in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells is crucial but should not be confused with the cell wall.
- 🧫 Both types of cells contain cytoplasm, which is the jelly-like substance within the cell membrane.
- 📚 The functions of the cell membrane and cytoplasm will be explored in later videos.
- 📘 There are plenty of questions on eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells available in the accompanying workbook, accessible via the provided link.
Q & A
What is the main difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
-The main difference is that eukaryotic cells have their genetic material enclosed within a nucleus, whereas prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus and their genetic material is not enclosed.
What is the role of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells?
-The nucleus in eukaryotic cells contains the genetic material, in other words, the DNA, of the cell.
What are the three main features of eukaryotic cells mentioned in the script?
-The three main features of eukaryotic cells are the presence of a nucleus, a cell membrane, and cytoplasm.
What is the difference between the cell membrane and the cell wall in prokaryotic cells?
-In prokaryotic cells, the cell membrane is a thin layer that surrounds the cell, while the cell wall is a more rigid structure that provides additional protection and support, especially in bacterial cells.
What is a plasmid in the context of prokaryotic cells?
-A plasmid is a small, circular piece of DNA found in some prokaryotic cells, which is separate from the main genetic material and can carry additional genes.
Why is it important to distinguish between the cell wall of a bacterial cell and a plant cell?
-It is important because the composition and function of the cell wall can vary significantly between different types of cells, and understanding these differences is crucial for studying cell biology.
What is the significance of the cytoplasm in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
-The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance within the cell membrane that contains the cell's organelles and is the site of many cellular processes.
How are eukaryotic cells generally larger than prokaryotic cells?
-Eukaryotic cells are generally larger because they have more complex internal structures, including a nucleus and various organelles, compared to the simpler structure of prokaryotic cells.
What is the purpose of the cell membrane in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
-The cell membrane serves as a barrier that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, maintaining the cell's internal environment.
What resource is mentioned in the script for further study on eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
-The script mentions a vision workbook with plenty of questions on eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells, which can be accessed by clicking on the provided link.
Can you describe the process of learning about the functions of the cell membrane and cytoplasm as mentioned in the script?
-The script suggests that the functions of the cell membrane and cytoplasm will be explored in later videos, indicating a progressive learning approach.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes

Comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells | High school biology | Khan Academy

Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells | Biology | Khan Academy

Perbedaan Sel Prokariotik & Sel Eukariotik | Pembelajaran Daring - Dunia Biologi
Prokaryotic cell Vs Eukaryotic cells|| Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell

Citologia 1/2: Estrutura Básica das Células | Anatomia e etc
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
