Penjelasan Mean Median dan Modus (Center of Point) Biostatistik
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explains key statistical concepts such as mean, median, and mode, commonly referred to as the 'center of point' in data analysis. Using real-world examples like patient visits to a clinic, the video guides viewers through the steps to calculate these measures. It covers how to compute the mean by summing data values, finding the median by identifying the middle value in ordered data, and determining the mode as the most frequent data point. The video is aimed at researchers and students, providing clear explanations and practical applications in data analysis.
Takeaways
- 😀 The concept of the 'Center of Point' or central tendency is essential in biostatistics to summarize and represent a set of data.
- 😀 The three main measures of central tendency are mean (average), median, and mode, each serving different purposes in data analysis.
- 😀 The mean (rata-rata) is calculated by adding all data points together and dividing by the number of data points.
- 😀 The median is the middle value of a dataset when it is ordered; if the dataset has an even number of values, the median is the average of the two middle values.
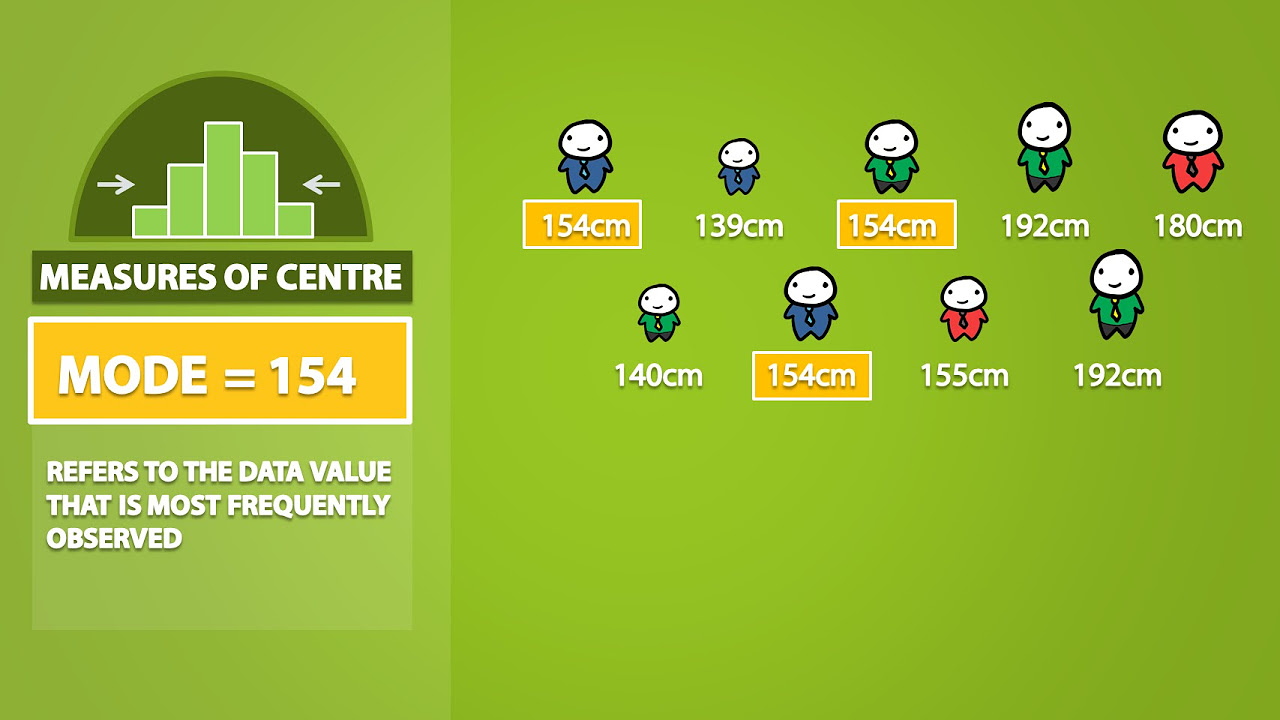
- 😀 The mode is the most frequent value in a dataset, used to identify the most common occurrences in the data.
- 😀 The mean is easy to calculate and widely used, but it can be affected by outliers in the data.
- 😀 The median is useful when dealing with skewed data, as it is less influenced by extreme values.
- 😀 The mode can be absent if no value repeats in the dataset or if the dataset is highly varied.
- 😀 In practical terms, for example, the mean number of patients visiting a clinic per month can be easily calculated by averaging monthly visit numbers.
- 😀 Statistical software like SPSS can be used for more complex calculations of the mean, median, and mode, but understanding manual calculation is also important.
- 😀 It's important to recognize when to use each measure of central tendency based on the data type and research context, as they provide different insights into the data.
Q & A
What is the center of point in biostatistics?
-The center of point, also known as central tendency, refers to a value that represents the center or middle of a dataset. It helps summarize data by identifying a typical or representative value from the dataset.
Why is the concept of center of point important in research?
-It is crucial in research as it helps researchers and students determine central values in data, particularly for categorical variables, which is essential for analyzing and presenting research findings clearly.
What are the main measures of central tendency?
-The three main measures of central tendency are the mean, median, and mode. Each provides a different way of summarizing data, with the mean being the average, the median being the middle value, and the mode being the most frequent value.
How is the mean calculated?
-The mean is calculated by summing all data points and dividing the total by the number of data points. The formula is: Mean = (X1 + X2 + ... + Xn) / N, where N is the total number of data points.
What is the median, and how is it calculated?
-The median is the middle value in a sorted dataset. For an odd number of data points, it is the middle value. For an even number of data points, it is the average of the two middle values. The formula for an even dataset is: Median = (Value at position (N+1)/2 + Value at position N/2) / 2.
What is the mode, and when is it useful?
-The mode is the value that appears most frequently in a dataset. It is useful when identifying the most common occurrence, especially in categorical data where other measures like mean and median may not be as informative.
How does the mean handle changes in data?
-The mean is sensitive to changes in data, meaning that any change in individual data points can affect the overall average. However, the procedure for calculating the mean remains the same regardless of the dataset's size or values.
How do you calculate the mean for monthly patient visits?
-To calculate the mean for monthly patient visits, you would sum the total number of patients across all months and divide by 12 (the number of months in a year). For example, if the monthly patient visits are given, sum all values and divide by 12.
What is the significance of median in biostatistics?
-The median is significant because it is not affected by extreme values (outliers) in the data. It provides a more accurate reflection of the center when data is skewed or contains outliers.
Can the mode be absent in a dataset?
-Yes, the mode can be absent in a dataset if all values appear with equal frequency, or if the dataset is highly varied. In such cases, there is no single value that occurs most often.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Ch 3 Lecture Video, Fall 2024: Measures of Central Tendency

STATISTIKA CARA MENCARI NILAI MEAN, MEDIAN, MODUS DATA KELOMPOK PART 1
Mode, Median, Mean, Range, and Standard Deviation (1.3)
Mean, Median and Mode in Statistics | Statistics Tutorial | MarinStatsLectures

Kurikulum Merdeka Matematika Kelas 8 Bab 6 Statistika

Statistika Dasar Ukuran Pemusatan Data (Mean, Modus, Median) Data Tunggal dan Data Kelompok
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
