Using Design Techniques for Clear and Appealing Data Visualization
Summary
TLDRThis video script emphasizes the importance of creating professional and effective data visualizations. It outlines key design concepts such as balance, white space, patterns, and color choices to enhance readability and clarity. The script also advises on using consistent visual types and minimal text to guide users without overwhelming them. It concludes with practical tips on choosing the right visualization type to accurately convey data, ensuring that the visuals are both appealing and informative.
Takeaways
- 📊 **Balance is Key**: Use alignment, repetition, contrast, hierarchy, symmetry, and intentional imbalance to create readable and organized visuals.
- 📐 **Whitespace**: Utilize white space to reduce clutter and focus on key data points, avoiding information overload.
- 🔍 **Simplicity**: Limit visuals to one per KPI and focus each screen on a specific topic, using interactions for deeper insights.
- 🔄 **Patterns**: Leverage human affinity for patterns to enhance data understanding through consistent color and visual representations.
- 🎨 **Consistent Colors**: Use contrasting colors to differentiate data clearly, and consider color palette tools for harmonious selections.
- 📈 **Consistent Visual Types**: Maintain the same type of visual for the same information to ensure consistency and ease of comparison.
- 📝 **Text Clarity**: Include only enough text to guide users through the data without overshadowing the visuals.
- 🔤 **Font Selection**: Stick to a maximum of two fonts that are easy to read and ensure clear labeling of axes and units.
- 📑 **Data Ordering**: Order data consistently to facilitate quick understanding and comparison.
- 📊 **Choose the Right Visual**: Select the most effective type of visual for the data presented, such as bar charts for comparing quantities.
- 👀 **Visual Test**: Quickly test visuals to ensure they convey the intended information effectively and without confusion.
Q & A
What is the main challenge in creating data visualizations?
-The main challenge is to make visuals that are not only attention-grabbing and easy to read but also clearly convey the intended data, avoiding the pitfall of unreadable chaos.
What is one of the basic design concepts discussed in the script for effective data visualization?
-Balance is one of the basic design concepts discussed, which includes alignment, repetition, contrast, hierarchy, symmetry, and intentional imbalance to enhance the readability and impact of data visualizations.
Why is white space important in data visualization?
-White space is crucial to reduce clutter and chaos, allowing for a clearer presentation of data and making it easier for the viewer to digest the information.
How can we use patterns to our advantage in data visualization?
-Patterns help our brains to quickly understand what we're looking at. Using consistent color patterns to represent the same data across all visuals can leverage this to enhance data comprehension.
What is the recommended approach to using color in data visualization?
-Contrasting colors should be used to clearly distinguish different data sets. It's advised not to overuse colors, and to use shading instead of different colors for multiple bars or lines on a chart.
How should text be used in data visualizations?
-Text should be used sparingly to guide the user through the data without complicating it or drawing attention away from the key information. It should be clear, concise, and placed strategically to enhance understanding.
What is the recommended number of fonts to use in a data visualization?
-It is recommended to use no more than two fonts to maintain readability and consistency, ensuring they are easy to read.
Why is it important to label axes in data visualizations?
-Labeling axes, including units where applicable, is important for providing context and ensuring that the viewer can accurately interpret the data presented.
How can the choice of visual type affect the perception of data?
-The type of visual chosen can greatly affect how data is perceived. For example, bar charts are better for showing differences in size, while pie charts may not effectively convey specific performance details.
What is the purpose of using a quick test with a visual?
-A quick test helps to ensure that the visual is effectively conveying the intended information and that the viewer can quickly grasp the key takeaways from the data presented.
What does the script suggest for improving the appeal and accuracy of data visualizations?
-The script suggests implementing design concepts such as balance, white space, patterns, color use, text placement, and choosing the right type of visual to make data visualizations more appealing and accurate.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
Data Visualization in 2024 | The Ultimate Guide

informatika Kl 8 bab 6 Analisis Data kurikulum Merdeka bag 32 hal 130 137

Projeto em SQL - Como analisar vendas de notebooks usando SQL
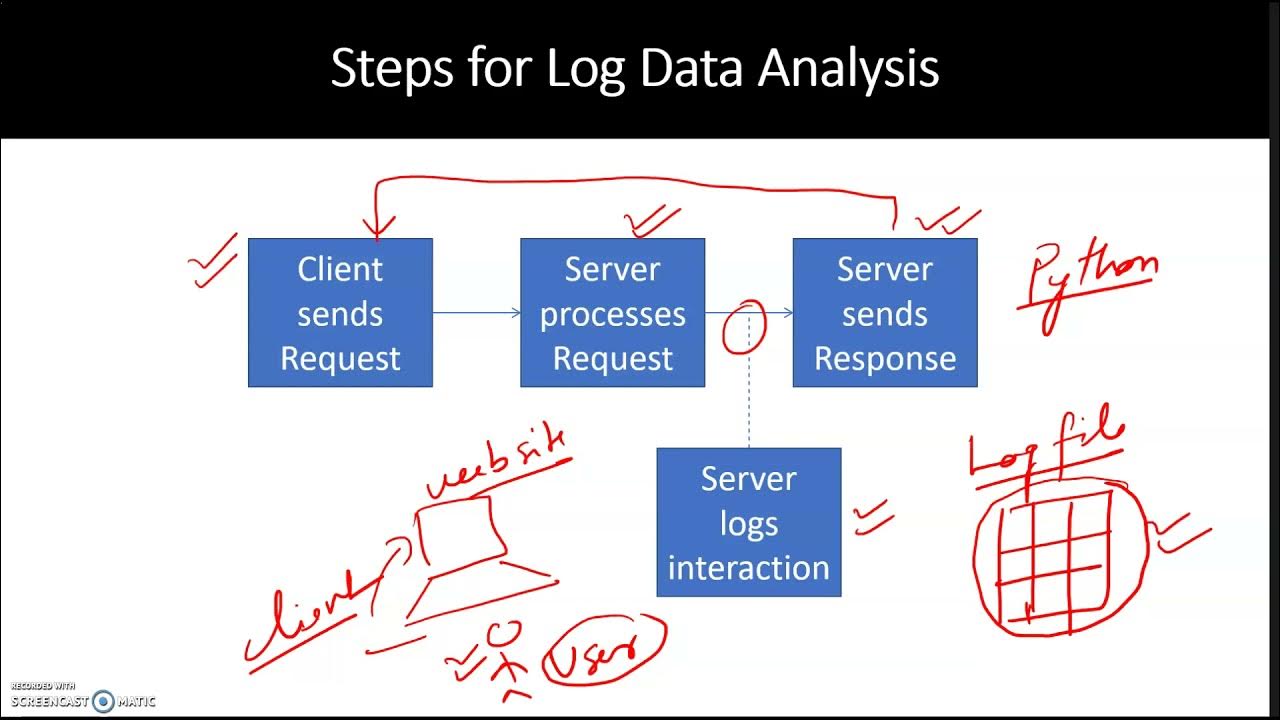
Data Analysis Processing Web Log Data

PSD - Data Visualization Part.02/02

How to use Power Query in Power BI | Microsoft Power BI for Beginners
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
