What is LED Light Emitting Diode | How Does LED Works | Electronic Devices & Circuits | Engineering
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the working and applications of light-emitting diodes (LEDs). LEDs are optical semiconductor devices that convert electrical energy into light when forward biased, emitting either visible light or infrared light. The process involves free electrons recombining with holes, releasing energy in the form of light. The video explores how LEDs work in detail, explaining the behavior of charge carriers and their recombination at the junction. It also highlights various applications of LEDs, such as in burglar alarm systems, traffic signals, digital computers, and automotive lighting.
Takeaways
- 😀 LEDs are semiconductor diodes that emit light when forward biased, converting electrical energy into light energy.
- 😀 LEDs can emit either visible light or invisible infrared light, with infrared LEDs being used for remote controls.
- 😀 The LED symbol resembles a regular PN junction diode, but with arrows pointing outward, signifying light emission.
- 😀 The most common colors of LEDs are orange, yellow, green, and red.
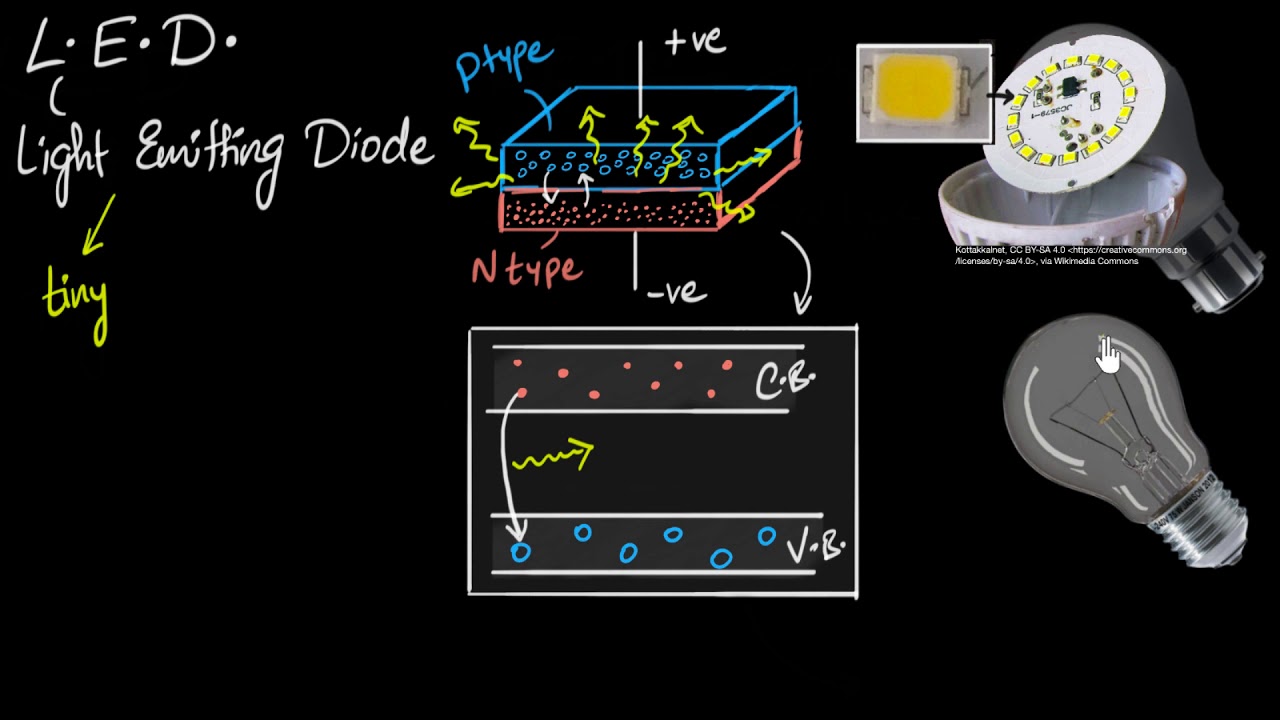
- 😀 LEDs work when forward biased, with free electrons from the N side recombining with holes from the P side in the depletion region.
- 😀 The recombination of electrons and holes in the depletion region results in the release of energy in the form of light.
- 😀 As free electrons and holes recombine, the width of the depletion region decreases, and more charge carriers cross the PN junction.
- 😀 Some free electrons and holes cross the PN junction before recombining in the depletion region, contributing to the emission of light.
- 😀 The light emitted by LEDs comes from the energy released by electrons moving from the conduction band to the valence band.
- 😀 LEDs are widely used in various applications, including burglar alarms, calculators, traffic signals, digital computers, watches, and even aviation lighting.
Q & A
What is a light-emitting diode (LED)?
-A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor device that emits light when electrical energy is applied. It converts electrical energy into light energy, either in the visible or infrared spectrum.
What are the most common colors of LEDs?
-The most common colors of LEDs are orange, yellow, green, and red.
How do LEDs work?
-LEDs work in a forward bias condition, where free electrons from the N-side and holes from the P-side are pushed toward the junction. When they recombine in the depletion region, energy is released in the form of light.
What happens during the recombination process in an LED?
-During recombination, free electrons from the N-side combine with holes from the P-side, releasing energy in the form of light. This recombination takes place in the depletion region, as well as in the P-type and N-type semiconductors.
What is the significance of the depletion region in an LED?
-The depletion region is where the recombination of electrons and holes occurs, and the release of energy in the form of light takes place. As recombination happens, the width of the depletion region decreases, allowing more charge carriers to cross the junction.
Why do free electrons and holes recombine in the depletion region?
-Free electrons from the conduction band recombine with holes in the valence band in the depletion region because the region has a deficit of electrons (positive ions), which are ready to accept electrons.
What is the role of forward bias in the operation of an LED?
-Forward bias in an LED ensures that free electrons from the N-side and holes from the P-side are pushed toward the junction, where recombination and light emission take place.
What applications are LEDs commonly used for?
-LEDs are used in various applications, including burglar alarm systems, calculators, picture phones, traffic signals, digital computers, multimeters, microprocessors, digital watches, automotive heat lamps, camera flashes, and aviation lighting.
What does the symbol of an LED look like?
-The symbol of an LED resembles a regular PN junction diode, but with arrows pointing away from the diode to indicate that light is being emitted.
How does the emission of light occur in an LED?
-The emission of light occurs when free electrons in the conduction band recombine with holes in the valence band, releasing energy as light before they recombine.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

LED light Emitting Diode (Unit 3 Special purpose diode and Transistors) in हिन्दी

How LED Works - Unravel the Mysteries of How LEDs Work!
LED working & advantages | Semiconductors | Physics | Khan Academy

Prinsip Kerja dan Fungsi LED

Light Emitting Diode (LED) Explained (Working, Advantages and Types of LED Explained)

(Nanorush 2024) How LEDs are Made : The Journey from Start to Bright!
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
