Ideal Fluid Flow
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker introduces the concept of ideal fluid flow, which involves four key conditions: nonviscous, incompressible, steady, and irrotational flow. Using relatable examples such as maple syrup, ketchup, and the flow of smoke from a candle flame, the speaker explains these concepts in simple terms. The discussion includes the distinction between laminar and turbulent flow, using visual animations to illustrate how fluids move through pipes. The video emphasizes that while real fluids are more complex, starting with ideal fluid flow helps in understanding basic fluid dynamics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Ideal fluid flow assumes that fluids are nonviscous, meaning they have no internal friction.
- 😀 Viscosity refers to a fluid's resistance to flow, with water having low viscosity and ketchup having a higher viscosity.
- 😀 Fluids in ideal flow are considered incompressible, meaning their density remains constant.
- 😀 Steady (laminar) flow is smooth and predictable, while turbulent flow is irregular and chaotic.
- 😀 In ideal fluid flow, the flow is steady, meaning it remains consistent over time without sudden changes.
- 😀 The flow of smoke from a candle flame illustrates both laminar (slow, smooth) and turbulent (fast, irregular) flow.
- 😀 The flow of water in rivers can show laminar flow at the top of waterfalls and turbulent flow at the bottom.
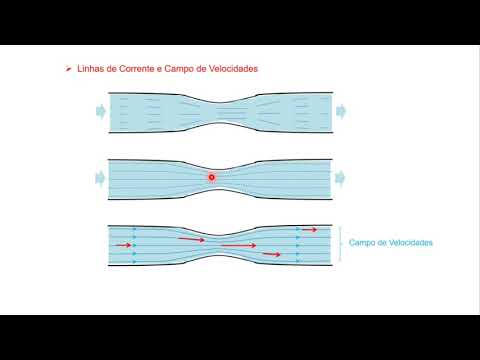
- 😀 Streamlines are used to represent the direction of fluid flow, with the velocity of fluid particles being tangent to the streamlines.
- 😀 Narrowing a pipe results in faster fluid flow, but the reasons behind this will be explored in future lessons.
- 😀 Irrotational flow means that the fluid does not have net angular velocity and does not rotate, which can be shown using a paddle wheel that stays stationary.
- 😀 Ideal fluid flow involves four key conditions: nonviscous, incompressible, steady, and irrotational flow.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video?
-The primary focus of the video is on the concept of ideal fluid flow, explaining its conditions and properties, and providing examples to illustrate these concepts.
What are the four conditions for ideal fluid flow?
-The four conditions for ideal fluid flow are: nonviscous fluid, incompressible fluid, steady (or laminar) flow, and irrotational flow.
What does it mean when a fluid is nonviscous?
-A nonviscous fluid has no viscosity, meaning it does not experience internal friction or resistance to flow. Kinetic energy in a nonviscous fluid is not converted into internal energy.
Can any fluid truly be nonviscous in real life?
-No, in reality, all fluids have some degree of viscosity, but ideal fluid flow assumes zero viscosity for simplification and understanding.
What is viscosity and how does it affect fluid flow?
-Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow or the internal friction between particles. Fluids with higher viscosity, like syrup or ketchup, resist movement more than those with lower viscosity, like water.
What does it mean for a fluid to be incompressible?
-An incompressible fluid has a constant density, meaning its volume doesn't change with pressure. Liquids tend to be incompressible, while gases are compressible.
What is the difference between steady (laminar) flow and turbulent flow?
-Steady (or laminar) flow is smooth, consistent, and predictable, while turbulent flow is irregular, chaotic, and inconsistent, often occurring at higher velocities.
Can you provide an example that demonstrates both laminar and turbulent flow?
-An example is the smoke from a recently extinguished candle. The smoke near the wick shows laminar flow, while the smoke higher up demonstrates turbulent flow. Another example is the flow of water in a river, where the flow at the top of a waterfall is laminar, and at the bottom, it is turbulent.
What are streamlines and how do they help visualize fluid flow?
-Streamlines are lines that represent the direction of fluid flow. In laminar flow, they remain consistent over time, and the distance between them indicates the flow speed: closer lines mean faster flow.
What does it mean for fluid flow to be irrotational?
-Irrotational flow means the fluid has no net angular velocity, meaning it doesn't rotate. If you place a paddle wheel in the fluid, it would not rotate, indicating that the fluid has no rotational motion.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)