Laying the foundations
Summary
TLDRThis video lecture revisits key genetic concepts critical for understanding the Hardy-Weinberg principle, including assortment, recombination, linkage, and genotype frequencies. The instructor explains how meiosis leads to random allele distribution and how genotype frequencies can be derived from allele frequencies using the Hardy-Weinberg formula. Students are challenged to engage with practical exercises to test their understanding, particularly in scenarios where allele frequencies differ between sexes. Emphasizing the importance of grasping these concepts prepares students for advanced topics in genetics.
Takeaways
- 😀 Assortment during meiosis refers to the random distribution of chromosomes into gametes, impacting genetic variation.
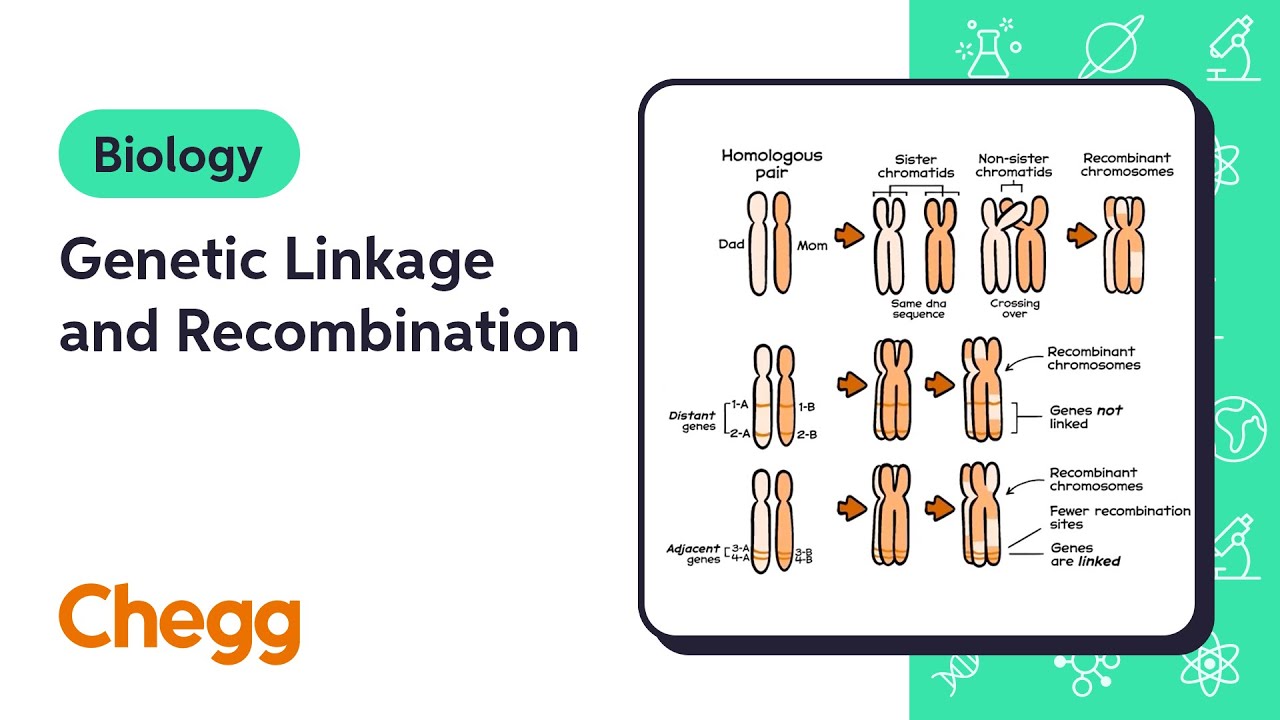
- 😀 Recombination allows for the mixing of genetic material from grandparents, creating unique chromosome combinations.
- 😀 Linkage is a complex concept in genetics that will be explored further, affecting how traits are inherited together.
- 😀 Genotype frequencies can be estimated from allele frequencies using the Hardy-Weinberg principle, which assumes random mating.
- 😀 The Hardy-Weinberg equation (p² + 2pq + q²) predicts genotype ratios based on allele frequencies in a population.
- 😀 The expected genotype frequencies can be derived from allele frequencies for a population in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
- 😀 It is essential to consider factors such as population size, mating patterns, and evolutionary pressures when applying the Hardy-Weinberg principle.
- 😀 In practical applications, students should be cautious of assumptions that may not hold true in real-life scenarios, such as differing allele frequencies between sexes.
- 😀 When allele frequencies differ, adjustments must be made to calculate expected genotype frequencies accurately.
- 😀 Understanding the foundational concepts of genetics is crucial for advancing into more complex topics in the field.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of this section of the course?
-The purpose is to revise key concepts essential for understanding the upcoming material, with a focus on foundational genetics.
What are the four key terms highlighted in the transcript?
-The four key terms are assortment, recombination, linkage, and genotype frequencies.
How is 'assortment' defined in the context of meiosis?
-Assortment refers to the random distribution of chromosomes during meiosis, resulting in gametes that carry different combinations of genetic material.
What role does 'recombination' play in genetic inheritance?
-Recombination allows for chromosomes to exchange segments, creating new allele combinations in gametes.
Why is the term 'linkage' considered elusive?
-Linkage is complex and requires deeper understanding to define, as it relates to the non-random association of alleles at different loci.
What does the Hardy-Weinberg principle illustrate?
-It illustrates how allele frequencies relate to genotype frequencies in a population under specific conditions.
What are the expected genotype frequencies according to Hardy-Weinberg?
-The expected frequencies are p² for homozygous dominant, q² for homozygous recessive, and 2pq for heterozygotes.
What assumptions are made in applying the Hardy-Weinberg principle?
-Assumptions include random mating, a large population size, no selection, and no mutation, migration, or gene flow.
What is the significance of the exercise mentioned at the end of the transcript?
-The exercise helps reinforce understanding of how genotype frequencies can evolve towards Hardy-Weinberg ratios over generations.
How can differing allele frequencies between sexes affect population genetics?
-Differing allele frequencies can lead to variations in expected genotype frequencies, complicating standard Hardy-Weinberg calculations.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahora5.0 / 5 (0 votes)