ELECTROCHEMICAL MACHINE (ECM): Construction and working of electrochemical Machining process.
Summary
TLDRElectrochemical machining (ECM) is an advanced metal removal process that utilizes electrochemical reactions to efficiently machine electrically conductive materials, especially hard metals. By immersing an anode and cathode in an electrolyte and applying voltage, material is removed at the atomic level, resulting in a precise and mirror-finish surface. The ECM setup comprises various components, including a power supply, tool, and electrolyte system. While it offers advantages like negligible tool wear and the ability to produce complex shapes, it also poses challenges such as corrosion risks and high initial costs. ECM is widely used in applications like die sinking, drilling, and micro-machining.
Takeaways
- 🔧 Electrochemical machining (ECM) is a method for removing metal using an electrochemical process, primarily suited for mass production.
- ⚡ The ECM process is effective for machining extremely hard materials that are challenging to work with conventional methods.
- ⚙️ ECM is limited to electrically conductive materials, making it specialized for certain applications.
- 🧪 The process involves immersing two electrodes (anode and cathode) in an electrolyte (e.g., NaCl) and applying voltage to initiate material removal.
- 🔍 Material removal in ECM occurs at the atomic level, leading to a mirror-finished surface on the workpiece.
- 💡 The electrolyte serves three main roles: conducting current, removing reaction products, and dissipating heat generated during machining.
- 📏 The setup includes key components like a power supply, tool, workpiece holder, pressure gauge, flow meter, and pump to manage the machining environment.
- 🛠️ Applications of ECM include dye sinking, drilling, profiling, grinding, and micro machining, especially for steam turbine blades.
- 👍 Advantages of ECM include negligible tool wear, the ability to produce complex shapes, no residual stress, excellent surface finish, and reduced heat generation.
- ⚠️ Disadvantages include the risk of corrosion, high power consumption, limitations to conductive materials, and significant initial investment costs.
Q & A
What is electrochemical machining (ECM)?
-Electrochemical machining (ECM) is a method of removing metal using an electrochemical process, typically used for mass production and for machining extremely hard or difficult materials.
What are the main components of an ECM setup?
-The main components of an ECM setup include a power supply, electrolyte, tool, workpiece holder, pressure gauge, flow meter, flow control valve, pressure relief valve, pump, reservoir tank, filter, centrifuge, and slug container.
How does the working principle of ECM function?
-In ECM, two electrodes—an anode (workpiece) and a cathode (tool)—are immersed in an electrolyte. When voltage is applied, material is removed from the anode at an atomic level, producing a mirror-finished surface.
What is the role of the electrolyte in the ECM process?
-The electrolyte serves three main roles: it carries current between the tool and workpiece, removes reaction products from the electrode gap, and dissipates heat generated during the process.
What types of materials can be machined using ECM?
-ECM is limited to electrically conductive materials, making it unsuitable for non-conductive materials.
What are the advantages of using ECM?
-Advantages of ECM include negligible tool wear, the ability to produce complex and concave shapes, no forces or residual stress due to lack of contact, excellent surface finishes, and less heat generation.
What disadvantages are associated with ECM?
-Disadvantages of ECM include the risk of corrosion for tools and workpieces, high power consumption, and significant initial investment costs.
How is sludge produced during the ECM process handled?
-Sludge produced during ECM is separated from the electrolyte, filtered, and stored in a slug container, allowing the cleaned electrolyte to be reused.
In what applications is ECM commonly used?
-ECM is used in applications such as die sinking, profiling and contouring, drilling, grinding, tree panning, micro-machining, and machining steam turbine blades.
How does the tool feed system work in ECM?
-The tool feed system advances the tool towards the workpiece, maintaining a required gap between them to ensure proper machining and avoid contact.
Outlines

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraMindmap

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraKeywords

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraHighlights

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraTranscripts

Esta sección está disponible solo para usuarios con suscripción. Por favor, mejora tu plan para acceder a esta parte.
Mejorar ahoraVer Más Videos Relacionados

Materiais e Processos de Fabricação para Engenharia de Produção: Usinagem não convencional

Electrochemical Grinding Process | How electrochemical grinding works

Materiais e Processos de Fabricação para Engenharia de Produção - Usinagem não convencional...
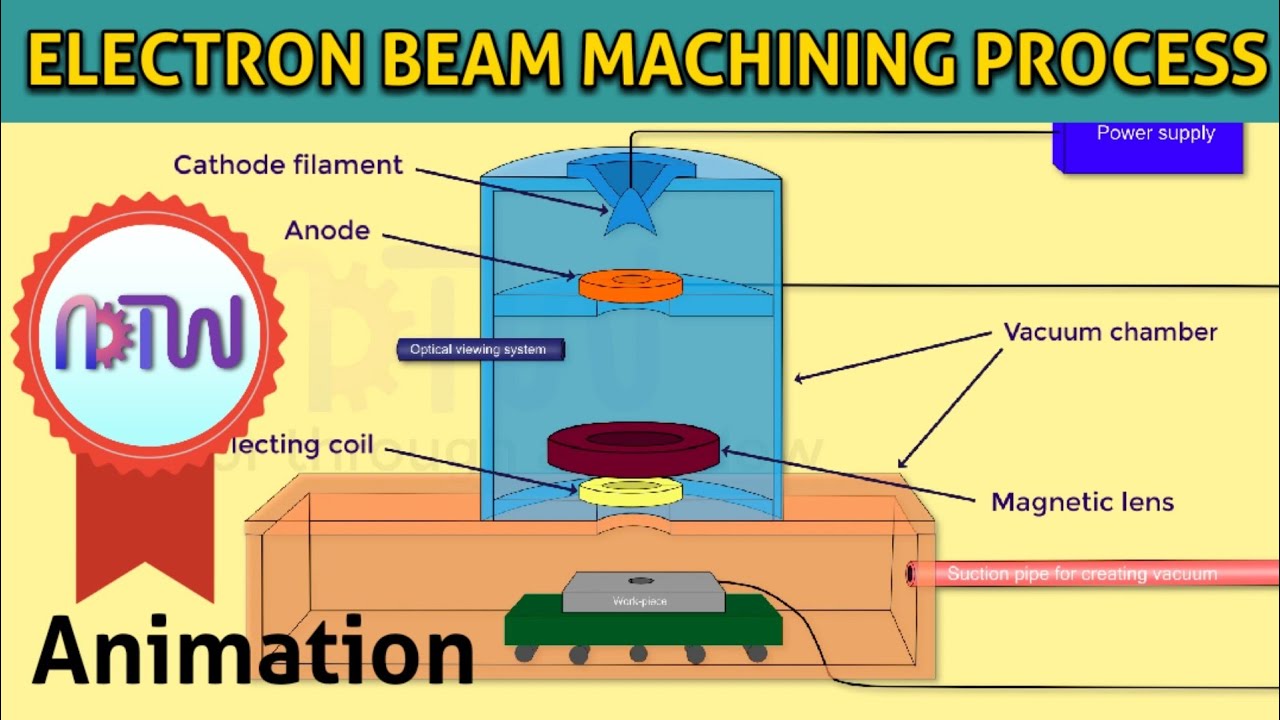
ELECTRON BEAM MACHINING PROCESS (EBM): Construction and Working of electron beam machining process.

Proses Pemesinan Non Tradisional part 1

WATER JET MACHINE PROCESS : Working of abrasive water Jet machining process (animation).
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
